Hemp-based ink offers superior sustainability compared to soy-based ink due to its faster growth cycle and lower pesticide requirements, reducing environmental impact. It produces vibrant, durable prints with excellent adhesion on various substrates, making it ideal for eco-friendly packaging and printing solutions. Unlike soy ink, hemp ink resists yellowing and maintains color integrity over time, enhancing print longevity.
Table of Comparison
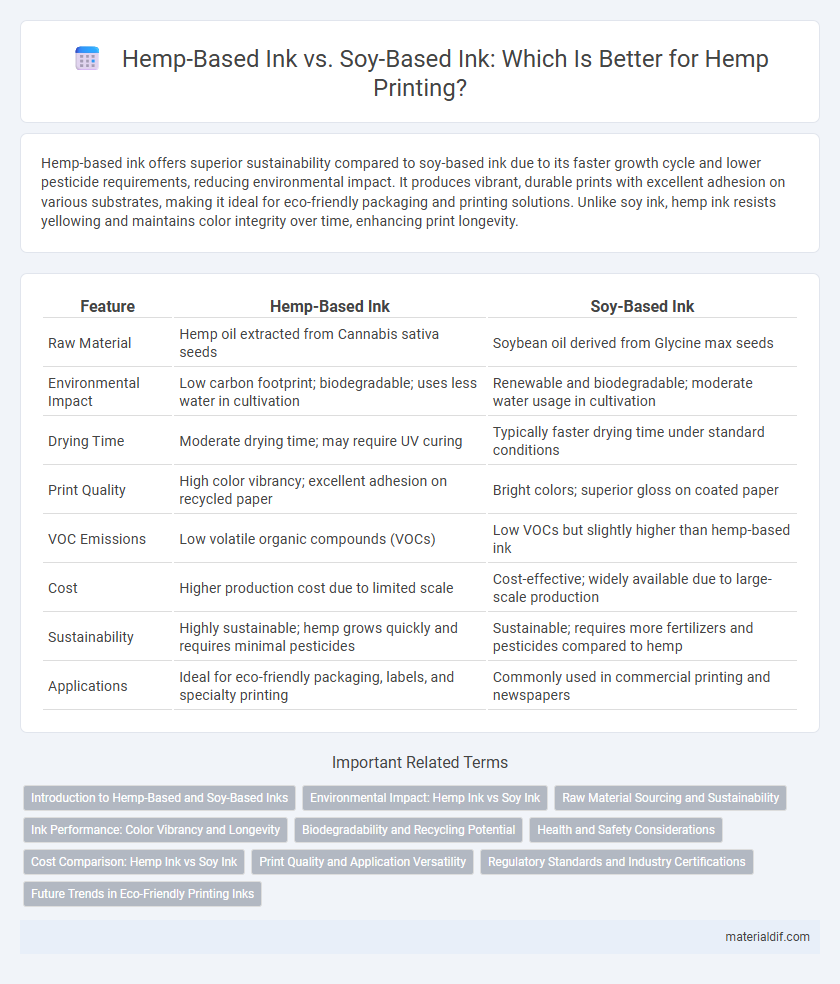
| Feature | Hemp-Based Ink | Soy-Based Ink |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Hemp oil extracted from Cannabis sativa seeds | Soybean oil derived from Glycine max seeds |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint; biodegradable; uses less water in cultivation | Renewable and biodegradable; moderate water usage in cultivation |
| Drying Time | Moderate drying time; may require UV curing | Typically faster drying time under standard conditions |
| Print Quality | High color vibrancy; excellent adhesion on recycled paper | Bright colors; superior gloss on coated paper |
| VOC Emissions | Low volatile organic compounds (VOCs) | Low VOCs but slightly higher than hemp-based ink |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to limited scale | Cost-effective; widely available due to large-scale production |
| Sustainability | Highly sustainable; hemp grows quickly and requires minimal pesticides | Sustainable; requires more fertilizers and pesticides compared to hemp |
| Applications | Ideal for eco-friendly packaging, labels, and specialty printing | Commonly used in commercial printing and newspapers |
Introduction to Hemp-Based and Soy-Based Inks
Hemp-based ink offers a sustainable alternative with higher durability and faster drying times compared to traditional soy-based ink, which is derived from soybean oil and prized for its vibrant color and biodegradability. The cellulose fibers in hemp contribute to enhanced ink adhesion and environmental benefits by requiring less water and fewer chemicals during production. Both ink types serve eco-friendly printing needs, but hemp-based ink provides increased longevity and resistance to fading, making it suitable for diverse applications including packaging and art prints.
