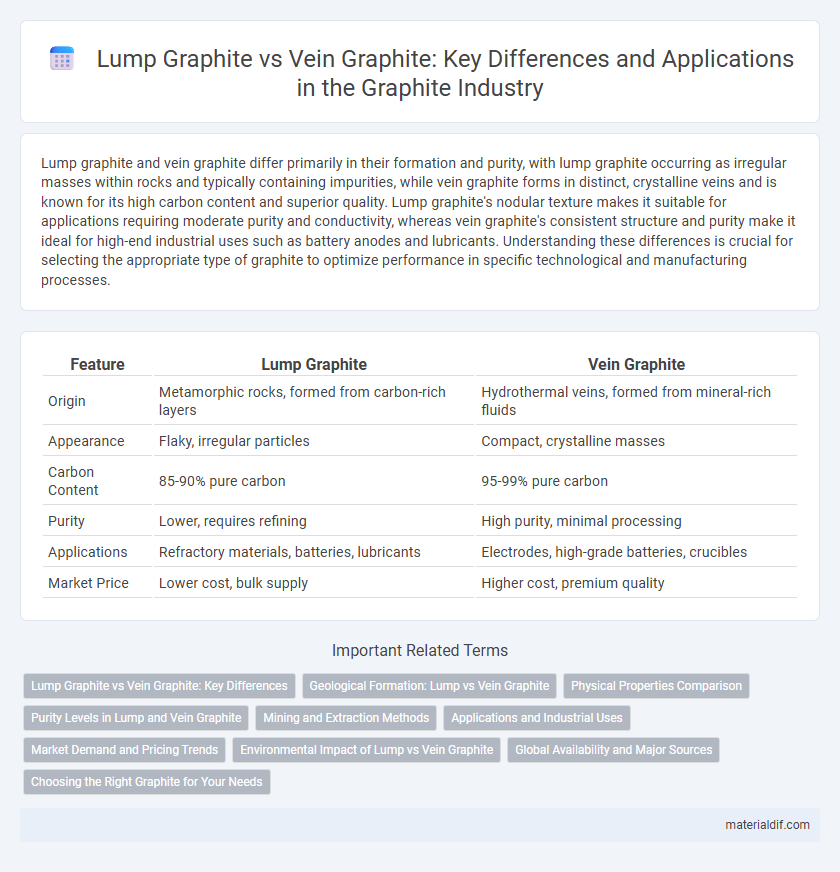
Lump graphite and vein graphite differ primarily in their formation and purity, with lump graphite occurring as irregular masses within rocks and typically containing impurities, while vein graphite forms in distinct, crystalline veins and is known for its high carbon content and superior quality. Lump graphite's nodular texture makes it suitable for applications requiring moderate purity and conductivity, whereas vein graphite's consistent structure and purity make it ideal for high-end industrial uses such as battery anodes and lubricants. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate type of graphite to optimize performance in specific technological and manufacturing processes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lump Graphite | Vein Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Metamorphic rocks, formed from carbon-rich layers | Hydrothermal veins, formed from mineral-rich fluids |
| Appearance | Flaky, irregular particles | Compact, crystalline masses |
| Carbon Content | 85-90% pure carbon | 95-99% pure carbon |
| Purity | Lower, requires refining | High purity, minimal processing |
| Applications | Refractory materials, batteries, lubricants | Electrodes, high-grade batteries, crucibles |
| Market Price | Lower cost, bulk supply | Higher cost, premium quality |
Lump Graphite vs Vein Graphite: Key Differences
Lump graphite features irregular, coarse grains formed from the direct crystallization of carbon, whereas vein graphite occurs in distinct, well-defined veins with a higher purity and crystallinity due to hydrothermal processes. Lump graphite typically has a lower crystalline structure and is more abundant, making it ideal for applications requiring high thermal conductivity and lubrication. Vein graphite's superior purity and structural uniformity make it preferable for high-performance batteries and advanced industrial uses.
