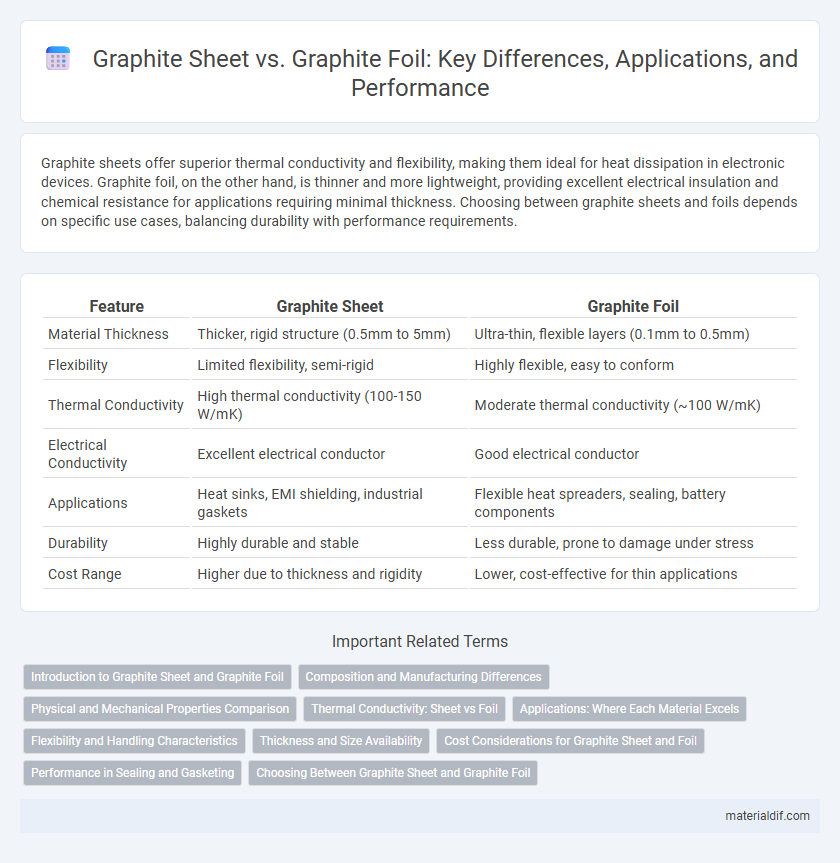
Graphite sheets offer superior thermal conductivity and flexibility, making them ideal for heat dissipation in electronic devices. Graphite foil, on the other hand, is thinner and more lightweight, providing excellent electrical insulation and chemical resistance for applications requiring minimal thickness. Choosing between graphite sheets and foils depends on specific use cases, balancing durability with performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphite Sheet | Graphite Foil |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thickness | Thicker, rigid structure (0.5mm to 5mm) | Ultra-thin, flexible layers (0.1mm to 0.5mm) |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility, semi-rigid | Highly flexible, easy to conform |
| Thermal Conductivity | High thermal conductivity (100-150 W/mK) | Moderate thermal conductivity (~100 W/mK) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent electrical conductor | Good electrical conductor |
| Applications | Heat sinks, EMI shielding, industrial gaskets | Flexible heat spreaders, sealing, battery components |
| Durability | Highly durable and stable | Less durable, prone to damage under stress |
| Cost Range | Higher due to thickness and rigidity | Lower, cost-effective for thin applications |
Introduction to Graphite Sheet and Graphite Foil
Graphite sheets are manufactured by compressing expanded graphite into a dense, flexible material ideal for thermal management and sealing applications, offering high thermal conductivity and chemical resistance. Graphite foil, in contrast, is a thinner, more pliable material produced by rolling exfoliated graphite, commonly used in gaskets, heat shields, and electrical insulation due to its excellent flexibility and adaptability. Both materials leverage graphite's inherent properties but differ in thickness, mechanical strength, and typical industrial uses.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Graphite sheets are typically manufactured by compressing natural graphite flakes with binders, resulting in a flexible but less dense material, while graphite foil is produced through repeated exfoliation and rolling processes to create a denser, pure graphite structure without binders. The composition of graphite sheets includes binders like resins or rubber to enhance flexibility and machinability, whereas graphite foil consists almost entirely of high-purity graphite, offering superior thermal conductivity and chemical resistance. Manufacturing techniques for graphite foil emphasize thin, uniform layers achieved by mechanical exfoliation, contrasting with the compression molding used for graphite sheets.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Graphite sheets exhibit higher density and better thermal conductivity compared to graphite foils, making them ideal for heat dissipation applications. Graphite foil is more flexible and lightweight with lower tensile strength, suitable for gasket and sealing purposes. Both materials offer excellent chemical resistance and electrical conductivity, but graphite sheets provide superior mechanical durability under compression.
