Hemp-based textiles offer superior durability and breathability compared to bamboo-based textiles, making them ideal for long-lasting apparel and home furnishings. Hemp fibers require less water and pesticides, resulting in a more sustainable and eco-friendly production process than bamboo textiles, which often undergo chemical-intensive processing. The natural antimicrobial properties of hemp further enhance its appeal, providing odor resistance and improved hygiene over bamboo alternatives.
Table of Comparison
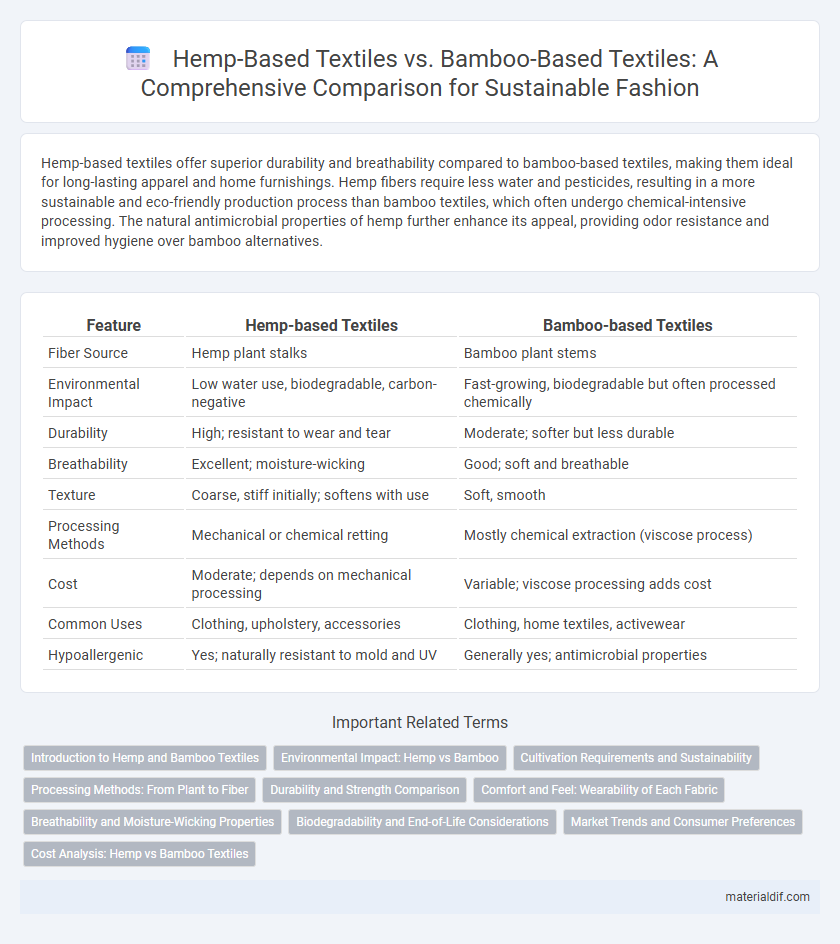
| Feature | Hemp-based Textiles | Bamboo-based Textiles |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Source | Hemp plant stalks | Bamboo plant stems |
| Environmental Impact | Low water use, biodegradable, carbon-negative | Fast-growing, biodegradable but often processed chemically |
| Durability | High; resistant to wear and tear | Moderate; softer but less durable |
| Breathability | Excellent; moisture-wicking | Good; soft and breathable |
| Texture | Coarse, stiff initially; softens with use | Soft, smooth |
| Processing Methods | Mechanical or chemical retting | Mostly chemical extraction (viscose process) |
| Cost | Moderate; depends on mechanical processing | Variable; viscose processing adds cost |
| Common Uses | Clothing, upholstery, accessories | Clothing, home textiles, activewear |
| Hypoallergenic | Yes; naturally resistant to mold and UV | Generally yes; antimicrobial properties |
Introduction to Hemp and Bamboo Textiles
Hemp textiles are derived from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, known for their durability, breathability, and natural resistance to pests and mold, making them an eco-friendly choice in sustainable fashion. Bamboo textiles are produced from bamboo grass, processed into viscose or lyocell fibers, offering a soft, silky texture with moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties valued in activewear. Both hemp and bamboo textiles contribute to reducing environmental impact, with hemp requiring fewer pesticides and less water, while bamboo grows rapidly and regenerates without replanting.
