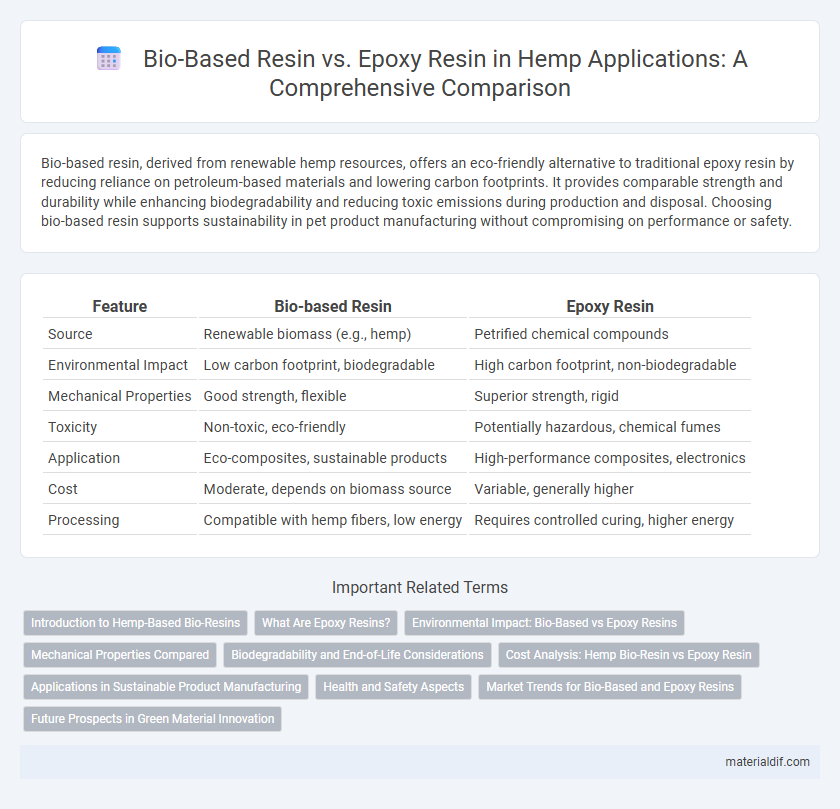
Bio-based resin, derived from renewable hemp resources, offers an eco-friendly alternative to traditional epoxy resin by reducing reliance on petroleum-based materials and lowering carbon footprints. It provides comparable strength and durability while enhancing biodegradability and reducing toxic emissions during production and disposal. Choosing bio-based resin supports sustainability in pet product manufacturing without compromising on performance or safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bio-based Resin | Epoxy Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable biomass (e.g., hemp) | Petrified chemical compounds |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Mechanical Properties | Good strength, flexible | Superior strength, rigid |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, eco-friendly | Potentially hazardous, chemical fumes |
| Application | Eco-composites, sustainable products | High-performance composites, electronics |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on biomass source | Variable, generally higher |
| Processing | Compatible with hemp fibers, low energy | Requires controlled curing, higher energy |
Introduction to Hemp-Based Bio-Resins
Hemp-based bio-resins are sustainably derived from renewable hemp fibers and oils, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based epoxy resins. These bio-resins exhibit comparable mechanical strength and thermal stability while significantly reducing carbon footprint and environmental impact. The integration of hemp enhances biodegradability and promotes circular economy principles in resin manufacturing.
What Are Epoxy Resins?
Epoxy resins are thermosetting polymers widely used for their strong adhesive properties, chemical resistance, and durability in industrial applications. Derived primarily from petrochemicals, epoxy resins form rigid, high-strength materials upon curing with hardeners, making them ideal for coatings, composites, and electronics. Unlike bio-based resins, epoxy resins are less sustainable but offer superior mechanical performance and moisture resistance.
Environmental Impact: Bio-Based vs Epoxy Resins
Bio-based resins derived from renewable resources like hemp exhibit significantly lower carbon footprints and reduced toxic emissions compared to conventional epoxy resins, which rely on petroleum-based chemicals. The biodegradability and lower volatility of bio-based resins minimize environmental pollution and health risks throughout their lifecycle. Epoxy resins contribute to persistent environmental contamination due to their non-biodegradable nature and release of hazardous substances during production and disposal.
Mechanical Properties Compared
Bio-based resins derived from hemp offer comparable tensile strength and flexibility to traditional epoxy resins, with tensile strengths often ranging from 30 to 60 MPa. Hemp-based bio-resins exhibit better impact resistance and improved elongation at break, enhancing durability in dynamic applications. Epoxy resins generally provide higher stiffness and superior adhesive properties, making them favorable for structural uses requiring high mechanical rigidity.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Bio-based resin derived from hemp offers superior biodegradability compared to traditional epoxy resin, breaking down naturally in the environment and reducing ecological impact. Hemp-based resins typically decompose within months to a few years under composting conditions, while epoxy resin can persist for decades, posing disposal challenges. End-of-life options for bio-based hemp resin include composting and incineration with lower toxic emissions, enhancing sustainability and reducing landfill accumulation.
Cost Analysis: Hemp Bio-Resin vs Epoxy Resin
Hemp bio-resin offers a significantly lower production cost compared to traditional epoxy resin due to its renewable raw material base and lower energy requirements in manufacturing. The cost per kilogram of hemp bio-resin can be up to 30% less than epoxy resin, making it a more economical option for large-scale applications. Market trends indicate rising demand for sustainable materials, which may further reduce the relative costs of hemp bio-resins through economies of scale.
Applications in Sustainable Product Manufacturing
Bio-based resin derived from natural materials like hemp offers a renewable and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional epoxy resin, widely used in sustainable product manufacturing. It enhances biodegradability and reduces carbon footprint while maintaining strong mechanical properties suitable for automotive parts, construction materials, and consumer goods. Innovations in bio-based resin formulations enable scalable production and integration into circular economy models, supporting green manufacturing goals.
Health and Safety Aspects
Bio-based resin derived from renewable hemp sources offers reduced toxicity and lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions compared to conventional epoxy resin, minimizing indoor air pollution and health risks. Hemp-based resins are generally biodegradable and emit fewer hazardous substances during manufacturing and disposal, enhancing workplace safety. In contrast, epoxy resins often release harmful chemicals like bisphenol-A and require intensive protective measures to prevent skin sensitization and respiratory issues.
Market Trends for Bio-Based and Epoxy Resins
The global bio-based resin market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 10% from 2024 to 2030, driven by increasing demand for sustainable materials in industries like automotive and construction. Epoxy resin remains dominant due to its superior mechanical properties and versatility, with the market expected to exceed $10 billion by 2030. Rising environmental regulations and consumer preference for eco-friendly products are accelerating the shift towards bio-based resins, creating new opportunities despite epoxy's established performance advantages.
Future Prospects in Green Material Innovation
Bio-based resin derived from hemp offers promising future prospects in green material innovation due to its renewable nature, lower carbon footprint, and biodegradability compared to traditional epoxy resin. Hemp-based resins enhance sustainability in composites and construction by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and toxic chemicals commonly used in epoxy formulations. Advances in bio-based resin technology are expected to boost performance and cost-effectiveness, accelerating adoption across automotive, packaging, and electronics industries.
Bio-based resin vs epoxy resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com