Hemp chips offer a more sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional wood chips for pet bedding, providing superior absorbency and odor control. Unlike wood chips, hemp chips are less likely to cause respiratory issues or allergies in pets due to their natural, chemical-free composition. Their lightweight texture and natural antimicrobial properties make hemp chips a healthier and eco-friendly choice for pet owners seeking optimal comfort and hygiene.
Table of Comparison
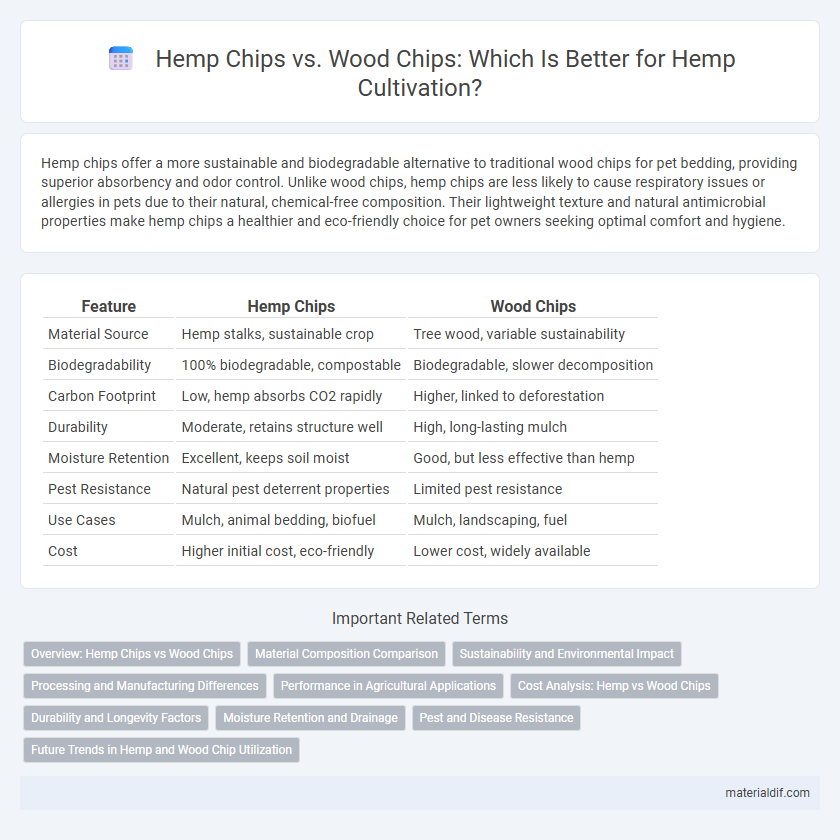
| Feature | Hemp Chips | Wood Chips |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Hemp stalks, sustainable crop | Tree wood, variable sustainability |
| Biodegradability | 100% biodegradable, compostable | Biodegradable, slower decomposition |
| Carbon Footprint | Low, hemp absorbs CO2 rapidly | Higher, linked to deforestation |
| Durability | Moderate, retains structure well | High, long-lasting mulch |
| Moisture Retention | Excellent, keeps soil moist | Good, but less effective than hemp |
| Pest Resistance | Natural pest deterrent properties | Limited pest resistance |
| Use Cases | Mulch, animal bedding, biofuel | Mulch, landscaping, fuel |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, eco-friendly | Lower cost, widely available |
Overview: Hemp Chips vs Wood Chips
Hemp chips offer a sustainable alternative to wood chips, providing faster biodegradation and excellent soil aeration for agricultural and gardening uses. Unlike wood chips, hemp chips contain higher cellulose content and lower lignin levels, enhancing nutrient availability and moisture retention. Their eco-friendly production reduces deforestation and carbon footprint, making hemp chips a preferred choice for sustainable landscaping and erosion control applications.
Material Composition Comparison
Hemp chips consist primarily of hemp hurds, which are the inner woody core of the hemp stalk, abundant in cellulose and low in lignin, resulting in a lightweight and highly absorbent material. Wood chips, derived from various tree species, contain higher lignin content, making them denser and more rigid but less absorbent compared to hemp chips. The lower lignin and higher cellulose ratio in hemp chips contribute to faster biodegradation and improved suitability for applications requiring moisture retention or bio-based insulation.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hemp chips offer superior sustainability compared to wood chips due to rapid renewability, with hemp reaching maturity in just 3-4 months versus decades for trees. Hemp cultivation requires less water, pesticides, and land, reducing environmental degradation and promoting soil health through phytoremediation. The biodegradability and carbon sequestration potential of hemp chips contribute to a significantly lower ecological footprint in comparison to traditional wood chips.
Processing and Manufacturing Differences
Hemp chips undergo a distinct processing method involving decortication to separate fibers from the core, resulting in a lightweight, nutrient-rich byproduct ideal for animal bedding and mulch. In contrast, wood chips are produced through mechanical chipping or grinding of logs and branches, emphasizing durability and moisture retention for landscaping and biomass fuel applications. The manufacturing of hemp chips requires controlled drying to prevent mold, whereas wood chips tolerate higher moisture content due to their denser lignin composition.
Performance in Agricultural Applications
Hemp chips offer superior water retention and faster decomposition rates compared to wood chips, enhancing soil aeration and nutrient availability for crops. Their natural pest-repellent properties reduce the need for chemical treatments, promoting healthier plant growth. Wood chips, while durable, tend to deplete nitrogen during decomposition, potentially hindering crop performance in agricultural settings.
Cost Analysis: Hemp vs Wood Chips
Hemp chips generally offer a cost-effective alternative to wood chips due to faster growth cycles and higher yield per acre, reducing raw material expenses. While wood chips may have lower initial prices in some regions, the sustainability and lower processing costs of hemp chips contribute to better long-term economic efficiency. Market fluctuations in timber supply and hemp farming scalability further influence the comparative cost dynamics between these two biomass options.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Hemp chips demonstrate superior durability compared to wood chips due to their natural resistance to mold, pests, and faster decomposition rates, which typically cause wood chips to break down within 1 to 3 years. The higher silica content in hemp chips enhances their longevity, making them an eco-friendly alternative that lasts longer in landscaping and mulching applications. Hemp's fibrous structure maintains integrity under moisture and sunlight exposure, extending its lifespan beyond traditional wood chip mulch.
Moisture Retention and Drainage
Hemp chips exhibit superior moisture retention compared to wood chips due to their porous structure, which holds water efficiently while preventing waterlogging. Wood chips tend to compact over time, reducing aeration and drainage capacity, leading to potential root suffocation. Optimal drainage in hemp chips promotes healthier root systems by balancing moisture retention and air circulation, enhancing plant growth.
Pest and Disease Resistance
Hemp chips exhibit significantly higher pest and disease resistance compared to wood chips, owing to hemp's natural antimicrobial and insect-repellent properties. The compounds found in hemp, such as cannabinoids and terpenes, deter common wood-borne pests and fungal pathogens, reducing the need for chemical treatments. This intrinsic resistance makes hemp chips a sustainable and low-maintenance alternative for landscaping and soil conditioning applications.
Future Trends in Hemp and Wood Chip Utilization
Hemp chips are rapidly gaining traction due to their sustainability, faster growth cycles, and superior carbon sequestration compared to traditional wood chips, positioning them as a key player in eco-friendly industries. Innovations in processing technologies are enhancing the usability of hemp chips in bio-composites, animal bedding, and biomass energy production, driving market expansion. Forecasts predict that hemp chip utilization will increase by over 20% annually, outpacing wood chips as regulatory frameworks support renewable materials and circular economy initiatives.
Hemp chips vs Wood chips Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com