Thermoplastic hemp composites offer enhanced recyclability and flexibility compared to thermoset resin counterparts, making them ideal for sustainable manufacturing. Thermoset resin-based hemp materials provide superior heat resistance and structural integrity but lack the ability to be remolded or recycled after curing. Choosing between thermoplastic hemp and thermoset resin depends on specific application requirements for durability, environmental impact, and processing methods.
Table of Comparison
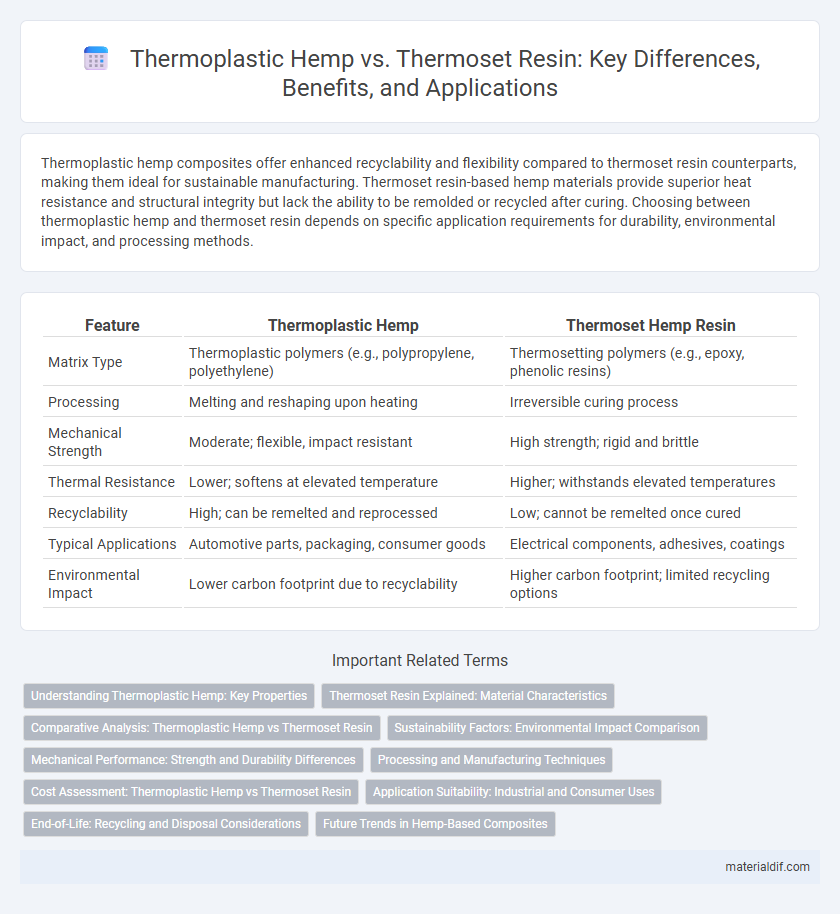
| Feature | Thermoplastic Hemp | Thermoset Hemp Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Matrix Type | Thermoplastic polymers (e.g., polypropylene, polyethylene) | Thermosetting polymers (e.g., epoxy, phenolic resins) |
| Processing | Melting and reshaping upon heating | Irreversible curing process |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate; flexible, impact resistant | High strength; rigid and brittle |
| Thermal Resistance | Lower; softens at elevated temperature | Higher; withstands elevated temperatures |
| Recyclability | High; can be remelted and reprocessed | Low; cannot be remelted once cured |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, packaging, consumer goods | Electrical components, adhesives, coatings |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint due to recyclability | Higher carbon footprint; limited recycling options |
Understanding Thermoplastic Hemp: Key Properties
Thermoplastic hemp composites exhibit remarkable flexibility and recyclability due to their ability to be repeatedly melted and reshaped, making them highly sustainable for various industrial applications. These materials possess excellent impact resistance and lightweight characteristics, driven by the natural fibers embedded within a thermoplastic matrix such as polypropylene or polyethylene. Their superior thermal stability and moisture resistance enhance durability, positioning thermoplastic hemp as a versatile alternative to traditional thermoset resin composites in automotive, construction, and packaging sectors.
