Hemp plastic offers a sustainable alternative to petroleum plastic by being biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, significantly reducing environmental impact and carbon footprint. Unlike petroleum-based plastics, hemp plastic decomposes naturally without releasing toxic pollutants, making it an eco-friendly choice for various industries. Its production also requires less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases, contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
Table of Comparison
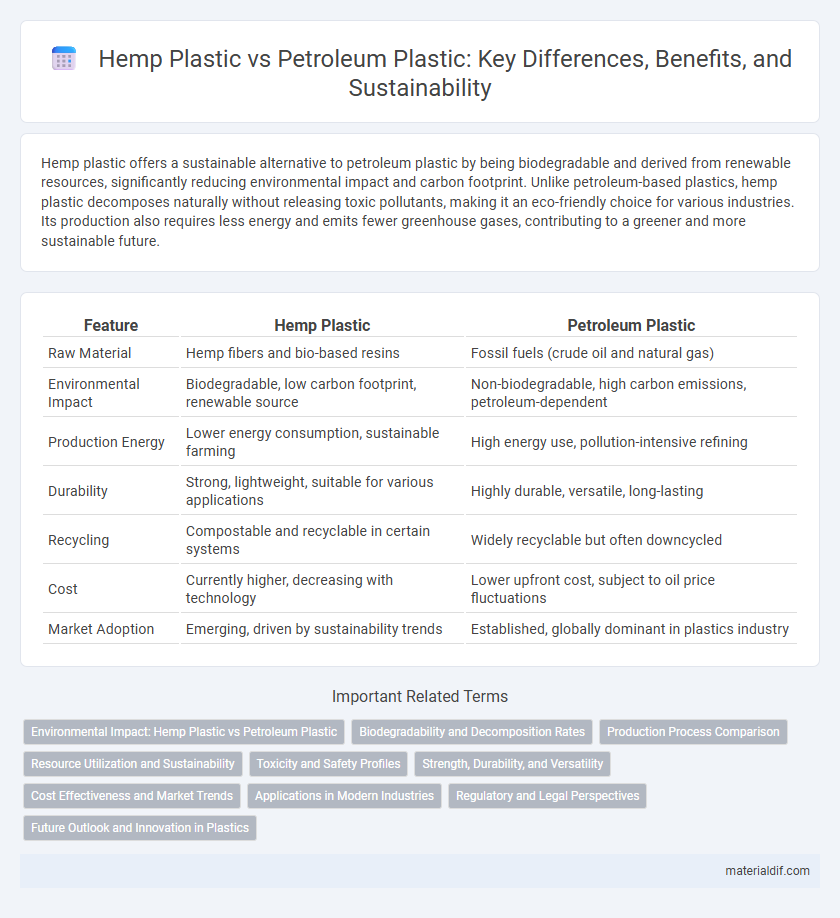
| Feature | Hemp Plastic | Petroleum Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Hemp fibers and bio-based resins | Fossil fuels (crude oil and natural gas) |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint, renewable source | Non-biodegradable, high carbon emissions, petroleum-dependent |
| Production Energy | Lower energy consumption, sustainable farming | High energy use, pollution-intensive refining |
| Durability | Strong, lightweight, suitable for various applications | Highly durable, versatile, long-lasting |
| Recycling | Compostable and recyclable in certain systems | Widely recyclable but often downcycled |
| Cost | Currently higher, decreasing with technology | Lower upfront cost, subject to oil price fluctuations |
| Market Adoption | Emerging, driven by sustainability trends | Established, globally dominant in plastics industry |
Environmental Impact: Hemp Plastic vs Petroleum Plastic
Hemp plastic significantly reduces environmental impact by being biodegradable and requiring less energy-intensive production compared to petroleum plastic, which contributes to long-lasting pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Cultivating hemp for bioplastics captures carbon dioxide, promoting carbon sequestration, unlike petroleum extraction that depletes fossil fuel reserves and releases toxic pollutants. Hemp plastic also supports soil health and biodiversity, whereas petroleum plastic manufacturing harms ecosystems through chemical waste and microplastic contamination.
