EDM graphite electrodes offer superior wear resistance and higher thermal stability compared to copper electrodes, making them ideal for precision machining applications. Graphite's low electrical resistance and excellent machinability allow for faster cutting speeds and longer tool life in EDM processes. Copper electrodes, while highly conductive, tend to wear faster and require more frequent replacement, increasing operational costs.
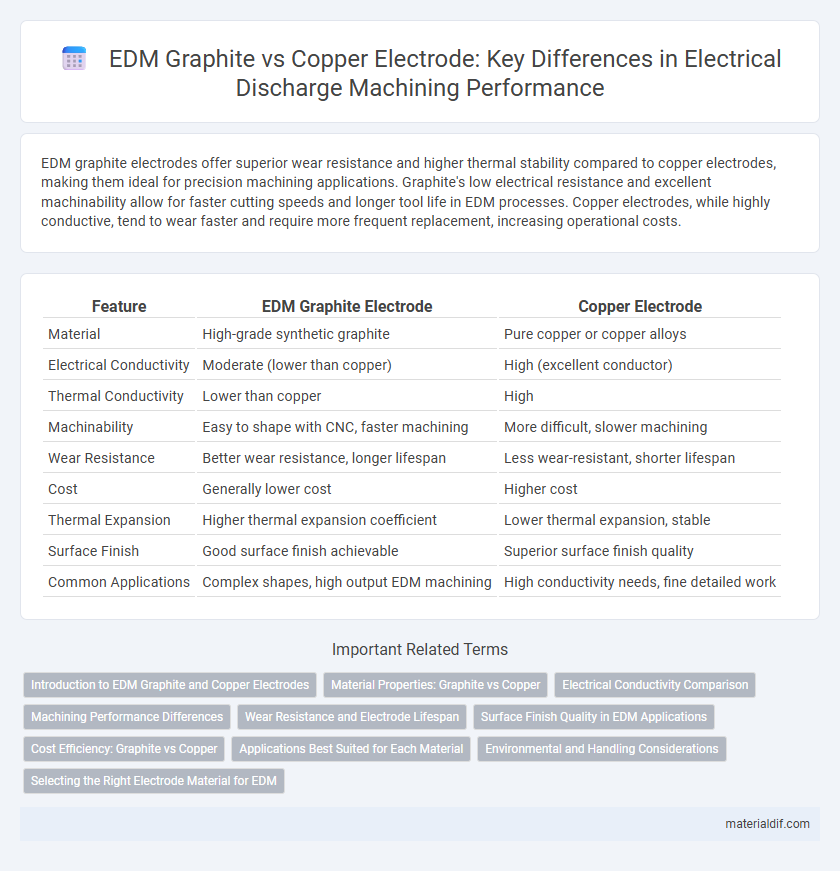
Table of Comparison
| Feature | EDM Graphite Electrode | Copper Electrode |
|---|---|---|
| Material | High-grade synthetic graphite | Pure copper or copper alloys |
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate (lower than copper) | High (excellent conductor) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower than copper | High |
| Machinability | Easy to shape with CNC, faster machining | More difficult, slower machining |
| Wear Resistance | Better wear resistance, longer lifespan | Less wear-resistant, shorter lifespan |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost |
| Thermal Expansion | Higher thermal expansion coefficient | Lower thermal expansion, stable |
| Surface Finish | Good surface finish achievable | Superior surface finish quality |
| Common Applications | Complex shapes, high output EDM machining | High conductivity needs, fine detailed work |
Introduction to EDM Graphite and Copper Electrodes
EDM graphite electrodes are widely used in electrical discharge machining due to their excellent thermal conductivity, wear resistance, and ability to produce fine surface finishes. Copper electrodes offer superior electrical conductivity and faster machining speeds but tend to wear more quickly compared to graphite. The choice between EDM graphite and copper electrodes depends on factors like machining precision, electrode wear rate, and the specific requirements of the workpiece material.
