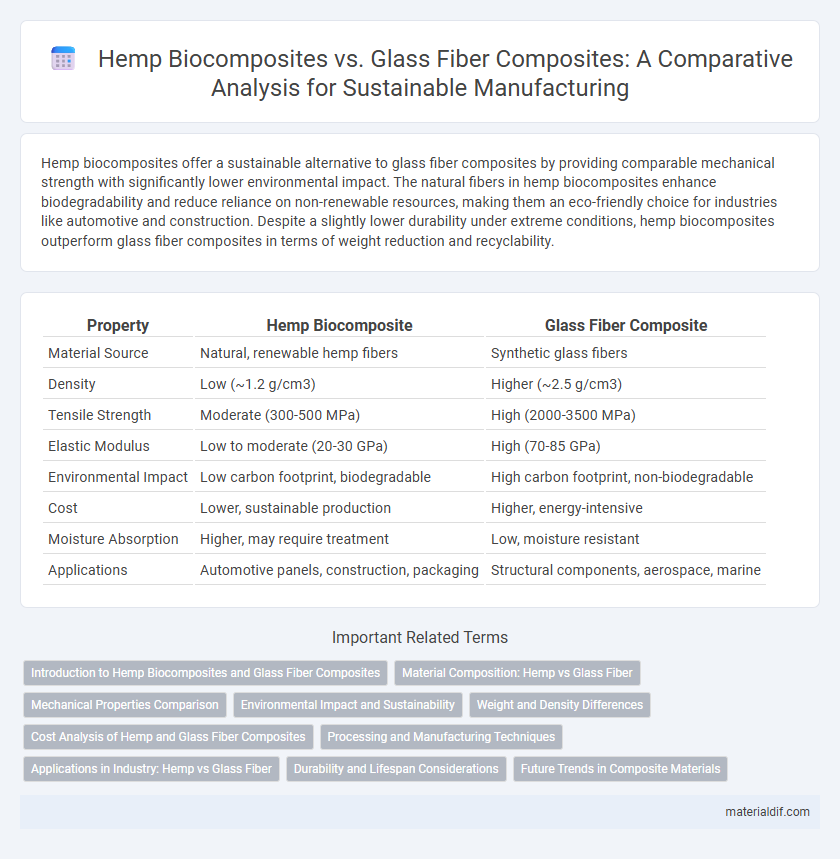
Hemp biocomposites offer a sustainable alternative to glass fiber composites by providing comparable mechanical strength with significantly lower environmental impact. The natural fibers in hemp biocomposites enhance biodegradability and reduce reliance on non-renewable resources, making them an eco-friendly choice for industries like automotive and construction. Despite a slightly lower durability under extreme conditions, hemp biocomposites outperform glass fiber composites in terms of weight reduction and recyclability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Biocomposite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural, renewable hemp fibers | Synthetic glass fibers |
| Density | Low (~1.2 g/cm3) | Higher (~2.5 g/cm3) |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate (300-500 MPa) | High (2000-3500 MPa) |
| Elastic Modulus | Low to moderate (20-30 GPa) | High (70-85 GPa) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Cost | Lower, sustainable production | Higher, energy-intensive |
| Moisture Absorption | Higher, may require treatment | Low, moisture resistant |
| Applications | Automotive panels, construction, packaging | Structural components, aerospace, marine |
Introduction to Hemp Biocomposites and Glass Fiber Composites
Hemp biocomposites are engineered materials combining natural hemp fibers with a polymer matrix, offering advantages in sustainability, biodegradability, and lightweight properties compared to traditional composites. Glass fiber composites consist of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, known for high strength, stiffness, and durability but involve higher environmental impact and recyclability challenges. The increasing interest in hemp biocomposites stems from their eco-friendly profile and competitive mechanical performance in automotive, construction, and packaging industries.
