Hemp biofuel offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels by producing lower carbon emissions and reducing dependency on non-renewable resources. Its rapid growth cycle and high biomass yield make hemp a cost-effective feedstock for biofuel production. Compared to fossil fuels, hemp biofuel contributes to cleaner energy solutions, promoting environmental preservation and energy security.
Table of Comparison
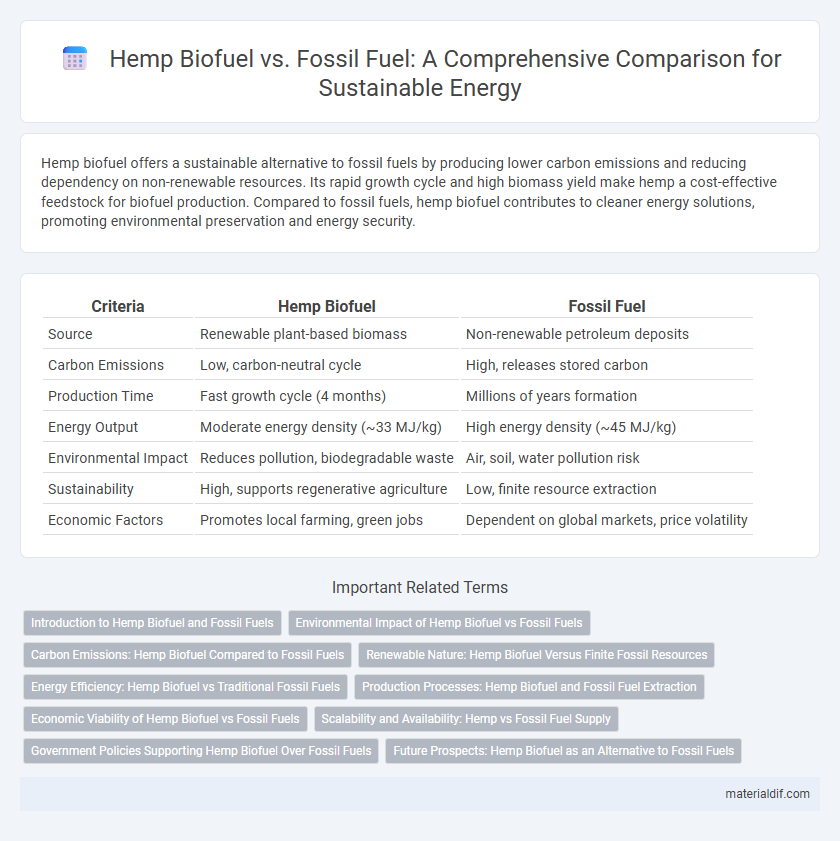
| Criteria | Hemp Biofuel | Fossil Fuel |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant-based biomass | Non-renewable petroleum deposits |
| Carbon Emissions | Low, carbon-neutral cycle | High, releases stored carbon |
| Production Time | Fast growth cycle (4 months) | Millions of years formation |
| Energy Output | Moderate energy density (~33 MJ/kg) | High energy density (~45 MJ/kg) |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces pollution, biodegradable waste | Air, soil, water pollution risk |
| Sustainability | High, supports regenerative agriculture | Low, finite resource extraction |
| Economic Factors | Promotes local farming, green jobs | Dependent on global markets, price volatility |
Introduction to Hemp Biofuel and Fossil Fuels
Hemp biofuel represents a renewable energy source derived from the seeds and stalks of the hemp plant, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. Unlike fossil fuels, which release high levels of carbon dioxide and contribute to climate change, hemp biofuel produces significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions during combustion. The rapid growth cycle and carbon sequestration properties of hemp enhance its potential as an eco-friendly biofuel feedstock, positioning it as a promising solution for reducing dependence on nonrenewable fossil energy.
