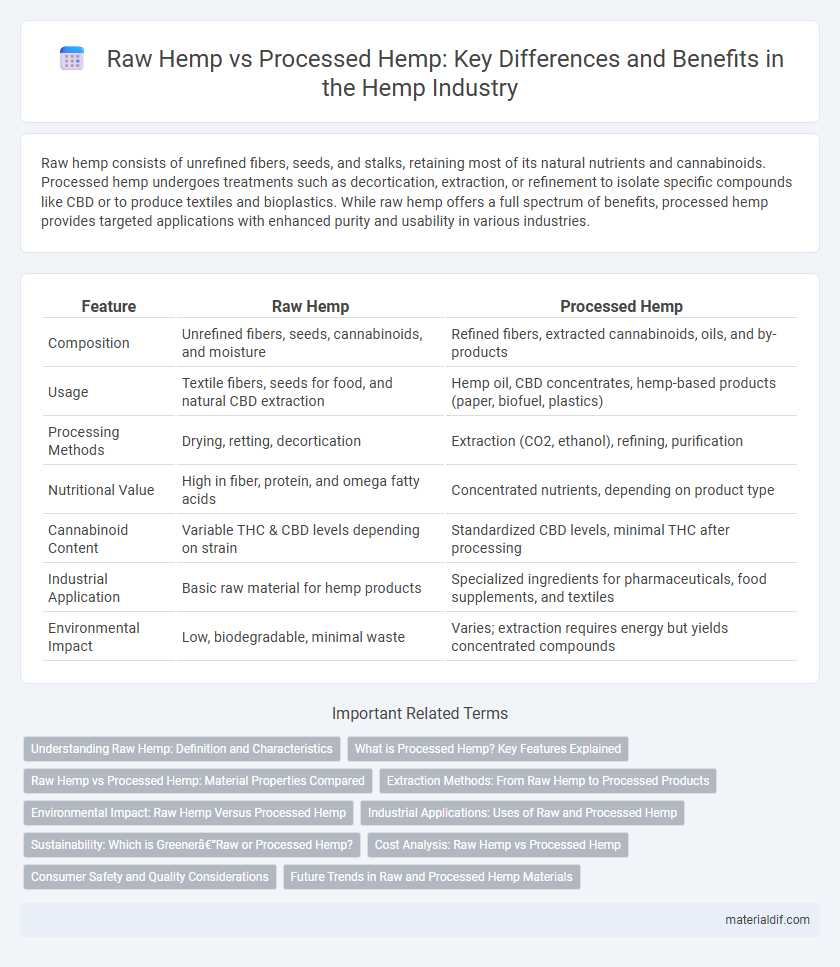
Raw hemp consists of unrefined fibers, seeds, and stalks, retaining most of its natural nutrients and cannabinoids. Processed hemp undergoes treatments such as decortication, extraction, or refinement to isolate specific compounds like CBD or to produce textiles and bioplastics. While raw hemp offers a full spectrum of benefits, processed hemp provides targeted applications with enhanced purity and usability in various industries.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raw Hemp | Processed Hemp |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Unrefined fibers, seeds, cannabinoids, and moisture | Refined fibers, extracted cannabinoids, oils, and by-products |
| Usage | Textile fibers, seeds for food, and natural CBD extraction | Hemp oil, CBD concentrates, hemp-based products (paper, biofuel, plastics) |
| Processing Methods | Drying, retting, decortication | Extraction (CO2, ethanol), refining, purification |
| Nutritional Value | High in fiber, protein, and omega fatty acids | Concentrated nutrients, depending on product type |
| Cannabinoid Content | Variable THC & CBD levels depending on strain | Standardized CBD levels, minimal THC after processing |
| Industrial Application | Basic raw material for hemp products | Specialized ingredients for pharmaceuticals, food supplements, and textiles |
| Environmental Impact | Low, biodegradable, minimal waste | Varies; extraction requires energy but yields concentrated compounds |
Understanding Raw Hemp: Definition and Characteristics
Raw hemp refers to the natural, unprocessed fibers and stalks harvested from the Cannabis sativa plant, retaining high cellulose content and minimal chemical alteration. Characterized by its coarse texture, moisture retention, and rich phytochemical compounds including cannabinoids and terpenes, raw hemp serves as the foundational material for various industrial applications. Understanding these intrinsic properties is essential for assessing hemp's suitability in bioproduct manufacturing, textile production, and sustainable construction materials.
