Hemp-derived rayon offers superior environmental benefits compared to bamboo-derived rayon due to its faster growth rate and lower pesticide requirements, making it a more sustainable fiber source. The strength and durability of hemp fibers result in high-quality rayon with enhanced longevity and less chemical processing. Choosing hemp-derived rayon supports eco-friendly textile production by reducing water usage and promoting biodegradable materials.
Table of Comparison
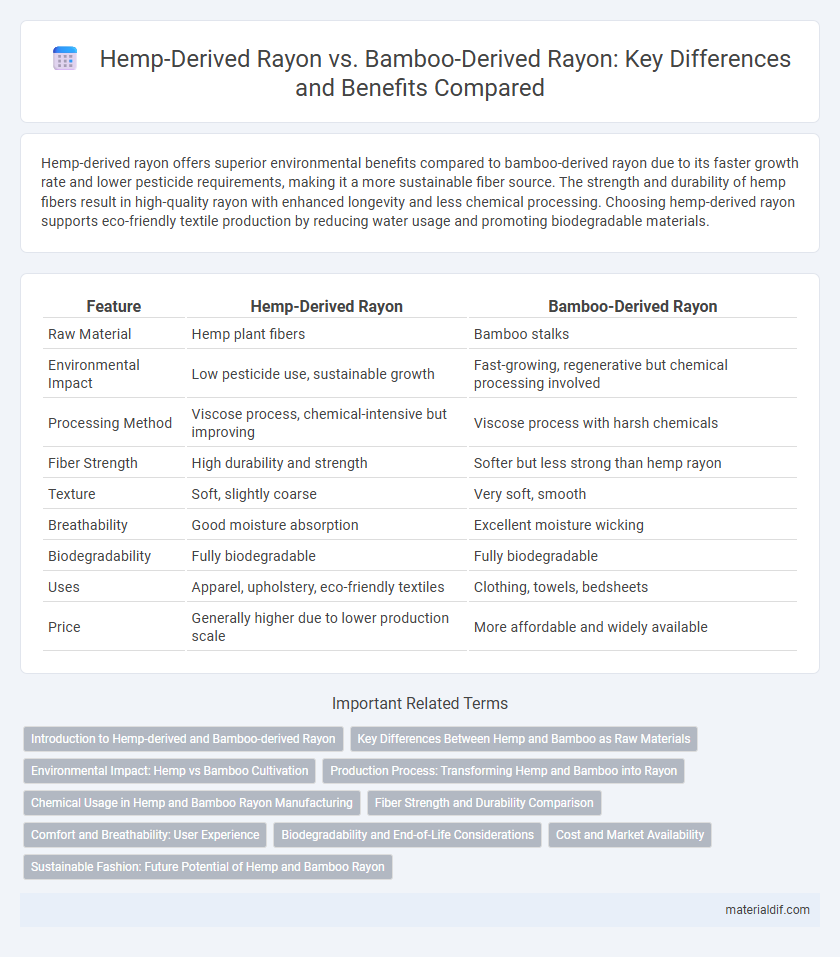
| Feature | Hemp-Derived Rayon | Bamboo-Derived Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Hemp plant fibers | Bamboo stalks |
| Environmental Impact | Low pesticide use, sustainable growth | Fast-growing, regenerative but chemical processing involved |
| Processing Method | Viscose process, chemical-intensive but improving | Viscose process with harsh chemicals |
| Fiber Strength | High durability and strength | Softer but less strong than hemp rayon |
| Texture | Soft, slightly coarse | Very soft, smooth |
| Breathability | Good moisture absorption | Excellent moisture wicking |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable | Fully biodegradable |
| Uses | Apparel, upholstery, eco-friendly textiles | Clothing, towels, bedsheets |
| Price | Generally higher due to lower production scale | More affordable and widely available |
Introduction to Hemp-derived and Bamboo-derived Rayon
Hemp-derived rayon is a sustainable fabric made by processing hemp fibers through chemical treatment to create a soft, breathable material with excellent durability and moisture-wicking properties. Bamboo-derived rayon is produced by chemically transforming bamboo cellulose into smooth, silky fibers known for their antibacterial qualities and high absorbency. Both rayons offer eco-friendly alternatives to traditional fabrics, with hemp providing superior strength and bamboo emphasizing softness and antimicrobial benefits.
