Dew retting and water retting are two primary methods used to extract fibers from hemp stalks by breaking down the pectin that binds them. Dew retting relies on natural moisture and microbial activity on the field, resulting in slower processing but producing fibers with higher tensile strength and less environmental impact. Water retting involves submerging hemp stalks in water to accelerate retting, yielding finer and softer fibers but requiring careful management to prevent water pollution.
Table of Comparison
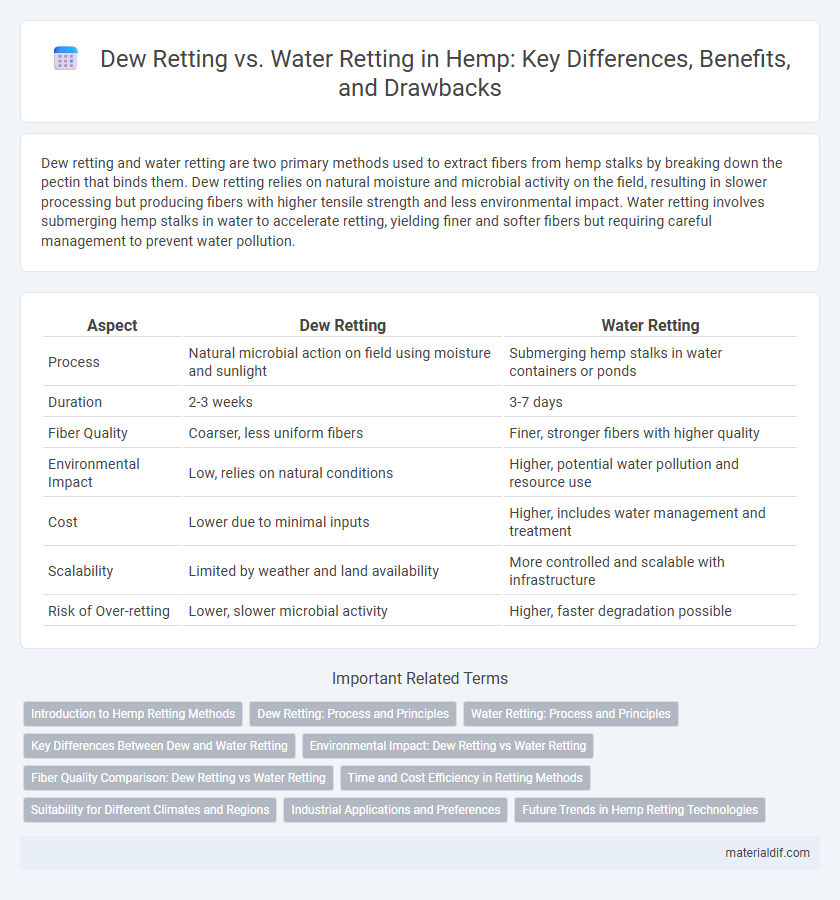
| Aspect | Dew Retting | Water Retting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Natural microbial action on field using moisture and sunlight | Submerging hemp stalks in water containers or ponds |
| Duration | 2-3 weeks | 3-7 days |
| Fiber Quality | Coarser, less uniform fibers | Finer, stronger fibers with higher quality |
| Environmental Impact | Low, relies on natural conditions | Higher, potential water pollution and resource use |
| Cost | Lower due to minimal inputs | Higher, includes water management and treatment |
| Scalability | Limited by weather and land availability | More controlled and scalable with infrastructure |
| Risk of Over-retting | Lower, slower microbial activity | Higher, faster degradation possible |
Introduction to Hemp Retting Methods
Hemp retting involves breaking down pectins to separate fibers from the stalk, with dew retting using natural moisture and microbes on the field surface, while water retting immerses stalks in water to accelerate microbial activity. Dew retting is slower, dependent on weather, and environmentally friendly, producing less wastewater compared to water retting, which delivers higher-quality fibers but requires precise water management. Both methods affect fiber yield, tensile strength, and chemical composition, influencing their suitability for textile, composite, and industrial applications.
