Decortication mechanically separates hemp fibers from the stalk, producing clean, long fibers ideal for textiles and composites with minimal environmental impact. Retting uses moisture and microbial action to break down pectin, allowing fibers to be easily separated but requires precise control to prevent fiber degradation. Choosing between decortication and retting depends on final product quality, processing time, and sustainability considerations.
Table of Comparison
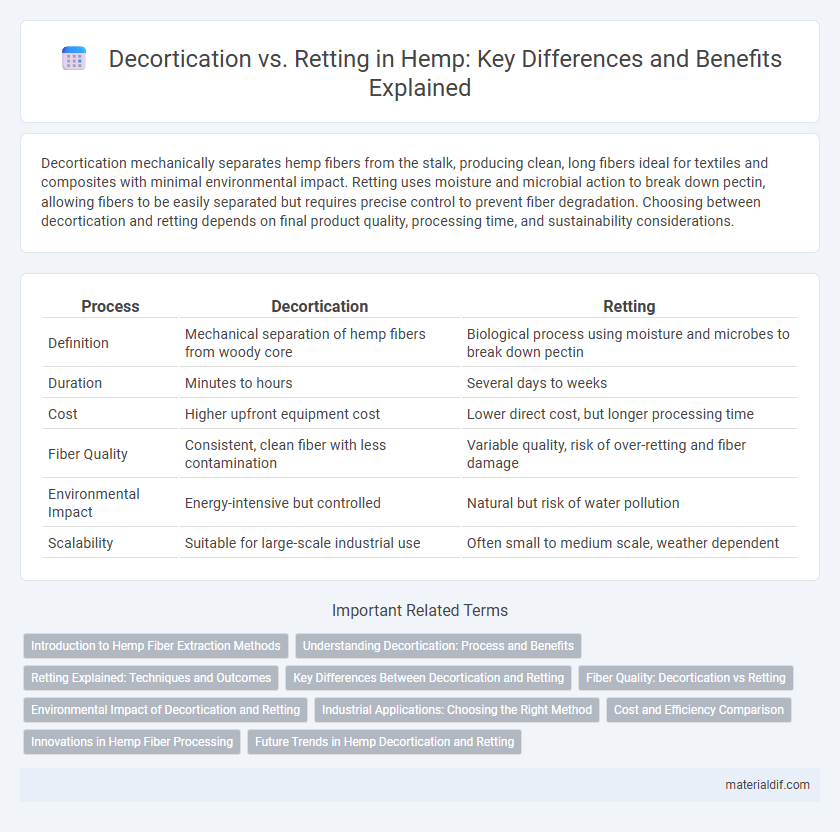
| Process | Decortication | Retting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mechanical separation of hemp fibers from woody core | Biological process using moisture and microbes to break down pectin |
| Duration | Minutes to hours | Several days to weeks |
| Cost | Higher upfront equipment cost | Lower direct cost, but longer processing time |
| Fiber Quality | Consistent, clean fiber with less contamination | Variable quality, risk of over-retting and fiber damage |
| Environmental Impact | Energy-intensive but controlled | Natural but risk of water pollution |
| Scalability | Suitable for large-scale industrial use | Often small to medium scale, weather dependent |
Introduction to Hemp Fiber Extraction Methods
Decortication and retting are two primary methods for extracting hemp fibers, each influencing fiber quality and processing efficiency. Decortication mechanically separates the hemp stalk into fibers and hurd, enabling faster, large-scale fiber extraction suitable for industrial applications. Retting relies on microbial action or chemical treatments to break down pectin, yielding softer, finer fibers ideal for textile production but requiring longer processing times.
Understanding Decortication: Process and Benefits
Decortication involves mechanically separating hemp fibers from the stalk, producing clean, long fibers ideal for textiles, composites, and paper. This process reduces water usage and processing time compared to retting, while maintaining fiber strength and quality. Efficient decortication supports sustainable hemp production by minimizing environmental impact and boosting fiber yield.
Retting Explained: Techniques and Outcomes
Retting is a controlled microbial or chemical process used to separate hemp fibers from the stalk by breaking down pectins, resulting in higher fiber quality and better tensile strength compared to decortication. Common retting techniques include water retting, dew retting, and enzymatic retting, each offering distinct impacts on fiber fineness, color, and yield. Efficient retting minimizes fiber damage and enhances the usability of hemp fibers in textiles, composites, and bioplastics, improving overall material performance.
Key Differences Between Decortication and Retting
Decortication mechanically separates hemp fibers from the stalk using specialized machinery, resulting in faster processing and higher fiber yield. Retting, a natural or chemical process, breaks down the pectin binding fibers through microbial activity or chemical treatment, which enhances fiber quality but requires more time. Key differences include decortication's efficiency and suitability for large-scale production versus retting's impact on fiber softness and fineness.
Fiber Quality: Decortication vs Retting
Decortication mechanically separates hemp fibers, preserving tensile strength and producing coarse, uniform fibers ideal for industrial applications like textiles and biocomposites. Retting, a biological process using moisture and microbes, yields softer, finer fibers with reduced lignin content but may compromise fiber durability and result in inconsistent quality. Choosing between decortication and retting depends on the desired fiber characteristics and end-use, with decortication favored for strength and retting preferred for softness and fineness.
Environmental Impact of Decortication and Retting
Decortication and retting are key processes in hemp fiber extraction with distinct environmental impacts. Decortication mechanically separates fibers, reducing water use and preventing water pollution compared to retting, which relies on microbial action in water or soil, often generating effluents rich in organic matter and nutrients that can harm aquatic ecosystems. Opting for decortication supports sustainable hemp processing by minimizing chemical inputs and wastewater discharge, aligning with eco-friendly agricultural practices.
Industrial Applications: Choosing the Right Method
Decortication offers rapid mechanical separation of hemp fibers, ideal for large-scale industrial applications requiring consistent fiber length and quality, such as textiles and composites. Retting relies on microbial or chemical processes to break down pectin, producing softer fibers favored in specialty paper and fine fabric manufacturing. Selecting between decortication and retting depends on the desired fiber attributes, processing time, and end-use requirements within industrial hemp production.
Cost and Efficiency Comparison
Decortication offers a faster, mechanized method for separating hemp fibers, resulting in lower labor costs and higher processing efficiency compared to retting, which relies on microbial or chemical breakdown and can take weeks to complete. Retting often produces finer fibers but incurs higher operational costs due to longer processing times and additional environmental management requirements. Cost-efficient decortication systems scale well for industrial hemp production, maximizing throughput while minimizing energy consumption and waste.
Innovations in Hemp Fiber Processing
Innovations in hemp fiber processing have revolutionized traditional decortication and retting methods, introducing enzyme-assisted retting that accelerates cellulose breakdown while preserving fiber quality. Advanced decortication machinery now employs precise mechanical separation techniques that reduce fiber damage and increase yield efficiency. These technological advancements enhance the sustainable extraction of high-strength hemp fibers for textile, construction, and composite applications.
Future Trends in Hemp Decortication and Retting
Advancements in hemp decortication are focusing on enhancing fiber purity and processing speed through automated, eco-friendly machinery that reduces chemical use. Retting methods are evolving with bio-based enzyme formulations to accelerate fiber separation while minimizing environmental impact. Future trends emphasize integrating decortication and retting processes into streamlined, sustainable production lines to meet growing industrial hemp demand.
Decortication vs Retting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com