Hemp plastic offers a sustainable alternative to conventional plastic by being biodegradable and derived from renewable hemp fibers, reducing environmental pollution and dependence on fossil fuels. Unlike traditional plastics made from non-renewable petroleum, hemp plastic decomposes faster and has a lower carbon footprint throughout its lifecycle. This eco-friendly characteristic makes hemp plastic a viable choice for industries seeking greener materials and reducing plastic waste.
Table of Comparison
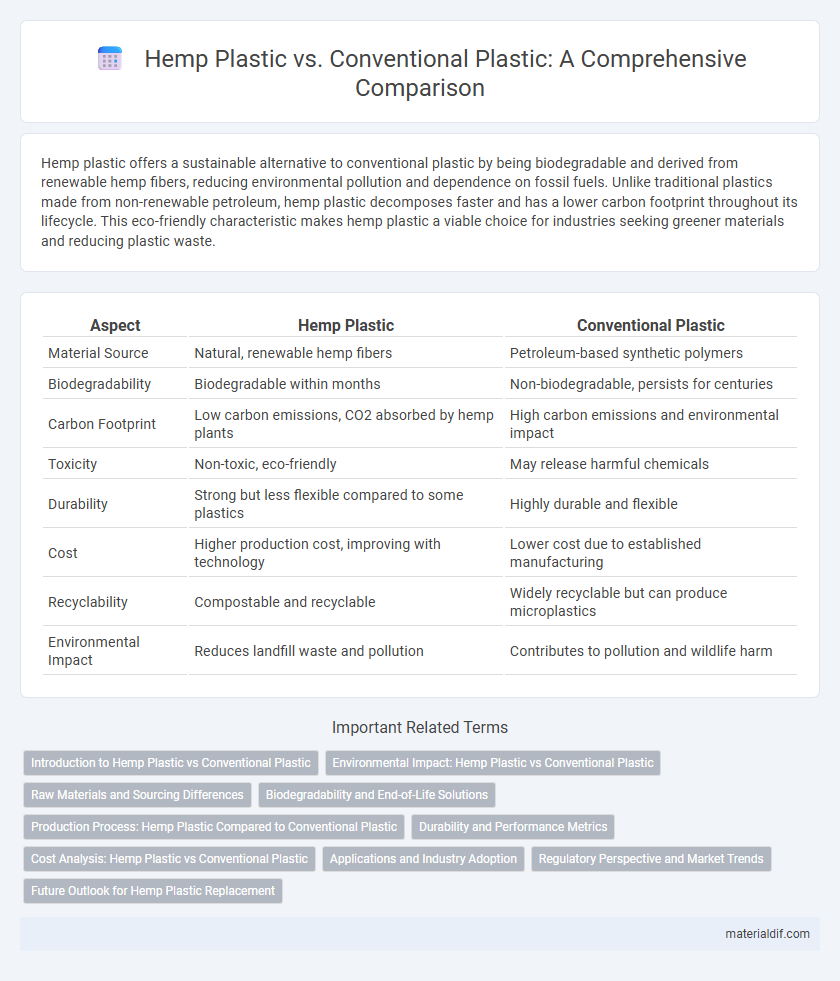
| Aspect | Hemp Plastic | Conventional Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural, renewable hemp fibers | Petroleum-based synthetic polymers |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable within months | Non-biodegradable, persists for centuries |
| Carbon Footprint | Low carbon emissions, CO2 absorbed by hemp plants | High carbon emissions and environmental impact |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, eco-friendly | May release harmful chemicals |
| Durability | Strong but less flexible compared to some plastics | Highly durable and flexible |
| Cost | Higher production cost, improving with technology | Lower cost due to established manufacturing |
| Recyclability | Compostable and recyclable | Widely recyclable but can produce microplastics |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste and pollution | Contributes to pollution and wildlife harm |
Introduction to Hemp Plastic vs Conventional Plastic
Hemp plastic, derived from renewable hemp fibers, offers a sustainable alternative to conventional plastic made from petroleum-based polymers. This bio-based material demonstrates enhanced biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional plastics, which contribute significantly to environmental pollution and fossil fuel depletion. Innovations in hemp plastic manufacturing enable its use in automotive, packaging, and consumer goods industries, promoting eco-friendly product development.