Thermoset Resin Explained: Material Characteristics
Thermoset resin in hemp composites offers a rigid and heat-resistant matrix that enhances mechanical strength and chemical stability. Unlike thermoplastics, thermoset resins cure into a permanent solid structure, providing superior thermal stability and dimensional integrity under high stress. These characteristics make thermoset-based hemp materials ideal for automotive, aerospace, and construction applications requiring durable and lightweight composites.
Comparative Analysis: Thermoplastic Hemp vs Thermoset Resin
Thermoplastic hemp composites offer superior recyclability and impact resistance compared to thermoset resin counterparts, which provide higher thermal stability and structural rigidity. The molecular structure of thermoplastics allows for repeated melting and reshaping, enhancing sustainability and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing. Conversely, thermoset resins form irreversible cross-linked bonds, resulting in stronger but non-recyclable materials ideal for high-stress applications.
Sustainability Factors: Environmental Impact Comparison
Thermoplastic hemp composites demonstrate a lower environmental impact compared to thermoset resin counterparts due to their recyclability and reduced energy consumption during processing. Thermoset resins often involve non-recyclable materials and emit higher levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to greater ecological harm. The use of thermoplastic hemp supports circular economy principles, minimizing waste and enabling multiple life cycles for the material.
Mechanical Performance: Strength and Durability Differences
Thermoplastic hemp composites exhibit higher impact resistance and greater flexibility due to their ability to be remelted and reformed, resulting in enhanced toughness and durability compared to thermoset resin-based hemp composites. Thermoset resin hemp composites offer superior tensile strength and thermal stability because of their cross-linked molecular structure, making them ideal for applications requiring rigid and heat-resistant materials. The choice between thermoplastic hemp and thermoset resin hemp hinges on specific performance requirements, with thermoplastics favored for recyclability and toughness, while thermosets are preferred for long-term strength and dimensional stability.
Processing and Manufacturing Techniques
Thermoplastic hemp composites benefit from heating and reshaping processes, enabling efficient extrusion, injection molding, and recycling due to their reversible melting behavior. Thermoset hemp resins require curing through chemical reactions to form irreversible cross-linked structures, leading to enhanced mechanical strength but limiting reshaping and recycling options. Manufacturing techniques for thermoset hemp typically involve compression molding or resin transfer molding, demanding controlled temperature and pressure conditions for optimal curing and durability.
Cost Assessment: Thermoplastic Hemp vs Thermoset Resin
Thermoplastic hemp composites generally offer lower production costs compared to thermoset resin counterparts due to faster molding cycles and recyclability, reducing material waste and energy consumption. Thermoset resin materials require longer curing times and specialized processing equipment, increasing operational expenses and limiting cost-efficiency in large-scale manufacturing. Cost assessment highlights thermoplastic hemp as a more economical choice for applications demanding lightweight, sustainable materials without compromising structural performance.
Application Suitability: Industrial and Consumer Uses
Thermoplastic hemp composites offer excellent flexibility, impact resistance, and recyclability, making them suitable for automotive interior panels, consumer electronics casings, and packaging materials. Thermoset hemp resins provide superior heat resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical stability, ideal for construction materials, adhesives, and high-performance automotive parts. Industrial applications favor thermoset resins where durability under stress is critical, while consumer goods benefit from thermoplastics' lightweight and moldability.
End-of-Life: Recycling and Disposal Considerations
Thermoplastic hemp composites can be melted and reshaped multiple times, enabling easier recycling and reducing landfill waste. Thermoset hemp resins undergo irreversible curing, complicating recycling efforts and often leading to incineration or landfill disposal. Efficient end-of-life management favors thermoplastic hemp for sustainable circular economy practices in composite applications.
Future Trends in Hemp-Based Composites
Thermoplastic hemp composites offer enhanced recyclability and faster processing times compared to thermoset resin composites, driving their adoption in sustainable manufacturing sectors. Ongoing advancements focus on improving fiber-matrix adhesion and mechanical performance to expand applications in automotive and construction industries. Future trends highlight increased use of bio-based thermoplastic matrices combined with hemp fibers for fully renewable, high-performance composite materials.
Thermoplastic Hemp vs Thermoset Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com