Hemp seed oil and linseed oil differ significantly in their fatty acid profiles, with hemp seed oil rich in omega-6 and omega-3 essential fatty acids in an ideal 3:1 ratio, promoting heart health and skin benefits. Linseed oil, derived from flax seeds, contains a higher concentration of omega-3 fatty acids but can be more prone to oxidation, making it less stable for cooking compared to hemp seed oil. Both oils serve diverse purposes in nutrition and industry, but hemp seed oil is often favored for its balanced nutrients and versatile culinary applications.
Table of Comparison
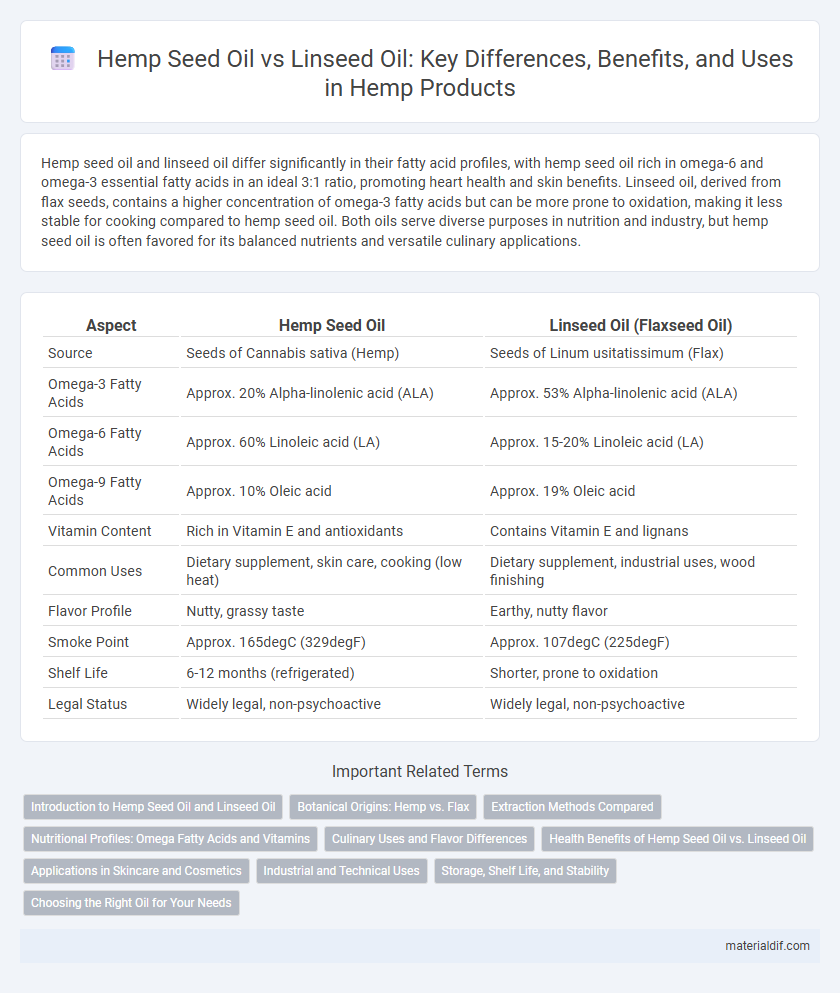
| Aspect | Hemp Seed Oil | Linseed Oil (Flaxseed Oil) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Seeds of Cannabis sativa (Hemp) | Seeds of Linum usitatissimum (Flax) |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Approx. 20% Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) | Approx. 53% Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) |
| Omega-6 Fatty Acids | Approx. 60% Linoleic acid (LA) | Approx. 15-20% Linoleic acid (LA) |
| Omega-9 Fatty Acids | Approx. 10% Oleic acid | Approx. 19% Oleic acid |
| Vitamin Content | Rich in Vitamin E and antioxidants | Contains Vitamin E and lignans |
| Common Uses | Dietary supplement, skin care, cooking (low heat) | Dietary supplement, industrial uses, wood finishing |
| Flavor Profile | Nutty, grassy taste | Earthy, nutty flavor |
| Smoke Point | Approx. 165degC (329degF) | Approx. 107degC (225degF) |
| Shelf Life | 6-12 months (refrigerated) | Shorter, prone to oxidation |
| Legal Status | Widely legal, non-psychoactive | Widely legal, non-psychoactive |
Introduction to Hemp Seed Oil and Linseed Oil
Hemp seed oil is derived from the seeds of the Cannabis sativa plant and is rich in essential fatty acids like omega-3 and omega-6, promoting skin health and cardiovascular benefits. Linseed oil, extracted from flax seeds, contains high levels of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid important for reducing inflammation and supporting brain function. Both oils serve diverse uses in nutrition, cosmetics, and industrial applications due to their unique fatty acid profiles and antioxidant properties.