Dew Retting: Process and Principles
Dew retting is an eco-friendly process used in hemp fiber extraction, relying on natural microbial activity to break down pectins that bind the fibers to the stalk. This method involves spreading harvested hemp stalks on fields to be exposed to moisture from dew, rain, and sunlight, creating optimal conditions for fungi and bacteria to degrade non-fibrous components. Dew retting preserves fiber strength and quality while minimizing water consumption compared to water retting, making it a sustainable choice in hemp processing.
Water Retting: Process and Principles
Water retting is a hemp fiber extraction process that involves submerging stalks in water to promote microbial activity, breaking down pectins that bind fibers to the woody core. This method relies on anaerobic bacteria thriving in stagnant or slow-flowing water environments, which effectively loosen the fibers for easier separation. The principles of water retting emphasize controlled temperature and water quality to optimize fiber quality and minimize degradation.
Key Differences Between Dew and Water Retting
Dew retting utilizes natural microbial action on hemp stalks left on the field surface, relying on moisture from dew and rain, which results in slower fiber separation and less environmental impact. Water retting submerges hemp stalks in water, accelerating the microbial degradation process for faster fiber extraction but often producing wastewater that requires treatment to prevent pollution. Key differences include retting speed, environmental consequences, and fiber quality consistency, with dew retting providing finer fiber and water retting yielding higher retting efficiency.
Environmental Impact: Dew Retting vs Water Retting
Dew retting uses natural moisture and microbes from the soil and air, resulting in lower water consumption and minimal wastewater discharge, making it environmentally friendly compared to water retting, which requires large amounts of water and generates nutrient-rich effluents that can lead to water pollution. Water retting's effluents often contain organic matter and tannins that may deplete oxygen in aquatic ecosystems, causing harm to aquatic life. Dew retting's slower process reduces chemical runoff and energy use, contributing to a smaller ecological footprint in fiber processing.
Fiber Quality Comparison: Dew Retting vs Water Retting
Dew retting produces fibers with higher tensile strength and a rougher texture, beneficial for textiles requiring durability, while water retting yields finer, smoother fibers preferred in high-quality fabric production. Water retting accelerates pectin breakdown, resulting in cleaner separation of fibers but risks over-retting and environmental pollution due to water contamination. Dew retting, reliant on natural microorganisms and environmental conditions, offers an eco-friendlier process with longer retting times that enhance fiber integrity.
Time and Cost Efficiency in Retting Methods
Dew retting typically takes 3 to 6 weeks, making it more time-consuming but cost-efficient due to minimal resource use, relying primarily on natural moisture and microbial activity. Water retting accelerates the process to 5 to 10 days by immersing hemp stalks in water, increasing labor and infrastructure expenses but enabling faster fiber extraction. Considering industrial scalability, dew retting offers lower operational costs, while water retting enhances productivity through reduced processing time.
Suitability for Different Climates and Regions
Dew retting is more suitable for temperate and humid climates where natural moisture and microbial activity can efficiently break down hemp stalks, making it ideal for regions with moderate rainfall. Water retting requires abundant water resources and is better adapted to wet, warmer climates or areas near water bodies to ensure complete fiber separation. Both retting methods depend on local environmental conditions to optimize fiber quality and yield.
Industrial Applications and Preferences
Dew retting involves natural microbial decomposition on fields, making it cost-effective and preferred for large-scale hemp fiber production in industries focused on sustainability and low water usage. Water retting, utilizing controlled submersion in water tanks, yields higher fiber quality but demands significant water resources and infrastructure, favoring high-end textile and composite manufacturing. Industrial applications prioritize dew retting for eco-friendly scalability, while water retting is chosen where fiber fineness and strength are critical.
Future Trends in Hemp Retting Technologies
Innovations in hemp retting are increasingly favoring enzyme-assisted and microbial methods over traditional dew and water retting due to their efficiency and environmental benefits. Dew retting remains cost-effective in certain climates but faces challenges such as inconsistent fiber quality and slower processing times. Future trends emphasize sustainable biotechnological approaches that reduce water usage and chemical inputs while enhancing fiber yield and strength for industrial applications.
Dew retting vs Water retting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com