Material Properties: Graphite vs Copper
Graphite electrodes exhibit high thermal conductivity and excellent electrical conductivity, combined with exceptional resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making them ideal for electric arc furnace applications. Copper electrodes offer superior electrical conductivity but are prone to rapid wear and oxidation at high temperatures, limiting their lifespan in high-heat environments. Graphite's porous structure allows for better coolant flow, enhancing durability compared to the dense, less thermally resilient copper electrodes.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
EDM graphite electrodes exhibit significantly higher electrical conductivity compared to copper electrodes, enabling faster machining speeds and improved spark stability in electrical discharge machining processes. Graphite's conductivity typically ranges from 10,000 to 30,000 S/m, whereas copper offers higher conductivity around 58,000 S/m but is prone to faster wear and deformation. The superior wear resistance and thermal stability of EDM graphite compensate for its lower conductivity, enhancing precision and electrode longevity in complex machining tasks.
Machining Performance Differences
EDM graphite electrodes offer superior machining performance compared to copper electrodes due to their high thermal conductivity and lower wear rate, enabling faster material removal and longer tool life. Graphite's porous structure enhances dielectric fluid circulation, resulting in improved surface finish and precision. In contrast, copper electrodes exhibit lower machining speeds and higher electrode wear, limiting their efficiency in complex or high-precision EDM applications.
Wear Resistance and Electrode Lifespan
EDM graphite electrodes exhibit superior wear resistance compared to copper electrodes due to their high thermal conductivity and low coefficient of thermal expansion, which reduce electrode degradation during machining. The enhanced wear resistance of graphite leads to a longer electrode lifespan, minimizing electrode replacement frequency and downtime in electrical discharge machining processes. Copper electrodes, while offering excellent electrical conductivity, generally wear faster under intense machining conditions, resulting in a shorter operational lifespan.
Surface Finish Quality in EDM Applications
EDM graphite electrodes provide superior surface finish quality compared to copper electrodes due to their higher melting point and thermal conductivity, which results in less electrode wear and more consistent spark erosion. The porous structure of EDM graphite reduces surface defects and thermal stresses during machining, enabling finer detail and smoother finishes. While copper electrodes may offer higher electrical conductivity, the dimensional stability and low expansion of EDM graphite ensure improved accuracy and surface integrity in precision EDM applications.
Cost Efficiency: Graphite vs Copper
Graphite electrodes typically offer higher cost efficiency compared to copper electrodes due to their lower material and manufacturing expenses. Graphite's durability and resistance to thermal shock reduce replacement frequency, resulting in decreased operational downtime and maintenance costs. Copper electrodes, while providing excellent electrical conductivity, often incur higher initial and upkeep costs, making graphite a more economical choice in industrial applications like electric arc furnaces.
Applications Best Suited for Each Material
EDM graphite electrodes are best suited for high-precision machining, complex shapes, and fine surface finishes in industries like aerospace, automotive, and mold making due to their superior wear resistance and thermal stability. Copper electrodes excel in applications requiring high electrical conductivity and efficient heat dissipation, such as high-speed machining and short-run production of simple components. Graphite is preferred for intricate designs and higher durability, while copper is ideal for faster machining of straightforward geometries.
Environmental and Handling Considerations
EDM graphite electrodes offer significant environmental advantages over copper electrodes due to their lower toxicity and reduced metal waste during machining processes. Graphite's inert nature minimizes harmful emissions and simplifies recycling compared to copper, which involves energy-intensive smelting and generates hazardous byproducts. Handling graphite electrodes is safer and more ergonomic since they are lighter and produce less dust, whereas copper electrodes require careful management to prevent heavy metal exposure and contamination.
Selecting the Right Electrode Material for EDM
Selecting the right electrode material for EDM is crucial for achieving precision and efficiency; EDM graphite offers superior electrical conductivity, higher melting point, and better wear resistance compared to copper electrodes. Graphite electrodes provide faster machining speeds, reduced sparking, and smoother surface finishes, making them ideal for complex or high-precision applications. Copper electrodes, while more affordable and easier to fabricate, tend to wear out faster and require more frequent replacement, impacting long-term cost-effectiveness and machining quality.
EDM Graphite vs Copper Electrode Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com