Environmental Impact of Hemp Biofuel vs Fossil Fuels
Hemp biofuel offers a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels, as it absorbs CO2 during its growth, reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike fossil fuels, which release stored carbon from millions of years ago, hemp biofuel production promotes a renewable cycle with less soil degradation and pollution. The cultivation of hemp also enhances soil health by improving nutrient content and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers, mitigating environmental damage commonly associated with fossil fuel extraction and use.
Carbon Emissions: Hemp Biofuel Compared to Fossil Fuels
Hemp biofuel produces significantly lower carbon emissions than traditional fossil fuels, as it absorbs CO2 during its growth cycle, effectively creating a carbon-neutral energy source. The combustion of hemp biofuel releases fewer greenhouse gases like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, reducing air pollution and mitigating climate change impacts. Life cycle assessments indicate that hemp biofuel can reduce carbon emissions by up to 60% compared to petroleum-based fuels, making it a more sustainable alternative for energy production.
Renewable Nature: Hemp Biofuel Versus Finite Fossil Resources
Hemp biofuel offers a renewable energy source derived from fast-growing crops that capture carbon dioxide during growth, reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. Unlike finite fossil fuel reserves, which are depleting and contribute significantly to environmental pollution, hemp biofuel can be sustainably produced year after year with minimal ecological impact. The renewable nature of hemp biofuel supports energy security and a transition towards cleaner, more sustainable power sources.
Energy Efficiency: Hemp Biofuel vs Traditional Fossil Fuels
Hemp biofuel offers a higher energy return on investment (EROI) compared to traditional fossil fuels, producing approximately 70-90% more usable energy per unit of input. The combustion of hemp biofuel emits significantly lower greenhouse gases, reducing carbon emissions by up to 60% relative to gasoline and diesel. Enhanced crop yields and shorter growth cycles make hemp a more sustainable and efficient raw material for bioenergy production.
Production Processes: Hemp Biofuel and Fossil Fuel Extraction
Hemp biofuel is produced through the fermentation of hemp biomass, converting cellulose and sugars into ethanol or biodiesel via methods like enzymatic hydrolysis and transesterification. Fossil fuel extraction involves drilling and mining to obtain crude oil or natural gas, followed by refining processes such as distillation and cracking to produce usable fuels. Hemp biofuel offers a renewable, lower-emission alternative with simpler biological conversion, while fossil fuel extraction relies on finite geological resources with significant environmental impacts.
Economic Viability of Hemp Biofuel vs Fossil Fuels
Hemp biofuel offers a renewable alternative with lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, but its economic viability depends on factors such as cultivation costs, processing technology, and market demand. While fossil fuels currently benefit from established infrastructure and economies of scale, hemp biofuel production can reduce dependency on imported oil and stabilize fuel prices through sustainable farming practices. Investment in advanced extraction methods and policy incentives could improve hemp biofuel competitiveness in the global energy market.
Scalability and Availability: Hemp vs Fossil Fuel Supply
Hemp biofuel offers a renewable alternative with faster growth cycles and lower land requirements compared to fossil fuels, enabling more scalable and sustainable production. Fossil fuel supplies are limited by finite reserves and geopolitical constraints, causing fluctuations in availability and price. Widespread hemp cultivation can enhance energy security by providing a more consistent and locally accessible biofuel source.
Government Policies Supporting Hemp Biofuel Over Fossil Fuels
Government policies increasingly favor hemp biofuel through subsidies, tax incentives, and research funding aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable energy sources. Regulations such as the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) and state-level mandates encourage hemp biofuel production by offering financial support and market access. These policies aim to accelerate the transition from fossil fuels by leveraging hemp's rapid growth cycle and lower environmental impact.
Future Prospects: Hemp Biofuel as an Alternative to Fossil Fuels
Hemp biofuel offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels by providing a renewable energy source with lower carbon emissions and faster crop cycles. Advances in hemp biomass conversion technology are improving fuel yield and efficiency, positioning hemp biofuel as a viable option for reducing dependence on non-renewable energy. As government policies increasingly support green energy, hemp biofuel is expected to play a significant role in the future energy landscape.
hemp biofuel vs fossil fuel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com