Hemp composites offer a sustainable alternative to fiberglass composites by providing lightweight, biodegradable, and renewable material options with comparable strength and durability for automotive and construction applications. Unlike fiberglass, hemp fibers absorb less energy during production, reducing environmental impact and overall carbon footprint. Enhanced acoustic and thermal insulation properties make hemp composites ideal for eco-friendly building solutions, promoting healthier indoor environments.
Table of Comparison
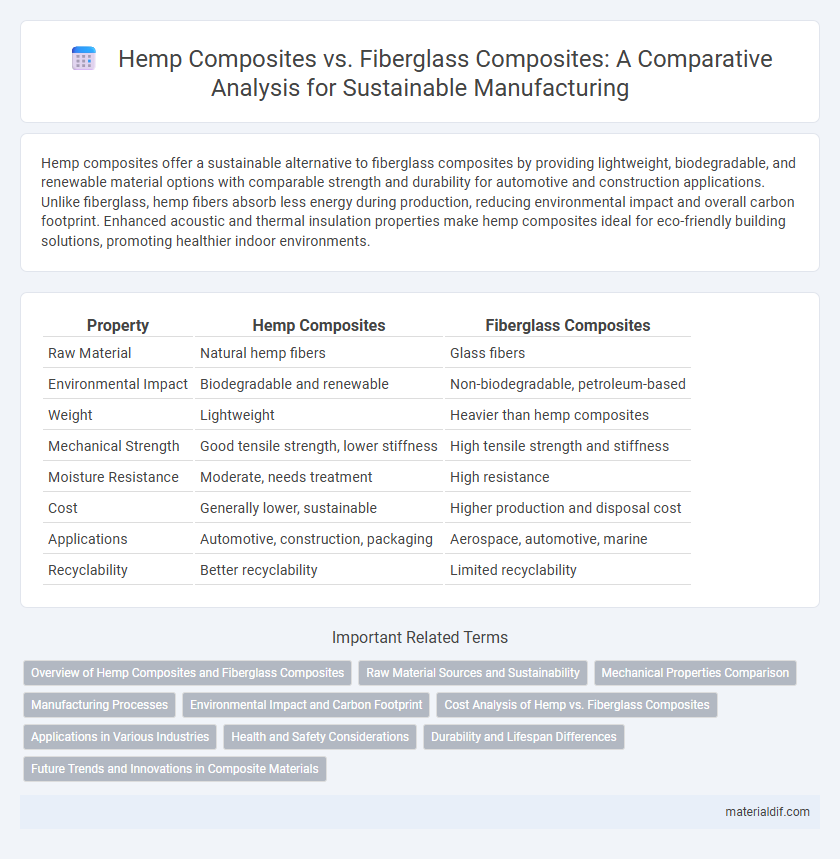
| Property | Hemp Composites | Fiberglass Composites |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Natural hemp fibers | Glass fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and renewable | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than hemp composites |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength, lower stiffness | High tensile strength and stiffness |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, needs treatment | High resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower, sustainable | Higher production and disposal cost |
| Applications | Automotive, construction, packaging | Aerospace, automotive, marine |
| Recyclability | Better recyclability | Limited recyclability |
Overview of Hemp Composites and Fiberglass Composites
Hemp composites consist of natural hemp fibers combined with polymer resins, offering lightweight, biodegradable, and renewable alternatives to traditional materials. Fiberglass composites are made from glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, providing high strength, durability, and resistance to environmental degradation. While fiberglass composites excel in mechanical performance, hemp composites are favored for sustainability, lower environmental impact, and reduced carbon footprint.
Raw Material Sources and Sustainability
Hemp composites utilize natural fibers derived from the stalks of the hemp plant, offering a renewable and biodegradable raw material source compared to fiberglass composites, which rely on non-renewable minerals like silica. The cultivation of hemp requires less water, pesticides, and energy, significantly reducing environmental impact and promoting soil health through crop rotation. Hemp composites also facilitate carbon sequestration during plant growth, enhancing sustainability by lowering the overall carbon footprint relative to energy-intensive fiberglass production.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Hemp composites exhibit lower tensile strength and stiffness compared to fiberglass composites, with typical tensile strengths ranging from 30 to 80 MPa versus fiberglass's 200 to 350 MPa. However, hemp composites offer superior impact resistance and are lighter in weight, providing advantages in applications requiring energy absorption and reduced mass. The biodegradability and lower environmental impact of hemp composites also make them a sustainable alternative in mechanical applications where performance demands allow.
Manufacturing Processes
Hemp composites are manufactured using sustainable processes such as compression molding, resin infusion, and extrusion, which require lower energy consumption compared to fiberglass's energy-intensive methods like high-temperature curing and autoclave processing. Hemp fibers offer better biodegradability and reduce environmental impact during production, while fiberglass manufacturing often involves hazardous chemicals and generates non-biodegradable waste. The integration of natural hemp fibers into bio-based resins facilitates easier recycling options and promotes circular economy practices in composite manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Carbon Footprint
Hemp composites exhibit a significantly lower environmental impact compared to fiberglass composites due to their renewable nature and biodegradability, reducing landfill waste and pollution. The carbon footprint of hemp composites is considerably smaller, as hemp plants absorb substantial amounts of CO2 during growth, offsetting emissions from production processes. In contrast, fiberglass composites rely on non-renewable resources and energy-intensive manufacturing, leading to higher greenhouse gas emissions and prolonged environmental degradation.
Cost Analysis of Hemp vs. Fiberglass Composites
Hemp composites offer a cost advantage over fiberglass composites primarily due to lower raw material and processing expenses, with hemp fibers being renewable and abundantly available. Manufacturing hemp composites generally consumes less energy and requires less intensive chemical treatments compared to fiberglass, reducing overall production costs. Long-term economic benefits also arise from hemp's biodegradability and reduced environmental impact, potentially lowering disposal and regulatory expenses.
Applications in Various Industries
Hemp composites offer lightweight, biodegradable alternatives to fiberglass composites, making them ideal for automotive, construction, and aerospace industries seeking sustainable materials. Their superior impact resistance and vibration dampening enhance performance in interior panels, insulation, and structural components. Industries leverage hemp composites to reduce carbon footprint while maintaining durability, driving innovation in eco-friendly manufacturing.
Health and Safety Considerations
Hemp composites offer significant health and safety advantages over fiberglass composites by reducing exposure to harmful dust and chemical irritants during manufacturing and handling. The natural fibers in hemp composites are biodegradable and non-toxic, minimizing respiratory issues and skin irritation commonly associated with fiberglass particles. Using hemp composites promotes a safer work environment, lowering risks of long-term health problems and enhancing sustainability in composite material applications.
Durability and Lifespan Differences
Hemp composites exhibit superior resistance to moisture and UV degradation compared to fiberglass composites, resulting in enhanced durability in outdoor and humid environments. The natural fibers in hemp composites provide better impact absorption and resistance to cracking over time, contributing to a longer lifespan. While fiberglass composites are prone to brittleness and delamination, hemp composites maintain structural integrity under cyclic stress, making them a sustainable and resilient alternative in various industrial applications.
Future Trends and Innovations in Composite Materials
Hemp composites are gaining traction as sustainable alternatives to fiberglass composites due to their lower environmental impact and comparable mechanical properties. Innovations in bio-based resin technologies and fiber treatment processes are enhancing the durability and performance of hemp composites, positioning them as viable options for automotive, construction, and aerospace industries. Future trends indicate increased integration of hemp fibers with advanced polymer matrices to optimize strength-to-weight ratios and biodegradability, driving a shift towards greener composite materials.
hemp composites vs fiberglass composites Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com