Graphite sheets offer superior flexibility and thermal conductivity, making them ideal for applications requiring efficient heat transfer and insulation, while graphite blocks provide enhanced mechanical strength and durability suited for structural components. The sheet's thin, pliable form allows for easy customization and layering in electronic devices, whereas blocks excel in high-pressure environments due to their robust composition. Choosing between graphite sheets and blocks depends on the balance between thermal performance and mechanical stability needed for specific industrial or technological uses.
Table of Comparison
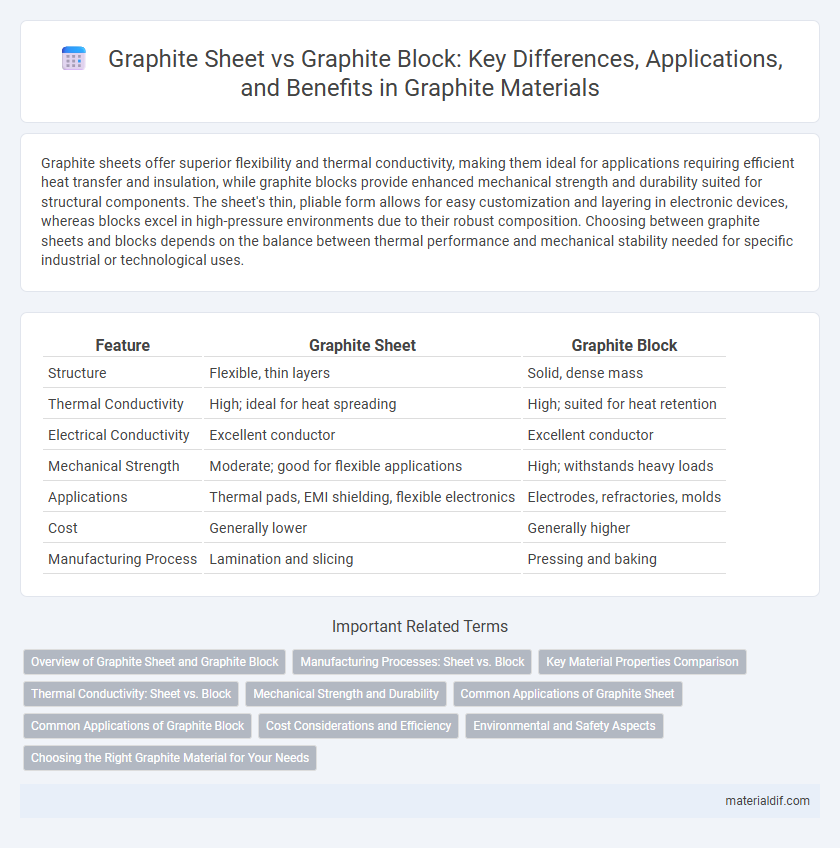
| Feature | Graphite Sheet | Graphite Block |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Flexible, thin layers | Solid, dense mass |
| Thermal Conductivity | High; ideal for heat spreading | High; suited for heat retention |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent conductor | Excellent conductor |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate; good for flexible applications | High; withstands heavy loads |
| Applications | Thermal pads, EMI shielding, flexible electronics | Electrodes, refractories, molds |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Manufacturing Process | Lamination and slicing | Pressing and baking |
Overview of Graphite Sheet and Graphite Block
Graphite sheets are thin, flexible materials known for excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, commonly used in electronics and heat management applications. Graphite blocks are dense, solid forms with high mechanical strength and chemical resistance, ideal for industrial uses such as electrodes, molds, and high-temperature components. Both materials offer unique advantages depending on flexibility, shape, and application requirements.
Manufacturing Processes: Sheet vs. Block
Graphite sheets are typically manufactured by compressing expanded graphite flakes under high pressure and heat, resulting in thin, flexible sheets with enhanced surface uniformity. In contrast, graphite blocks are produced through the molding and baking of graphite powder mixed with binders, followed by high-temperature graphitization, yielding dense, rigid structures ideal for heavy-duty applications. These distinct manufacturing processes influence the mechanical properties, thermal conductivity, and application suitability of graphite sheets versus blocks.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Graphite sheets exhibit superior flexibility, high thermal conductivity up to 1500 W/m*K, and excellent electrical conductivity, making them ideal for heat dissipation and electrical applications where conformability is essential. Graphite blocks, on the other hand, offer higher mechanical strength, greater density, and enhanced structural stability, with typical compressive strengths exceeding 30 MPa, suited for high-load industrial components. Both materials share high-temperature resistance above 3000degC in inert atmospheres, but sheets prioritize thermal management and adaptability, while blocks emphasize durability and load-bearing capacity.
Thermal Conductivity: Sheet vs. Block
Graphite sheets typically offer higher in-plane thermal conductivity, often exceeding 150 W/m*K, making them ideal for efficient heat spreading applications. Graphite blocks, while possessing good thermal conductivity, generally exhibit lower values around 80-120 W/m*K due to their bulk structure and anisotropic properties. The choice between graphite sheet and block depends on the specific thermal management requirements, with sheets favored for rapid lateral heat dissipation and blocks suited for structural heat conduction.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Graphite sheets exhibit superior flexibility and impact resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring mechanical shock absorption and vibration damping. In contrast, graphite blocks provide higher compressive strength and wear resistance, suitable for structural components subjected to heavy mechanical loads. The durability of graphite blocks surpasses that of sheets in high-stress environments, while sheets offer enhanced resilience in dynamic mechanical conditions.
Common Applications of Graphite Sheet
Graphite sheets are widely used in applications requiring excellent thermal management, such as heat spreaders in electronics and battery packs due to their high thermal conductivity and flexibility. Their lightweight and compressible nature makes them ideal for gasketing and sealing in high-temperature environments across automotive and aerospace industries. Unlike graphite blocks, which are preferred for structural and machining applications, graphite sheets excel in providing uniform heat distribution and electrical conductivity in compact, surface-contact applications.
Common Applications of Graphite Block
Graphite blocks are commonly used in high-temperature industrial applications such as electric arc furnaces, vacuum sintering, and metallurgical processes due to their excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock. Unlike graphite sheets, which are often utilized for sealing and gasketing, graphite blocks provide structural integrity and durability in environments requiring mechanical strength and chemical inertness. Their adaptability in manufacturing electrodes and molds makes graphite blocks essential in metal refining and chemical processing industries.
Cost Considerations and Efficiency
Graphite sheets typically offer lower material costs and greater flexibility, making them more cost-effective for lightweight thermal management applications. Graphite blocks provide higher density and structural strength, resulting in improved thermal conductivity and efficiency for heavy-duty industrial uses but at a higher price point. Selecting between sheets and blocks depends on balancing budget constraints with the required thermal performance and durability.
Environmental and Safety Aspects
Graphite sheets offer enhanced environmental benefits due to their superior flexibility and reduced material waste during production compared to graphite blocks. The lower density and ease of cutting graphite sheets minimize dust generation, improving workplace air quality and reducing inhalation risks associated with graphite particulate matter. Graphite blocks, while structurally robust, require more machining, which can lead to higher emissions of fine graphite dust, necessitating stringent safety measures to protect workers.
Choosing the Right Graphite Material for Your Needs
Graphite sheets offer excellent flexibility and thermal conductivity, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight and thin heat dissipation solutions. Graphite blocks provide higher density and structural strength, suitable for machining and high-temperature environments where durability is critical. Selecting between graphite sheets and blocks depends on your specific thermal management needs, mechanical stress tolerances, and application flexibility requirements.
Graphite Sheet vs Graphite Block Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com