Environmental Impact: Hemp Plastic vs Conventional Plastic
Hemp plastic significantly reduces environmental impact compared to conventional plastic by being biodegradable and derived from renewable hemp fibers, which absorb carbon dioxide during growth. Conventional plastics rely heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and persistent pollution in landfills and oceans. The use of hemp plastic lowers carbon footprint and decreases reliance on non-renewable resources, offering a sustainable alternative for reducing plastic waste and environmental degradation.
Raw Materials and Sourcing Differences
Hemp plastic is derived from natural fibers extracted from P. sativa stalks, offering a renewable and biodegradable alternative to petroleum-based conventional plastic made from fossil fuels like crude oil and natural gas. Sourcing hemp for bioplastic production involves sustainable farming practices with rapid crop growth and minimal pesticide use, contrasting with the environmentally intensive extraction and refinement processes required for conventional plastics. The raw material difference significantly impacts carbon footprints, as hemp cultivation absorbs CO2, while fossil fuel extraction contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Solutions
Hemp plastic offers superior biodegradability compared to conventional plastic, breaking down naturally within months rather than centuries, which significantly reduces environmental pollution. Its end-of-life solutions include composting and industrial biodegradation, enabling organic recycling and minimizing landfill accumulation. In contrast, conventional plastic relies heavily on mechanical recycling or incineration, processes that often result in microplastic pollution and toxic emissions.
Production Process: Hemp Plastic Compared to Conventional Plastic
Hemp plastic is produced from cellulose fibers extracted from the hemp plant, utilizing a renewable resource that requires less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases during manufacturing compared to conventional plastics derived from petroleum-based polymers. The production process of hemp plastic involves biopolymer extraction and molding, which significantly reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers carbon footprint. In contrast, conventional plastic production depends on petrochemical refining and polymerization, consuming higher amounts of non-renewable energy and generating toxic byproducts.
Durability and Performance Metrics
Hemp plastic exhibits superior durability compared to conventional plastic, offering enhanced resistance to UV radiation and biodegradation, which extends its lifespan in various applications. Performance metrics indicate that hemp-based composites have higher tensile strength and impact resistance, making them suitable for automotive and packaging industries. The natural fiber reinforcement in hemp plastic also improves flexibility and reduces weight while maintaining structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: Hemp Plastic vs Conventional Plastic
Hemp plastic offers a cost advantage over conventional plastic by utilizing renewable biomass, which reduces raw material expenses and environmental compliance costs. Although initial production investments for hemp plastic are higher, ongoing manufacturing benefits from lower energy consumption and waste management fees. Long-term cost analysis indicates hemp plastic's potential for savings through decreased reliance on petroleum and enhanced biodegradability.
Applications and Industry Adoption
Hemp plastic, derived from renewable hemp fibers and biopolymers, offers eco-friendly alternatives in automotive, packaging, and consumer goods industries, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon footprints. Conventional plastic, primarily petroleum-based, dominates mass production due to cost-efficiency and established manufacturing processes but faces increasing regulatory restrictions and environmental concerns. Growing industry adoption of hemp plastic is driven by sustainability goals, biodegradable properties, and rising consumer demand for green materials in sectors like automotive interiors, electronics casings, and sustainable packaging solutions.
Regulatory Perspective and Market Trends
Hemp plastic is gaining regulatory support due to its biodegradability and lower environmental impact compared to conventional plastic, which faces increasing restrictions and bans in several regions. Market trends indicate a growing demand for hemp-based bioplastics driven by government incentives and consumer preference for sustainable alternatives. Regulatory frameworks in the EU and North America are accelerating the adoption of hemp plastics by imposing stricter limits on single-use petroleum-based plastics.
Future Outlook for Hemp Plastic Replacement
Hemp plastic offers a promising future as a sustainable alternative to conventional plastic due to its biodegradability and lower carbon footprint. Advances in hemp fiber extraction and bio-resin development are enhancing its strength and versatility, making it suitable for automotive, packaging, and consumer goods industries. Increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly products are driving rapid growth and investment in hemp plastic technologies, potentially paving the way for widespread adoption.
Hemp Plastic vs Conventional Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com