Environmental Impact: Hemp Ink vs Soy Ink
Hemp-based ink offers a lower environmental footprint than soy-based ink due to hemp's rapid growth and minimal pesticide needs, which reduce resource consumption and soil degradation. The carbon sequestration potential of hemp cultivation further offsets emissions associated with ink production, enhancing sustainability credentials. Unlike soy ink, which relies on intensive agricultural inputs and deforestation risks, hemp ink contributes to biodiversity preservation and improved ecosystem health.
Raw Material Sourcing and Sustainability
Hemp-based ink utilizes fibers from the Cannabis sativa plant, offering rapid renewability due to hemp's fast growth cycle of four months, significantly reducing environmental impact compared to traditional crops. Raw material sourcing for hemp ink requires less water, pesticides, and herbicides, enhancing its sustainability profile relative to soy-based ink, which depends on soybean cultivation often linked to deforestation and intensive agrochemical use. Prioritizing hemp-based ink supports eco-friendly printing solutions by minimizing resource depletion and promoting regenerative agricultural practices.
Ink Performance: Color Vibrancy and Longevity
Hemp-based ink delivers superior color vibrancy due to its high pigment absorption properties, resulting in sharper and more vivid prints compared to soy-based ink. The natural fibers in hemp ink contribute to enhanced longevity, resisting fading and maintaining print quality over time even under exposure to light and environmental factors. This durability makes hemp-based ink an optimal choice for sustainable printing applications requiring long-lasting, high-impact visuals.
Biodegradability and Recycling Potential
Hemp-based ink offers superior biodegradability due to its natural cellulose fibers that break down more efficiently in environmental conditions compared to soy-based ink, which contains residual oils slowing decomposition. The recycling potential of hemp-based ink is higher, as its composition avoids contaminants typically found in soy inks, resulting in cleaner paper fiber recovery during recycling processes. This enhanced recyclability supports sustainable printing practices and reduces the environmental footprint of printed materials.
Health and Safety Considerations
Hemp-based ink contains fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) than soy-based ink, reducing indoor air pollution and associated respiratory risks. Hemp oil's natural antifungal and antibacterial properties minimize potential microbial contamination, enhancing workplace safety. Both inks are biodegradable, but hemp-based formulations often use fewer synthetic additives, lowering the risk of skin irritation and allergic reactions during printing processes.
Cost Comparison: Hemp Ink vs Soy Ink
Hemp-based ink typically costs more than soy-based ink due to higher raw material processing expenses and less established supply chains. Soy ink benefits from economies of scale and widespread agricultural production, resulting in lower price points for commercial printing. Despite the premium price, hemp ink offers enhanced durability and environmental benefits that may justify the additional investment for sustainable printing needs.
Print Quality and Application Versatility
Hemp-based ink delivers superior print quality with vibrant colors and sharp details due to its naturally high pigment retention and enhanced adhesion properties. This ink exhibits excellent application versatility, compatible with various paper types including recycled and uncoated stocks, ensuring consistent performance across different printing techniques. Compared to soy-based ink, hemp-based ink resists smudging and fading better, making it ideal for high-end packaging and fine art prints.
Regulatory Standards and Industry Certifications
Hemp-based ink often meets stricter regulatory standards due to its natural, non-toxic composition, aligning with certifications such as USDA Organic and EN 13432 for compostability. In contrast, soy-based ink, while also environmentally friendly, may face limitations in certifications related to biodegradability and volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Both inks undergo rigorous industry certifications like FSC approval and EPA's Safer Choice label, but hemp-based ink tends to lead in compliance with emerging sustainability regulations.
Future Trends in Eco-Friendly Printing Inks
Hemp-based ink demonstrates superior eco-friendly properties compared to soy-based ink, offering faster drying times and higher resistance to smudging, which is critical for sustainable packaging solutions. Innovations in hemp cultivation and processing are driving down costs, making hemp-based inks a viable alternative with a lower carbon footprint and enhanced biodegradability. Industry forecasts predict increased adoption of hemp-based inks due to rising demand for non-toxic, renewable materials aligned with global sustainability goals in printing technology.
hemp-based ink vs soy-based ink Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com