Biodegradability and Decomposition Rates
Hemp plastic exhibits significantly faster biodegradability and decomposition rates compared to petroleum-based plastic, often breaking down within 12 months under natural conditions. Petroleum plastics can take hundreds of years to degrade, posing long-term environmental hazards. The natural fibers and organic composition of hemp plastics facilitate microbial activity that accelerates decomposition, reducing landfill accumulation and pollution.
Production Process Comparison
Hemp plastic production involves extracting cellulose fibers from hemp stalks, which are then processed into bioplastics through a combination of biochemical and mechanical methods, yielding a renewable and biodegradable material. Petroleum plastic manufacturing relies on refining crude oil through energy-intensive processes like cracking and polymerization, resulting in non-biodegradable plastics with significant carbon emissions. The hemp plastic production process offers a lower environmental footprint by utilizing sustainable biomass and reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
Resource Utilization and Sustainability
Hemp plastic requires significantly less fossil fuel input compared to petroleum plastic, utilizing renewable biomass that regenerates within months. The cultivation of hemp absorbs CO2, reducing the carbon footprint associated with plastic production, while petroleum plastics contribute to greenhouse gas emissions derived from finite oil reserves. Hemp's biodegradability and lower energy consumption in manufacturing enhance its sustainability profile, positioning it as an eco-friendly alternative to petroleum-based plastics in resource utilization.
Toxicity and Safety Profiles
Hemp plastic offers a significantly lower toxicity profile compared to petroleum-based plastic, as it is biodegradable and free from harmful additives like phthalates and BPA commonly found in conventional plastics. Studies indicate that hemp bioplastics do not release persistent organic pollutants or toxic chemicals during degradation, enhancing environmental safety and reducing health risks. In contrast, petroleum plastics contribute to toxic pollution and pose hazards through microplastic contamination and chemical leaching, impacting ecosystems and human health.
Strength, Durability, and Versatility
Hemp plastic offers superior strength and durability compared to traditional petroleum-based plastics due to its natural fiber reinforcement, which enhances impact resistance and reduces brittleness. Its biodegradability and versatility allow it to be molded into various shapes for automotive, packaging, and consumer goods, providing an eco-friendly alternative with comparable or better performance. The renewable nature of hemp also contributes to a smaller carbon footprint, supporting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Cost Effectiveness and Market Trends
Hemp plastic offers promising cost-effectiveness through lower raw material expenses and reduced environmental compliance costs compared to petroleum plastic. Market trends indicate a growing demand for sustainable alternatives, with hemp plastic gaining traction in industries aiming to reduce carbon footprints and reliance on fossil fuels. Investment in hemp-based bioplastics is expected to rise as consumer preference shifts towards eco-friendly packaging and manufacturing solutions.
Applications in Modern Industries
Hemp plastic offers a sustainable alternative to petroleum plastic across various modern industries, including automotive, packaging, and consumer goods, due to its biodegradability and lower carbon footprint. Industries utilize hemp plastic for manufacturing lightweight vehicle components, eco-friendly packaging materials, and durable consumer products, enhancing environmental compliance and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. The renewable nature of hemp biomass supports circular economy initiatives, positioning hemp plastic as a critical material in advancing green manufacturing and sustainable supply chains.
Regulatory and Legal Perspectives
Hemp plastic benefits from increasingly favorable regulatory frameworks due to its biodegradable nature and lower environmental impact compared to petroleum-based plastics, which face stricter regulations targeting carbon emissions and plastic waste management. Many governments are implementing policies that incentivize the use of sustainable materials like hemp bioplastics through subsidies and relaxed compliance requirements. Legal restrictions on single-use petroleum plastics further boost hemp plastic adoption as companies seek eco-friendly alternatives to meet evolving environmental legislation.
Future Outlook and Innovation in Plastics
Hemp plastic offers a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastics, with ongoing innovations focusing on enhancing its durability and biodegradability to meet industrial standards. Advances in biopolymer extraction and composite technologies are driving the scalability of hemp plastics, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. Future outlooks emphasize integrating hemp plastics into circular economies, promoting eco-friendly packaging and automotive components with reduced environmental footprints.
hemp plastic vs petroleum plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com