Hemp fabric offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to polyester fabric, making it ideal for comfortable, eco-friendly clothing. Unlike synthetic polyester, hemp is biodegradable and requires fewer pesticides and less water during cultivation, reducing environmental impact. Hemp fabric also gains softness with use and is naturally resistant to UV rays and mold, enhancing durability without harmful chemicals.
Table of Comparison
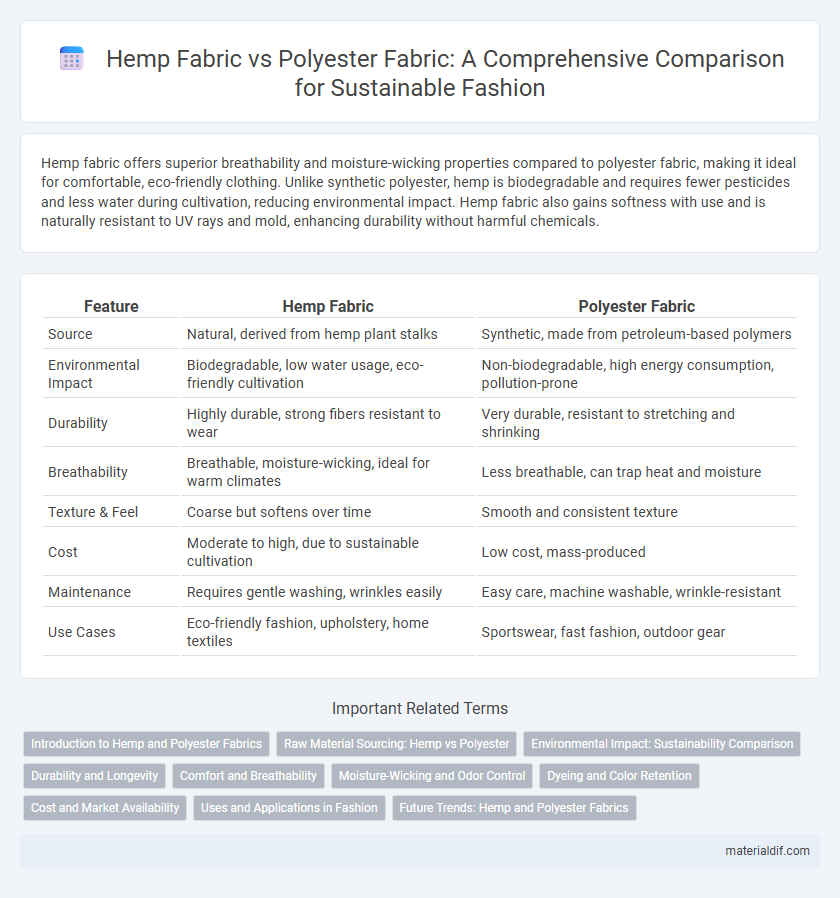
| Feature | Hemp Fabric | Polyester Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, derived from hemp plant stalks | Synthetic, made from petroleum-based polymers |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low water usage, eco-friendly cultivation | Non-biodegradable, high energy consumption, pollution-prone |
| Durability | Highly durable, strong fibers resistant to wear | Very durable, resistant to stretching and shrinking |
| Breathability | Breathable, moisture-wicking, ideal for warm climates | Less breathable, can trap heat and moisture |
| Texture & Feel | Coarse but softens over time | Smooth and consistent texture |
| Cost | Moderate to high, due to sustainable cultivation | Low cost, mass-produced |
| Maintenance | Requires gentle washing, wrinkles easily | Easy care, machine washable, wrinkle-resistant |
| Use Cases | Eco-friendly fashion, upholstery, home textiles | Sportswear, fast fashion, outdoor gear |
Introduction to Hemp and Polyester Fabrics
Hemp fabric is a natural textile made from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, known for its durability, breathability, and eco-friendly properties. Polyester fabric, a synthetic material derived from petroleum, offers high strength, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking capabilities commonly used in fast fashion. The growing interest in sustainable alternatives highlights hemp fabric's advantages over polyester in terms of biodegradability and environmental impact.
