Water-retting and enzyme-retting are two common methods used to extract fibers from hemp stalks. Water-retting involves submerging hemp stalks in water to encourage microbial activity that breaks down the pectin binding the fibers, resulting in strong, coarse fibers but requiring careful management to avoid environmental pollution. Enzyme-retting uses specific enzymes to target pectin selectively, producing finer, more uniform fibers with less environmental impact and shorter processing times compared to traditional water-retting.
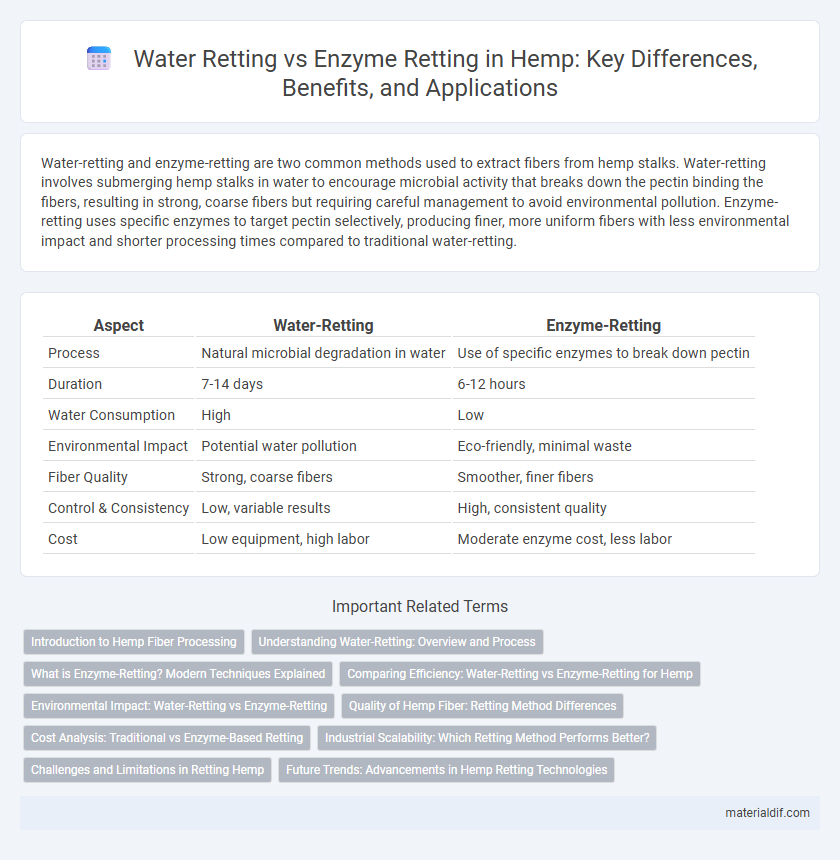
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Water-Retting | Enzyme-Retting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Natural microbial degradation in water | Use of specific enzymes to break down pectin |
| Duration | 7-14 days | 6-12 hours |
| Water Consumption | High | Low |
| Environmental Impact | Potential water pollution | Eco-friendly, minimal waste |
| Fiber Quality | Strong, coarse fibers | Smoother, finer fibers |
| Control & Consistency | Low, variable results | High, consistent quality |
| Cost | Low equipment, high labor | Moderate enzyme cost, less labor |
Introduction to Hemp Fiber Processing
Water-retting and enzyme-retting are two primary methods for extracting hemp fibers, each influencing fiber quality and environmental impact. Water-retting involves submerging hemp stalks in water to promote microbial decomposition of pectin, resulting in softer fibers but higher water usage and potential wastewater concerns. Enzyme-retting employs specific enzymes to selectively break down pectin, offering controlled processing times, improved fiber strength, and reduced environmental footprint compared to traditional water-retting.
Understanding Water-Retting: Overview and Process
Water-retting is a traditional method used in hemp fiber extraction that involves submerging hemp stalks in water to allow microbial activity to break down the pectin binding the fibers. This natural decomposition process typically takes 7 to 14 days, depending on water temperature and bacterial presence, resulting in fibers suitable for textiles and composites. Understanding the environmental conditions and timing is crucial for achieving optimal fiber quality through water-retting.
