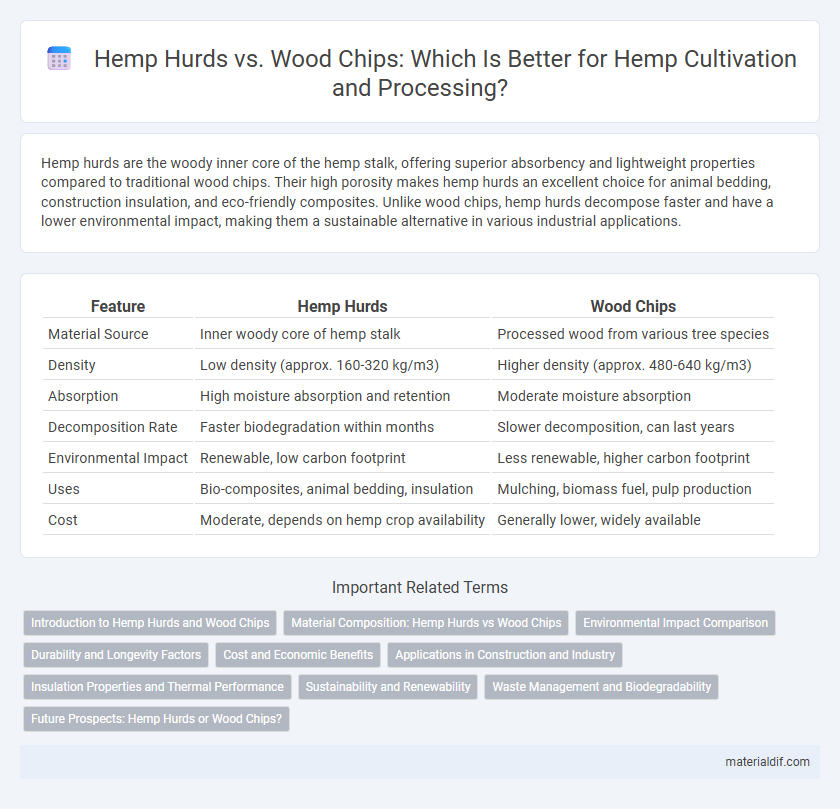
Hemp hurds are the woody inner core of the hemp stalk, offering superior absorbency and lightweight properties compared to traditional wood chips. Their high porosity makes hemp hurds an excellent choice for animal bedding, construction insulation, and eco-friendly composites. Unlike wood chips, hemp hurds decompose faster and have a lower environmental impact, making them a sustainable alternative in various industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Hurds | Wood Chips |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Inner woody core of hemp stalk | Processed wood from various tree species |
| Density | Low density (approx. 160-320 kg/m3) | Higher density (approx. 480-640 kg/m3) |
| Absorption | High moisture absorption and retention | Moderate moisture absorption |
| Decomposition Rate | Faster biodegradation within months | Slower decomposition, can last years |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, low carbon footprint | Less renewable, higher carbon footprint |
| Uses | Bio-composites, animal bedding, insulation | Mulching, biomass fuel, pulp production |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on hemp crop availability | Generally lower, widely available |
Introduction to Hemp Hurds and Wood Chips
Hemp hurds, the inner woody core of the hemp stalk, offer a lightweight, absorbent, and sustainable alternative to traditional wood chips, commonly used in animal bedding, mulching, and construction materials. Their porous structure provides superior moisture retention and air circulation compared to denser wood chips, enhancing applications in horticulture and bio-composites. The rapid renewability and lower environmental impact of hemp hurds position them as a viable, eco-friendly substitute in industries dependent on lignocellulosic biomass.
Material Composition: Hemp Hurds vs Wood Chips
Hemp hurds consist primarily of lignin and cellulose, offering a lightweight and porous structure that enhances insulation and moisture regulation. Wood chips contain higher cellulose and hemicellulose levels but have denser lignin content, resulting in greater rigidity and slower decomposition rates. The unique material composition of hemp hurds makes them more sustainable and efficient for eco-friendly construction and agricultural applications compared to traditional wood chips.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Hemp hurds have a significantly lower environmental impact than wood chips due to their rapid renewability and lower carbon footprint during processing. Hemp cultivation requires less water, fewer pesticides, and regenerates soil health, unlike traditional timber harvesting which contributes to deforestation and habitat loss. The biodegradability and carbon sequestration properties of hemp hurds make them a more sustainable choice for construction and manufacturing applications compared to conventional wood chips.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Hemp hurds exhibit superior durability compared to wood chips due to their higher resistance to decay and moisture absorption, enhancing the lifespan of composite materials. The unique lignin and cellulose composition in hemp hurds contributes to improved structural integrity and resistance to fungal growth. Wood chips, while widely available, tend to degrade faster under environmental stress, limiting their longevity in construction and industrial applications.
Cost and Economic Benefits
Hemp hurds offer a cost-effective alternative to wood chips due to lower processing expenses and faster renewability, which reduces material costs for manufacturers. The economic benefits of hemp hurds include sustainable supply chains and potential subsidies for eco-friendly materials, enhancing profitability for businesses. Compared to wood chips, hemp hurds also improve waste management efficiency, lowering overall operational costs in industries like construction and paper production.
Applications in Construction and Industry
Hemp hurds offer superior insulation and lightweight properties compared to traditional wood chips, making them ideal for eco-friendly construction materials such as hempcrete and particleboards. Their high absorbency and natural resistance to pests enhance durability and reduce the need for chemical treatments in industrial applications. These characteristics position hemp hurds as a sustainable alternative to wood chips in building insulation and composite manufacturing.
Insulation Properties and Thermal Performance
Hemp hurds exhibit superior insulation properties compared to wood chips due to their lower thermal conductivity, enhancing energy efficiency in building applications. The cellulose-rich structure of hemp hurds allows for better moisture regulation and breathability, reducing thermal bridging and improving indoor climate control. Wood chips, while more abundant, generally provide less effective thermal performance and higher susceptibility to mold and decay in insulation materials.
Sustainability and Renewability
Hemp hurds offer superior sustainability compared to wood chips due to their rapid growth cycle and low resource requirements, enabling faster biomass replenishment. Their biodegradability and carbon sequestration potential make hemp hurds a renewable alternative that reduces deforestation and environmental impact. Wood chips, while widely used, often contribute to habitat loss and slower ecosystem recovery, emphasizing hemp hurds' advantage in eco-friendly material sourcing.
Waste Management and Biodegradability
Hemp hurds demonstrate superior biodegradability compared to wood chips, breaking down more rapidly in composting environments, which reduces landfill accumulation and lowers waste management costs. The higher cellulose and lower lignin content in hemp hurds enhances microbial decomposition, making them an eco-friendly alternative for biodegradable mulch and packaging materials. Utilizing hemp hurds in waste management systems supports sustainable practices by minimizing persistent organic waste and promoting carbon-neutral recycling cycles.
Future Prospects: Hemp Hurds or Wood Chips?
Hemp hurds present promising future prospects as a sustainable alternative to wood chips due to their rapid growth cycle and higher cellulose content, enhancing paper and bio-composite production efficiency. Innovations in processing technologies further reduce costs and environmental impacts compared to traditional wood chips, fostering a shift toward hemp-based materials. Market trends indicate increasing adoption driven by regulatory support for renewable resources and consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Hemp hurds vs Wood chips Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com