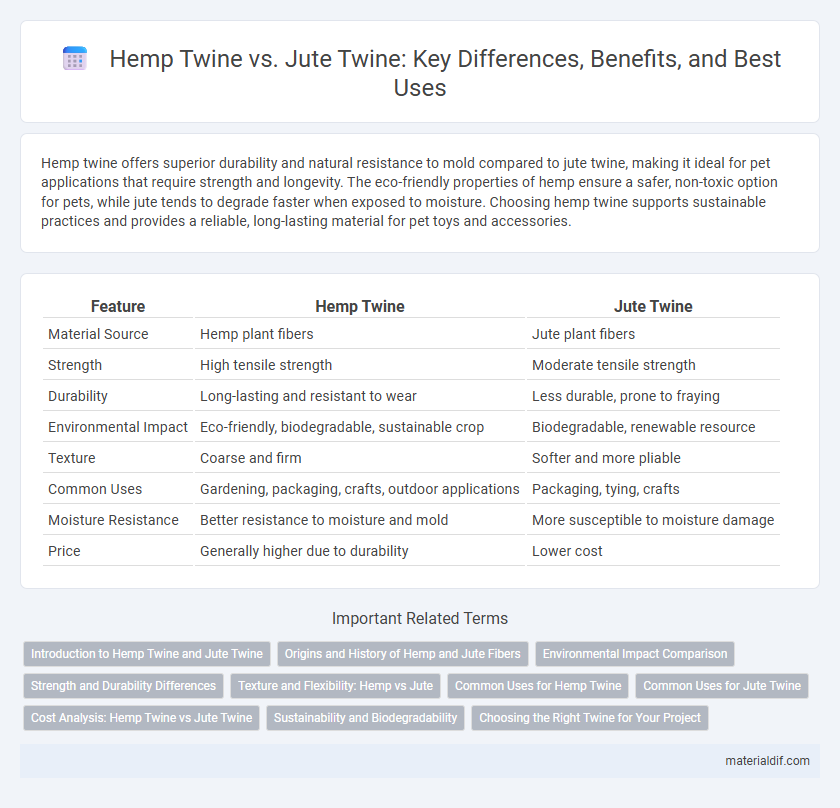
Hemp twine offers superior durability and natural resistance to mold compared to jute twine, making it ideal for pet applications that require strength and longevity. The eco-friendly properties of hemp ensure a safer, non-toxic option for pets, while jute tends to degrade faster when exposed to moisture. Choosing hemp twine supports sustainable practices and provides a reliable, long-lasting material for pet toys and accessories.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Twine | Jute Twine |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Hemp plant fibers | Jute plant fibers |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Durability | Long-lasting and resistant to wear | Less durable, prone to fraying |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, sustainable crop | Biodegradable, renewable resource |
| Texture | Coarse and firm | Softer and more pliable |
| Common Uses | Gardening, packaging, crafts, outdoor applications | Packaging, tying, crafts |
| Moisture Resistance | Better resistance to moisture and mold | More susceptible to moisture damage |
| Price | Generally higher due to durability | Lower cost |
Introduction to Hemp Twine and Jute Twine
Hemp twine is crafted from the durable fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, known for its strength, resistance to mold, and environmental sustainability. Jute twine, derived from the jute plant, is a soft, biodegradable fiber favored for its affordability and versatility in packaging and gardening. Both hemp and jute twines offer natural alternatives to synthetic materials, with hemp twine excelling in durability and jute twine prized for its softness and cost-effectiveness.
Origins and History of Hemp and Jute Fibers
Hemp twine originates from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, cultivated for thousands of years across Asia and Europe, prized for its durability and resistance to rot. Jute twine comes from the jute plant, primarily grown in the Indian subcontinent, with a history dating back over 4,000 years as a biodegradable and affordable fiber used in textiles and ropes. Both fibers have shaped traditional crafts and agriculture, with hemp historically favored in maritime applications and jute dominating in packaging and sackcloth industries.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Hemp twine is more environmentally sustainable than jute twine due to its faster growth rate and lower water and pesticide requirements, resulting in reduced ecological footprint. Hemp cultivation improves soil health through phytoremediation and carbon sequestration, enhancing biodiversity compared to jute. Biodegradability and renewability of hemp fibers further contribute to its superior environmental impact over jute twine.
Strength and Durability Differences
Hemp twine exhibits superior strength compared to jute twine due to its longer fibers and higher tensile strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Durability-wise, hemp twine resists moisture, UV exposure, and microbial degradation better than jute, resulting in a longer lifespan in outdoor and harsh environments. While jute twine offers flexibility and affordability, hemp twine stands out for projects demanding enhanced load-bearing capacity and sustained performance.
Texture and Flexibility: Hemp vs Jute
Hemp twine features a coarse, rough texture with high tensile strength, making it durable yet slightly stiff, ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring strong grip. Jute twine offers a softer, smoother texture and greater flexibility, allowing easier knotting and handling for lightweight crafts or packaging. The natural fibers of hemp provide more rigidity, while jute's pliable fibers enhance maneuverability and comfort in use.
Common Uses for Hemp Twine
Hemp twine is widely used for gardening, macrame, and packaging due to its superior strength and natural resistance to mold and UV damage. It serves as an eco-friendly option for binding plants, creating durable crafts, and wrapping parcels securely. Unlike jute twine, hemp twine offers enhanced durability, making it ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty applications.
Common Uses for Jute Twine
Jute twine is commonly used in gardening for tying plants and supporting climbing vegetables due to its natural strength and biodegradability. It also finds frequent application in crafting and packaging, providing an eco-friendly alternative for bundling and wrapping. Its coarse texture and durability make it ideal for agricultural and landscaping tasks where sturdy, natural fiber is preferred.
Cost Analysis: Hemp Twine vs Jute Twine
Hemp twine typically commands a higher price than jute twine due to its superior durability and eco-friendly cultivation process. The cost per pound of hemp twine ranges from $5 to $8, while jute twine is generally priced between $2 and $4 per pound, making jute a more budget-friendly option for bulk applications. When calculating total expenses, factors such as tensile strength, longevity, and environmental impact should be considered alongside the initial purchase price to determine overall value.
Sustainability and Biodegradability
Hemp twine offers superior sustainability due to its rapid growth cycle and minimal need for pesticides, making it an eco-friendly alternative to jute twine. Both hemp and jute twines are biodegradable, but hemp fibers decompose more quickly, reducing environmental impact. Choosing hemp twine supports sustainable agriculture and promotes efficient biodegradability in natural fiber products.
Choosing the Right Twine for Your Project
Hemp twine offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for heavy-duty tasks and outdoor projects requiring long-lasting performance. Jute twine is softer and more flexible, suitable for decorative uses, gardening, and light bundling where cost-effectiveness and biodegradability are priorities. Selecting hemp twine ensures enhanced tensile strength and longevity, while jute twine provides a more economical and eco-friendly option for less demanding applications.
Hemp Twine vs Jute Twine Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com