Geological Formation: Lump vs Vein Graphite
Lump graphite forms as dense, compact masses resulting from high-temperature metamorphic processes that convert organic material within sedimentary rocks into crystalline carbon. Vein graphite occurs in fissures and veins, crystallizing from hydrothermal fluids under lower temperature conditions, often associated with pegmatite intrusions. The distinct geological formation processes influence the purity, crystal size, and extraction methods of lump and vein graphite deposits.
Physical Properties Comparison
Lump graphite exhibits a massive or granular structure with variable particle size and moderate purity, while vein graphite forms distinct, crystalline veins with high purity and dense, flaky flakes. Lump graphite typically has lower hardness and thermal conductivity compared to vein graphite, which demonstrates superior conductivity and structural integrity. These physical differences influence their applications, with vein graphite preferred for high-performance uses requiring high purity and conductivity.
Purity Levels in Lump and Vein Graphite
Lump graphite typically exhibits purity levels ranging from 85% to 95% carbon content, while vein graphite is known for its exceptionally high purity, often exceeding 90% and reaching up to 99% carbon content. The higher purity of vein graphite makes it highly sought after for specialized applications requiring superior conductivity and chemical resistance. Purity variations between lump and vein graphite directly impact their performance in industrial processes such as battery anodes and lubricants.
Mining and Extraction Methods
Lump graphite is typically extracted through open-pit mining due to its near-surface deposits, which allows for easier access and lower extraction costs. Vein graphite mining involves underground methods, including narrow vein mining techniques, to carefully follow and extract the graphite-rich quartz veins embedded in metamorphic rocks. The differing geologic formations dictate tailored extraction protocols, with lump graphite favoring large-scale surface operations and vein graphite requiring precision underground excavation to maximize yield and purity.
Applications and Industrial Uses
Lump graphite features large, flake-like crystal structures ideal for lubricant manufacturing, battery anodes, and refractory materials due to its high purity and conductivity. Vein graphite, characterized by dense, compact masses, excels in applications requiring high thermal stability and electrical conductivity, such as in electrodes, crucibles, and nuclear reactors. Industrial uses of lump graphite emphasize energy storage and mechanical durability, while vein graphite is preferred for specialized high-temperature and high-strength components.
Market Demand and Pricing Trends
Lump graphite, primarily sourced from Sri Lanka, commands higher prices due to its superior purity and larger flake sizes, making it highly sought after in battery anodes and refractory applications. Vein graphite, while abundant and cheaper, faces growing demand fluctuations linked to its lower carbon content and rising competition from synthetic alternatives. Market trends indicate sustained premium pricing for lump graphite driven by limited supply and escalating demand in electric vehicle and renewable energy sectors.
Environmental Impact of Lump vs Vein Graphite
Lump graphite mining typically causes more environmental disruption due to surface excavation techniques, leading to habitat destruction and soil erosion, whereas vein graphite extraction involves underground mining which has a smaller surface footprint but higher energy consumption. Vein graphite often requires more intensive processing, increasing carbon emissions compared to lump graphite's more straightforward beneficiation. Both forms impact water resources, but lump graphite operations have a higher risk of contamination due to open-pit mining practices.
Global Availability and Major Sources
Lump graphite is predominantly sourced from Sri Lanka, China, and Tanzania, known for its high purity and crystallinity, making these countries key global suppliers. Vein graphite, characterized by its distinct crystal veins, is primarily available from Sri Lanka, the largest producer, with smaller contributions from Madagascar and Brazil. Global availability of lump graphite is broader due to multiple mining regions, whereas vein graphite remains more geographically concentrated and limited in supply.
Choosing the Right Graphite for Your Needs
Lump graphite offers a naturally occurring, high-purity form with excellent electrical conductivity and heat resistance, making it ideal for battery anodes and refractory applications. Vein graphite, characterized by its shiny, crystalline structure and superior purity, is preferred in applications requiring high thermal conductivity and lubricity, such as in lubricants and brushes for electric motors. Selecting the right graphite depends on the required purity, conductivity, and mechanical properties to ensure optimal performance in industrial or commercial use.
Lump Graphite vs Vein Graphite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com