Hemp yarn offers superior durability and resistance to mold compared to flax yarn, making it ideal for heavy-duty textiles and outdoor applications. While flax yarn provides a softer, smoother texture suited for delicate fabrics, hemp yarn's strength and eco-friendly properties position it as a sustainable alternative in the textile industry. Both fibers contribute to natural fabric production, but hemp yarn's robustness and moisture-wicking capabilities give it a competitive edge in functional and long-lasting products.
Table of Comparison
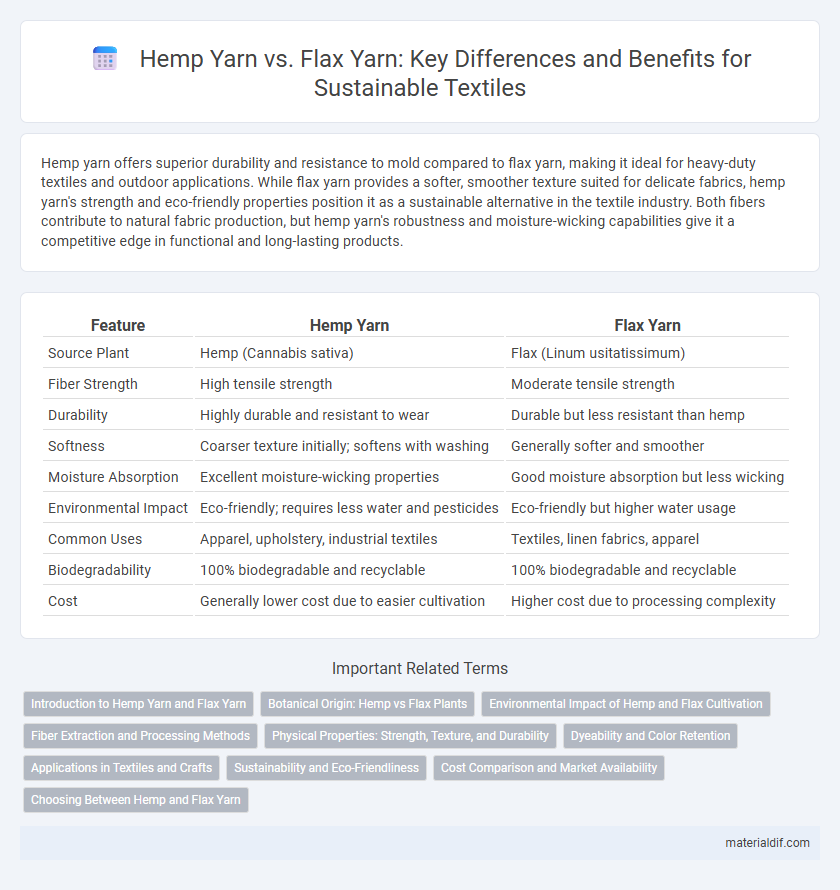
| Feature | Hemp Yarn | Flax Yarn |
|---|---|---|
| Source Plant | Hemp (Cannabis sativa) | Flax (Linum usitatissimum) |
| Fiber Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Durability | Highly durable and resistant to wear | Durable but less resistant than hemp |
| Softness | Coarser texture initially; softens with washing | Generally softer and smoother |
| Moisture Absorption | Excellent moisture-wicking properties | Good moisture absorption but less wicking |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; requires less water and pesticides | Eco-friendly but higher water usage |
| Common Uses | Apparel, upholstery, industrial textiles | Textiles, linen fabrics, apparel |
| Biodegradability | 100% biodegradable and recyclable | 100% biodegradable and recyclable |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to easier cultivation | Higher cost due to processing complexity |
Introduction to Hemp Yarn and Flax Yarn
Hemp yarn is derived from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, known for its strength, durability, and resistance to mold, making it ideal for textiles requiring longevity. Flax yarn, produced from the flax plant, primarily used to make linen, is valued for its smooth texture, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties. Both yarns offer sustainable alternatives in eco-friendly fabrics, with hemp providing robustness and flax delivering softness in textile applications.