What is Enzyme-Retting? Modern Techniques Explained
Enzyme-retting is a modern, eco-friendly method of extracting fibers from hemp by using specific enzymes to break down pectin and other binding materials in the stalks. This controlled biochemical process accelerates fiber separation compared to traditional water-retting, reducing environmental impact and improving fiber quality. Advanced enzyme formulations optimize fiber strength, softness, and yield, making enzyme-retting a preferred technique in sustainable hemp fiber production.
Comparing Efficiency: Water-Retting vs Enzyme-Retting for Hemp
Water-retting involves submerging hemp stalks in water to promote microbial activity that separates fibers, often requiring 7 to 14 days and consistent temperature control. Enzyme-retting uses specific pectinolytic enzymes to target and break down pectin bonds more rapidly, significantly reducing processing time to 24-48 hours while yielding higher-quality bast fibers. Efficiency-wise, enzyme-retting offers superior fiber yield and uniformity with less environmental impact compared to water-retting's longer duration and potential water pollution challenges.
Environmental Impact: Water-Retting vs Enzyme-Retting
Water-retting involves submerging hemp stalks in water to promote microbial activity that breaks down pectins, but it generates significant water pollution and high energy consumption due to wastewater treatment needs. Enzyme-retting uses specific cellulase or pectinase enzymes to efficiently degrade pectins with minimal environmental footprint, reducing chemical use and water waste. The enzyme-retting process is considered more sustainable and eco-friendly, aligning with green manufacturing practices in the textile and bioproduct industries.
Quality of Hemp Fiber: Retting Method Differences
Water-retting produces coarser hemp fibers with higher lignin content, resulting in lower tensile strength and reduced fiber quality compared to enzyme-retting. Enzyme-retting uses specific pectinase enzymes to selectively break down pectins, yielding finer, softer, and more consistent fibers with improved mechanical properties. The choice of retting method significantly influences fiber purity, strength, and suitability for high-performance textile applications.
Cost Analysis: Traditional vs Enzyme-Based Retting
Water-retting of hemp involves submerging stalks in water for 7-14 days, incurring high labor and water treatment costs, while enzyme-retting uses specialized cellulase and pectinase enzymes, reducing processing time to 24-48 hours and lowering labor expenses. Enzyme-retting demands an upfront investment in enzyme procurement, typically ranging from $10 to $50 per kilogram, but offers increased fiber yield and quality, resulting in higher market value and overall cost savings. Comparing both methods, enzyme-retting provides a more efficient and sustainable solution, minimizing environmental impact and operational costs despite the initial enzyme costs.
Industrial Scalability: Which Retting Method Performs Better?
Water-retting, involving microbial fermentation in large tanks or natural water bodies, offers scalable processing for hemp fibers but requires extensive water use and longer processing times, which can limit industrial throughput. Enzyme-retting uses specific pectinase enzymes to efficiently break down hemp stalks, enabling faster fiber separation with less environmental impact and better control over fiber quality, making it more suitable for industrial scalability. Enzyme-retting's precision and reduced water consumption position it as the preferred method in large-scale hemp fiber production.
Challenges and Limitations in Retting Hemp
Water-retting of hemp poses challenges such as high water consumption, potential environmental pollution from effluent discharge, and lengthy processing times that increase operational costs. Enzyme-retting offers a more controlled process but faces limitations including high enzyme costs, sensitivity to temperature and pH variations, and inconsistent fiber quality due to incomplete retting. Both methods require optimization to balance efficiency, sustainability, and fiber integrity for commercial hemp production.
Future Trends: Advancements in Hemp Retting Technologies
Future trends in hemp retting emphasize advancements in enzyme-retting techniques, which offer faster processing times and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional water-retting methods. Innovations in tailored enzyme formulations enhance fiber quality and consistency, promoting scalability for industrial applications. Integration of biotechnology with sustainable practices drives the evolution of hemp retting toward more eco-friendly and cost-effective solutions.
Water-retting vs Enzyme-retting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com