What is Processed Hemp? Key Features Explained
Processed hemp refers to hemp fibers, oils, or extracts that have undergone mechanical or chemical treatments to enhance usability and functionality. Key features include removal of impurities, concentration of cannabinoids like CBD, and transformation into products such as textiles, bioplastics, or health supplements. This processing improves durability, potency, and application versatility compared to raw hemp's natural, unrefined state.
Raw Hemp vs Processed Hemp: Material Properties Compared
Raw hemp retains its natural fiber strength, higher cellulose content, and superior tensile properties, making it ideal for biodegradable composites and textiles. Processed hemp undergoes treatments such as retting, decortication, and chemical processing, which enhance flexibility, uniformity, and compatibility with industrial applications. The differences in moisture content, fiber length, and lignin concentration between raw and processed hemp directly affect durability, elasticity, and ease of manufacturing in construction and apparel industries.
Extraction Methods: From Raw Hemp to Processed Products
Raw hemp contains cannabinoids, terpenes, and other bioactive compounds that require precise extraction methods such as CO2 extraction, ethanol extraction, or hydrocarbon extraction to isolate and concentrate these valuable constituents. Each extraction technique influences the purity, potency, and overall quality of processed hemp products like CBD oils, tinctures, and edibles. Optimizing extraction parameters enhances the yield of targeted compounds while minimizing contaminants and preserving the plant's therapeutic profile.
Environmental Impact: Raw Hemp Versus Processed Hemp
Raw hemp cultivation requires minimal chemical inputs and promotes soil health through phytoremediation, making it environmentally advantageous. Processed hemp, however, involves energy-intensive methods such as decortication and chemical treatments, increasing carbon emissions and water usage. Choosing raw hemp over processed variants significantly reduces the ecological footprint associated with hemp products.
Industrial Applications: Uses of Raw and Processed Hemp
Raw hemp fibers are primarily utilized in the textile and construction industries, offering natural strength and durability for products such as ropes, insulation, and biocomposites. Processed hemp extracts, including hemp oil and CBD, find applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food industries due to their concentrated bioactive compounds and nutritional value. The versatility of hemp biomass supports sustainable manufacturing practices across industrial sectors, emphasizing eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic materials.
Sustainability: Which is Greener—Raw or Processed Hemp?
Raw hemp requires fewer resources and generates minimal waste compared to processed hemp, making it inherently more sustainable. Processing hemp involves energy-intensive steps such as decortication, retting, and chemical treatments, which increase its environmental footprint. Utilizing raw hemp in applications like construction or textiles reduces carbon emissions and supports eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Cost Analysis: Raw Hemp vs Processed Hemp
Raw hemp generally incurs lower initial costs due to minimal processing requirements, making it more cost-effective for large-scale agricultural use. Processed hemp, including hemp fiber, oil, and CBD extracts, demands advanced technology and labor, significantly increasing production expenses and market prices. However, processed hemp products offer higher value and profitability, balancing the higher upfront investment with greater revenue potential in niche markets.
Consumer Safety and Quality Considerations
Raw hemp contains natural cannabinoids, terpenes, and fibers that may harbor impurities such as pesticides, heavy metals, and microbial contaminants if not properly cultivated and harvested. Processed hemp undergoes extraction, refinement, and testing procedures to ensure removal of harmful substances and compliance with safety standards, enhancing consumer quality and product consistency. Reliable third-party lab testing and certification play critical roles in verifying the purity and potency of processed hemp products for safe consumer use.
Future Trends in Raw and Processed Hemp Materials
Future trends in raw and processed hemp materials emphasize increasing demand for sustainable, high-strength fibers and bio-based composites driven by the automotive and construction industries. Innovations in processing techniques, such as enzymatic retting and advanced decortication, enhance fiber quality and reduce environmental impact, supporting scalability and cost-efficiency. Market growth is also propelled by expanding applications in textiles, bioplastics, and nutraceuticals, where both raw and processed hemp offer versatile, eco-friendly alternatives to conventional materials.
raw hemp vs processed hemp Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com