Raw Material Sourcing: Hemp vs Polyester
Hemp fabric originates from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, making it a renewable, biodegradable resource that requires minimal pesticides and water compared to cotton. Polyester fabric is derived from petroleum-based synthetic polymers, relying heavily on fossil fuels and energy-intensive processes that contribute to environmental pollution. The sustainable cultivation of hemp contrasts sharply with the petrochemical-dependent production of polyester, affecting the overall ecological footprint of each fabric.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Comparison
Hemp fabric is significantly more sustainable than polyester due to its biodegradable nature and minimal resource requirements, including low water usage and no need for harmful pesticides. Polyester, derived from petroleum, contributes to microplastic pollution and requires high energy consumption during production, leading to a larger carbon footprint. Choosing hemp reduces environmental damage by supporting renewable agriculture and cutting down on non-biodegradable waste.
Durability and Longevity
Hemp fabric offers superior durability and longevity compared to polyester, as its natural fibers are resistant to wear and tear, making it ideal for long-lasting textiles. Unlike polyester, a synthetic material prone to pilling and weakening over time, hemp maintains its strength even after repeated washing and exposure to sunlight. This resilience makes hemp fabric a sustainable choice for consumers seeking environmentally friendly yet durable clothing and upholstery.
Comfort and Breathability
Hemp fabric offers superior comfort and breathability compared to polyester fabric due to its natural fibers that allow better air circulation and moisture absorption. The breathable structure of hemp helps regulate body temperature, making it ideal for warm climates and active wear. Polyester, being synthetic, tends to trap heat and moisture, often resulting in less comfort during extended wear.
Moisture-Wicking and Odor Control
Hemp fabric exhibits superior moisture-wicking properties compared to polyester fabric due to its natural fibers, which absorb and release moisture efficiently, keeping the skin dry and comfortable. Hemp's antimicrobial qualities inhibit odor-causing bacteria, making it highly effective in odor control, whereas polyester tends to retain odors because of its synthetic composition. These characteristics make hemp fabric a preferred choice for activewear and sustainable clothing focused on breathability and freshness.
Dyeing and Color Retention
Hemp fabric exhibits superior dye absorption and color retention compared to polyester fabric due to its natural cellulose fibers, which allow dyes to penetrate deeply and evenly. Polyester, a synthetic fiber, typically requires specialized disperse dyes and high-temperature dyeing processes, resulting in less vibrant and less durable colors over time. Hemp's eco-friendly dyeing process also reduces chemical usage, offering longer-lasting hues and a more sustainable option for colored textiles.
Cost and Market Availability
Hemp fabric generally costs more than polyester fabric due to its sustainable cultivation and processing methods, making it a premium choice in eco-conscious markets. Polyester fabric, derived from petrochemicals, remains more affordable and widely available, dominating the mass-market textile industry. Market availability of hemp fabric is expanding but still limited compared to the extensive distribution and production scale of polyester fabric worldwide.
Uses and Applications in Fashion
Hemp fabric, valued for its breathability, moisture-wicking, and durability, is increasingly utilized in sustainable fashion for eco-friendly apparel, casual wear, and accessories. Polyester fabric, favored for its wrinkle resistance, color retention, and affordability, dominates activewear, outerwear, and fast fashion due to its versatility and low production cost. Designers leverage hemp's natural texture and biodegradability for organic and artisanal garments, while polyester remains preferred for performance-focused and mass-produced clothing lines.
Future Trends: Hemp and Polyester Fabrics
Hemp fabric is gaining momentum in sustainable fashion due to its biodegradable properties, breathability, and durability, positioning it as a leading eco-friendly alternative to polyester. Polyester, derived from petroleum, remains widely used for its affordability and moisture-wicking qualities but faces increasing scrutiny over environmental impact and microplastic pollution. Future trends indicate a growing consumer preference for hemp and other natural fibers as industries prioritize circular economy practices and regulatory pressures to reduce synthetic fiber waste intensify.
Hemp fabric vs Polyester fabric Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com