Material Composition: Hemp vs Glass Fiber
Hemp biocomposites consist primarily of natural hemp fibers combined with biodegradable polymers or resins, offering a renewable and eco-friendly alternative to synthetic materials. In contrast, glass fiber composites are made from inorganic glass fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, providing high strength and durability but lacking biodegradability. The material composition of hemp biocomposites leads to lower density and improved environmental sustainability compared to the heavier and non-biodegradable glass fiber composites.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Hemp biocomposites exhibit lower density and higher specific strength compared to glass fiber composites, making them advantageous for lightweight applications. Tensile strength of hemp composites ranges between 30-70 MPa, while glass fiber composites typically reach 200-350 MPa, indicating superior stiffness and durability of glass fibers. However, hemp biocomposites show better impact resistance and biodegradability, offering sustainable alternatives in eco-friendly mechanical performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp biocomposites significantly reduce environmental impact compared to glass fiber composites due to their renewable nature and lower energy consumption during production. Hemp fibers are biodegradable, contribute to carbon sequestration, and require less water and pesticides than glass fibers. The sustainability of hemp biocomposites is enhanced by their ability to support circular economy practices and reduce reliance on non-renewable resources in manufacturing.
Weight and Density Differences
Hemp biocomposites exhibit significantly lower density, typically around 1.2 g/cm3, compared to glass fiber composites which range between 1.8 and 2.0 g/cm3. This reduced density directly translates to lighter weight structures, making hemp biocomposites advantageous for applications requiring weight savings. The lower density also contributes to enhanced sustainability and ease of handling in manufacturing processes.
Cost Analysis of Hemp and Glass Fiber Composites
Hemp biocomposites typically offer a lower material cost compared to glass fiber composites, driven by the renewable and abundant nature of hemp fibers. Manufacturing processes for hemp composites often require less energy and lower equipment expenses, contributing to overall cost savings. However, glass fiber composites may incur higher costs due to the price of raw glass fibers and more complex production methods, despite their superior mechanical properties.
Processing and Manufacturing Techniques
Hemp biocomposites are processed using low-energy manufacturing techniques such as compression molding and injection molding, which are more environmentally friendly compared to the high-temperature curing needed for glass fiber composites. The natural fibers in hemp biocomposites allow for faster cycle times and reduced tool wear during production, enhancing cost-efficiency and scalability. Glass fiber composites require specialized handling due to their abrasive nature and the need for precise resin mixing, increasing complexity and production costs.
Applications in Industry: Hemp vs Glass Fiber
Hemp biocomposites find increasing use in automotive panels, construction materials, and consumer goods due to their lightweight, biodegradable properties, and low environmental impact compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Glass fiber composites remain dominant in aerospace, marine, and high-performance sports equipment owing to their superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance. Industrial applications favor hemp biocomposites for sustainable packaging and insulation, while glass fiber composites are preferred where durability and high structural integrity are critical.
Durability and Lifespan Considerations
Hemp biocomposites exhibit superior biodegradability and resistance to moisture-induced degradation compared to glass fiber composites, enhancing their long-term environmental sustainability. While glass fiber composites offer higher initial mechanical strength and rigidity, hemp biocomposites provide adequate durability for many applications with the added benefit of lower weight and reduced energy consumption during production. Lifespan considerations highlight that hemp biocomposites require specialized treatments to improve UV resistance and fungal attack resilience, but their renewable nature and recyclability offset these challenges over the product lifecycle.
Future Trends in Composite Materials
Hemp biocomposites demonstrate significant potential in the future of composite materials due to their sustainability, biodegradability, and lower environmental impact compared to glass fiber composites. Advances in processing technologies and fiber treatments are enhancing the mechanical properties and durability of hemp composites, making them increasingly competitive for automotive and construction applications. Industry trends indicate a growing preference for hemp biocomposites driven by regulatory pressures and consumer demand for eco-friendly materials.
Hemp biocomposite vs glass fiber composite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com