Environmental Impact: Hemp vs Bamboo
Hemp-based textiles generate significantly lower carbon emissions compared to bamboo, as hemp cultivation requires less water, fewer pesticides, and enriches the soil through nitrogen fixation. Bamboo production often involves intensive processing using chemicals to break down fibers, leading to higher environmental pollution and energy consumption. Hemp's rapid growth and regenerative properties position it as a more sustainable and eco-friendly option for textile manufacturing than bamboo.
Cultivation Requirements and Sustainability
Hemp-based textiles require minimal water, pesticides, and synthetic fertilizers, thriving in diverse soil conditions, which enhances their sustainability compared to bamboo-based textiles that need specific temperate climates and more intensive water management. Hemp plants contribute to soil health through phytoremediation and carbon sequestration, making them a more environmentally friendly crop with faster growth cycles and higher biomass yield per hectare. Bamboo textiles often involve chemical-intensive processing to soften fibers, whereas hemp fibers are naturally durable and biodegradable, further supporting eco-conscious textile production.
Processing Methods: From Plant to Fiber
Hemp-based textiles undergo a mechanical process called decortication, which separates the long bast fibers from the woody core, followed by retting to loosen the fibers for spinning. Bamboo-based textiles typically require chemical processing or mechanical crushing combined with enzyme treatments to extract viscose fibers, which often results in a less sustainable footprint compared to hemp. The natural strength and durability of hemp fibers demand less chemical intervention, making hemp-based textiles more eco-friendly in fiber extraction.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Hemp-based textiles exhibit superior durability and strength compared to bamboo-based textiles due to hemp fibers' longer staple length and higher tensile strength, making them ideal for products subjected to heavy wear. The natural toughness of hemp fibers results in fabric that resists tearing and stretching, maintaining its integrity over time. In contrast, bamboo textiles tend to be softer but generally lack the robustness required for long-lasting performance under stress.
Comfort and Feel: Wearability of Each Fabric
Hemp-based textiles offer exceptional durability and breathability, providing a firm yet soft texture that improves with washing, making them ideal for long-lasting comfortable wear. Bamboo-based textiles feature a silky smooth and lightweight feel with natural moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties, enhancing overall softness and comfort for sensitive skin. Both fabrics excel in wearability, but bamboo stands out for immediate softness while hemp gains comfort over time through increased fabric flexibility.
Breathability and Moisture-Wicking Properties
Hemp-based textiles exhibit superior breathability due to their natural fiber structure, allowing for enhanced airflow and moisture evaporation compared to bamboo-based textiles. The moisture-wicking properties of hemp fibers efficiently draw sweat away from the skin, promoting a cooler and dryer fabric experience. Bamboo textiles, while soft, tend to retain more moisture, making hemp a preferred choice for high-performance, breathable clothing.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Hemp-based textiles exhibit superior biodegradability, breaking down naturally within months due to their low chemical treatment during processing, enhancing soil health post-disposal. Bamboo-based textiles often undergo heavy chemical processes like viscose or rayon production, which reduce their biodegradability and complicate end-of-life composting. Choosing hemp textiles promotes a more sustainable lifecycle with reduced environmental impact, supporting circular fashion initiatives.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Hemp-based textiles are gaining traction in the sustainable fashion market due to their durability, breathability, and eco-friendly cultivation practices, attracting environmentally conscious consumers. Bamboo-based textiles, favored for their softness and moisture-wicking properties, appeal to consumers seeking comfort and hypoallergenic fabrics, driving steady demand growth. Market trends indicate a rising preference for hemp textiles in high-performance and eco-luxury segments, while bamboo maintains dominance in casual wear and activewear, reflecting distinct consumer priorities in sustainability and functionality.
Cost Analysis: Hemp vs Bamboo Textiles
Hemp-based textiles generally incur higher initial processing costs due to the fiber's coarser texture and more complex retting process, impacting overall production expenses. Bamboo textiles benefit from lower raw material costs and faster fiber extraction, contributing to more economical manufacturing but often involve chemical-intensive processing that can increase environmental costs. When comparing cost efficiency, hemp offers greater durability and longevity, potentially reducing long-term textile replacement expenses compared to bamboo alternatives.
Hemp-based Textiles vs Bamboo-based Textiles Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com