Botanical Origin: Hemp vs Flax Plants
Hemp yarn is derived from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, known for its sturdy stalks and rapid growth, making it a sustainable source of natural fiber. Flax yarn, in contrast, comes from the Linum usitatissimum plant, which produces finer fibers primarily used in linen textiles. Both plants belong to different botanical families, with hemp in the Cannabaceae family and flax in the Linaceae family, influencing the texture and durability of their respective yarns.
Environmental Impact of Hemp and Flax Cultivation
Hemp cultivation requires significantly less water and pesticides compared to flax, resulting in a lower environmental footprint and reduced soil depletion. Flax fields often demand more intensive use of fertilizers and irrigation, which can contribute to higher greenhouse gas emissions and water pollution. Hemp's rapid growth and ability to improve soil health make it a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious yarn production.
Fiber Extraction and Processing Methods
Hemp yarn extraction relies on retting, which involves microbial or chemical treatments to separate the bast fibers, followed by decortication and combing processes to produce strong, coarse fibers ideal for durable textiles. Flax yarn processing also begins with retting, but often employs water or dew retting to break down pectins, facilitating easier fiber separation, and is noted for producing finer, softer fibers suitable for lightweight fabrics. Both fibers require scutching and hackling post-retting, but hemp's longer fibers result in rougher yarn compared to the smoother, finer flax yarn derived from shorter, more pliable fibers.
Physical Properties: Strength, Texture, and Durability
Hemp yarn exhibits exceptional strength and durability, often surpassing flax yarn due to its robust fiber structure, making it ideal for heavy-duty textiles. The texture of hemp yarn is coarser and more rigid compared to the smoother and finer flax yarn, which contributes to a different tactile experience and suitability for specific fabric types. Hemp's resistance to wear and environmental degradation enhances its longevity, while flax yarn, though durable, may be more prone to wear under intense use.
Dyeability and Color Retention
Hemp yarn exhibits superior dyeability due to its natural coarseness and open fiber structure, allowing deeper pigment absorption compared to flax yarn. Hemp fibers maintain vibrant color retention over time, resisting fading and washing, making it ideal for long-lasting textiles. Flax yarn, while offering a softer texture, generally shows less colorfastness, with dyes tending to wash out more quickly under repeated laundering.
Applications in Textiles and Crafts
Hemp yarn offers superior durability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for heavy-duty textiles such as upholstery, ropes, and eco-friendly clothing. Flax yarn, derived from the flax plant, is prized for its softness and smooth texture, commonly used in fine linen fabrics, tablecloths, and delicate crafts. Both fibers support sustainable production but differ in application versatility, with hemp favored in rugged, long-lasting products and flax preferred for lightweight, breathable textiles.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Hemp yarn outperforms flax yarn in sustainability due to its rapid growth cycle, requiring less water and pesticides compared to flax cultivation. The durability and biodegradability of hemp fibers make hemp yarn an eco-friendly choice for reducing environmental impact. Both fibers support sustainable textile production, but hemp's lower resource demands give it a stronger advantage in eco-conscious manufacturing.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Hemp yarn tends to be more cost-effective than flax yarn due to lower cultivation and processing expenses, making it appealing for budget-conscious textile producers. Market availability of hemp yarn is expanding rapidly as industrial hemp cultivation increases globally, whereas flax yarn remains more niche with limited suppliers. Cost disparities and broader accessibility position hemp yarn as a competitive alternative in sustainable fabric markets.
Choosing Between Hemp and Flax Yarn
Hemp yarn offers superior durability and moisture-wicking properties compared to flax yarn, making it ideal for heavy-duty textiles and outdoor fabrics. Flax yarn, derived from the flax plant, provides a softer texture and a natural luster, preferred in fine linens and apparel where comfort and aesthetic appeal are prioritized. Selecting between hemp and flax yarn depends on the specific application, balancing hemp's strength with flax's smoothness and drape.
Hemp yarn vs Flax yarn Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com