Botanical Origins: Hemp vs. Flax
Hemp seed oil is extracted from the seeds of Cannabis sativa, a species known for its hardy growth and rich cannabinoid profile without psychoactive effects. Linseed oil, also called flaxseed oil, comes from the seeds of Linum usitatissimum, a plant prized for its fibers and omega-3 fatty acids. Both oils differ significantly in botanical origin, affecting their fatty acid composition and usage in nutrition and industry.
Extraction Methods Compared
Hemp seed oil is extracted primarily through cold pressing, preserving its high content of essential fatty acids like omega-3 and omega-6, while maintaining a balanced nutty flavor and rich nutrient profile. Linseed oil, derived from flax seeds, is also commonly cold-pressed but may undergo heat treatment or solvent extraction to increase yield, potentially affecting its nutritional integrity and flavor. Cold-pressed hemp seed oil retains more antioxidants and bioactive compounds compared to linseed oil processed with heat or solvents, making extraction methods a key factor in oil quality and health benefits.
Nutritional Profiles: Omega Fatty Acids and Vitamins
Hemp seed oil contains an optimal balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, particularly rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) and linoleic acid (LA), supporting cardiovascular health and inflammation reduction. Linseed oil, derived from flax seeds, boasts a higher concentration of omega-3 ALA but lacks the essential omega-6 fatty acids present in hemp seed oil. Both oils provide vitamin E as an antioxidant, though hemp seed oil offers additional vitamin D and B complex vitamins contributing to enhanced nutritional benefits.
Culinary Uses and Flavor Differences
Hemp seed oil offers a nutty, earthy flavor that enhances salad dressings, smoothies, and cold dishes, while linseed oil (flaxseed oil) has a milder, slightly grassy taste best suited for drizzling over vegetables or mixing in dips. Both oils are rich in omega-3 fatty acids but differ in smoke points; hemp seed oil has a low smoke point around 330degF (165degC), making it unsuitable for high-heat cooking, whereas linseed oil is rarely used for cooking due to its propensity to oxidize quickly. Flavor profiles and stability significantly influence their culinary applications, with hemp seed oil favored for its robust taste and linseed oil primarily used as a nutritional supplement.
Health Benefits of Hemp Seed Oil vs. Linseed Oil
Hemp seed oil contains an optimal balance of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids at approximately 3:1, promoting heart health and reducing inflammation more effectively than linseed oil, which has a higher omega-3 ratio but fewer antioxidants. Rich in gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), hemp seed oil supports skin health and hormonal balance, whereas linseed oil is primarily recognized for its alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) content. Hemp seed oil also provides essential vitamins E and minerals that contribute to cellular protection and overall wellness, making it a superior choice for comprehensive health benefits.
Applications in Skincare and Cosmetics
Hemp seed oil is rich in essential fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins E and C, making it ideal for moisturizing, anti-inflammatory, and anti-aging skincare products. Linseed oil, derived from flax seeds, offers similar fatty acids but is more prone to oxidation, limiting its use in long-lasting cosmetic formulations. Skincare brands prefer hemp seed oil for its stable composition and benefits in soothing sensitive skin and improving skin elasticity.
Industrial and Technical Uses
Hemp seed oil and linseed oil serve distinct industrial roles, with hemp seed oil prized for its stability and resistance to oxidation, making it suitable for use in cosmetics, lubricants, and bio-based plastics. Linseed oil, rich in alpha-linolenic acid, is primarily used as a drying oil in paints, varnishes, and wood finishes due to its excellent film-forming properties. Industrial applications of hemp seed oil leverage its non-drying nature, whereas linseed oil's drying capability is critical in coatings and additive manufacturing.
Storage, Shelf Life, and Stability
Hemp seed oil offers superior oxidative stability compared to linseed oil, resulting in a longer shelf life of up to 12 months when stored in a cool, dark place. Linseed oil tends to oxidize and polymerize faster, requiring refrigeration to maintain freshness and often lasting only 6 months. Proper airtight storage significantly extends the stability of both oils by minimizing exposure to light, heat, and oxygen.
Choosing the Right Oil for Your Needs
Hemp seed oil contains a balanced ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, making it ideal for skin hydration and anti-inflammatory benefits, while linseed oil (flaxseed oil) offers a higher concentration of omega-3 alpha-linolenic acid, supporting cardiovascular health and inflammation reduction. When choosing the right oil, consider hemp seed oil for topical applications or nutritional support promoting skin elasticity and overall wellness, whereas linseed oil suits dietary supplementation aimed at enhancing heart function and reducing chronic inflammation. Both oils provide essential fatty acids but differ in nutrient profiles and optimal use cases, guiding a choice based on specific health goals.
Hemp seed oil vs linseed oil Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com