Thermal Conductivity: Sheet vs Foil
Graphite sheets typically exhibit higher in-plane thermal conductivity, ranging from 150 to 200 W/m*K, due to their denser structure and alignment of graphene layers. Graphite foils, while thinner and more flexible, generally have lower thermal conductivity values, around 100 to 150 W/m*K, attributed to their looser laminar arrangement. The choice between graphite sheet and foil depends on the thermal management requirements, where sheets offer superior heat dissipation and foils provide conformability with moderate thermal performance.
Applications: Where Each Material Excels
Graphite sheets excel in applications requiring high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, such as heat spreaders in electronics and battery thermal management systems. Graphite foil is ideal for sealing, gasketing, and shielding applications due to its flexibility, chemical resistance, and ability to withstand high pressure and temperature fluctuations. Choosing between graphite sheet and foil depends on specific industry needs like electronics cooling versus industrial sealing solutions.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Graphite sheets offer enhanced flexibility due to their pliable, fabric-like structure, making them ideal for applications requiring conformability to uneven surfaces. In contrast, graphite foil is denser and stiffer, providing superior mechanical strength but reduced flexibility. Handling graphite sheets is easier in tight or irregular spaces, while graphite foil demands more care to prevent creasing or damage during installation.
Thickness and Size Availability
Graphite sheets typically offer greater thickness options, ranging from 0.1 mm to several millimeters, ideal for heavy-duty thermal management and sealing applications. Graphite foil is generally thinner, available in thicknesses as low as 0.025 mm, suited for flexible, lightweight insulation and shielding. Size availability for graphite sheets is often larger, with standard dimensions up to 1000 mm by 1000 mm, while graphite foils are commonly supplied in rolls or sheets with widths up to 500 mm.
Cost Considerations for Graphite Sheet and Foil
Graphite sheets generally incur higher manufacturing costs due to their thicker composition and complex processing methods, making them a more expensive option compared to graphite foils. Graphite foils are produced through exfoliation and rolling processes, resulting in a thinner, flexible material that offers more cost-effective scalability for applications requiring lightweight thermal management. When budget constraints are critical, graphite foils present a more economical alternative without significantly compromising thermal conductivity and durability.
Performance in Sealing and Gasketing
Graphite sheets exhibit superior sealing performance due to their enhanced thickness and durability, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Graphite foils, while thinner and more flexible, offer excellent conformability but may lack the mechanical strength required for demanding gasketing environments. Selecting between graphite sheet and foil depends on balancing the need for robustness versus flexibility to optimize sealing efficacy in specific industrial contexts.
Choosing Between Graphite Sheet and Graphite Foil
Graphite sheets and graphite foils differ primarily in thickness, flexibility, and thermal conductivity, impacting their suitability for various applications. Graphite sheets, usually thicker and more rigid, provide superior mechanical strength and are ideal for high-pressure sealing and thermal management tasks. In contrast, graphite foils offer enhanced conformability and better thermal expansion compensation, making them preferable for flexible electronic devices and fine thermal interface layers.
Graphite Sheet vs Graphite Foil Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com