Key Differences Between Hemp and Bamboo as Raw Materials
Hemp-derived rayon originates from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, characterized by its long, strong, and coarse fibers which contribute to more durable and breathable textiles. Bamboo-derived rayon is produced from bamboo cellulose, notable for its softness and smooth texture but involves more chemical processing, which can affect environmental sustainability. The key differences lie in fiber strength, processing intensity, and sustainability, with hemp offering greater resilience and reduced chemical use compared to bamboo.
Environmental Impact: Hemp vs Bamboo Cultivation
Hemp-derived rayon boasts a significantly lower environmental footprint compared to bamboo-derived rayon due to hemp's rapid growth rate and minimal need for pesticides or irrigation. Hemp cultivation enriches soil health through phytoremediation, reducing the risk of soil degradation often associated with intensive bamboo farming. Bamboo farming can lead to deforestation and biodiversity loss, whereas hemp's sustainable cultivation practices promote ecosystem balance and carbon sequestration.
Production Process: Transforming Hemp and Bamboo into Rayon
The production of hemp-derived rayon involves chemically processing hemp fibers using the viscose or Lyocell method, which breaks down cellulose into a soluble form before regenerating it into fine, strong fibers. Bamboo-derived rayon follows a similar chemical process but typically requires harsher treatments to remove lignin and non-cellulosic materials due to bamboo's dense fiber structure. Both processes convert raw plant materials into versatile rayon, but hemp's higher cellulose content and easier fiber separation make its production more environmentally efficient and yield a more sustainable fabric.
Chemical Usage in Hemp and Bamboo Rayon Manufacturing
Hemp-derived rayon manufacturing typically involves fewer chemical treatments compared to bamboo-derived rayon, which often requires intensive use of sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide in the viscose process. The reduced chemical footprint in hemp rayon production results from hemp fibers' naturally high cellulose content and lower lignin levels, facilitating easier pulping and bleaching. Consequently, hemp rayon offers a more environmentally sustainable alternative with less toxic chemical discharge than conventional bamboo rayon manufacturing.
Fiber Strength and Durability Comparison
Hemp-derived rayon exhibits superior fiber strength compared to bamboo-derived rayon, making it more resistant to wear and tear in textile applications. The cellulose extracted from hemp fibers is longer and more robust, contributing to enhanced durability and prolonged fabric lifespan. Bamboo-derived rayon, while soft and lightweight, tends to have shorter fibers that result in less tensile strength and quicker degradation over time.
Comfort and Breathability: User Experience
Hemp-derived rayon offers superior durability and moisture-wicking properties, resulting in enhanced comfort and breathability compared to bamboo-derived rayon. Its natural fibers provide better ventilation, reducing heat retention and promoting a cooler user experience. This makes hemp-based fabrics a preferred choice for breathable, comfortable clothing.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Hemp-derived rayon exhibits superior biodegradability compared to bamboo-derived rayon due to its natural cellulose structure and fewer chemical additives in processing, promoting faster decomposition in natural environments. End-of-life considerations favor hemp rayon as it breaks down more efficiently without releasing toxic residues, thereby reducing environmental impact in landfills or composting systems. Choosing hemp-derived rayon aligns with sustainable textile practices by ensuring eco-friendly disposal and minimizing long-term pollution.
Cost and Market Availability
Hemp-derived rayon typically costs more to produce due to the complex retting and processing methods required, resulting in a smaller market share compared to bamboo-derived rayon, which benefits from lower raw material costs and widespread cultivation. Bamboo-derived rayon dominates the market thanks to its higher availability and established supply chains, making it a more affordable option for manufacturers. Limited commercial hemp fiber production and regulatory challenges contribute to its restricted market availability despite its environmental advantages.
Sustainable Fashion: Future Potential of Hemp and Bamboo Rayon
Hemp-derived rayon offers a sustainable alternative in fashion due to its rapid growth rate, low water requirements, and minimal pesticide use compared to bamboo-derived rayon, which often involves intensive chemical processing that can harm the environment. The biodegradability and durability of hemp fibers contribute to longer-lasting garments, reducing textile waste in the fast fashion industry. Innovations in eco-friendly processing methods for both hemp and bamboo rayon are driving their potential to become key materials in sustainable fashion's future, promoting circular economy principles and reducing carbon footprints.
Hemp-derived rayon vs Bamboo-derived rayon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com