Graphite paper offers superior flexibility and ease of application, making it ideal for detailed art projects and precision industrial uses, while graphite foil provides enhanced durability and thermal conductivity, suitable for high-temperature insulation and sealing applications. The smooth surface of graphite paper ensures clean, precise transfers, whereas graphite foil's thicker structure grants better mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Choosing between them depends on the specific requirements of flexibility, durability, and thermal performance in your project.
Table of Comparison
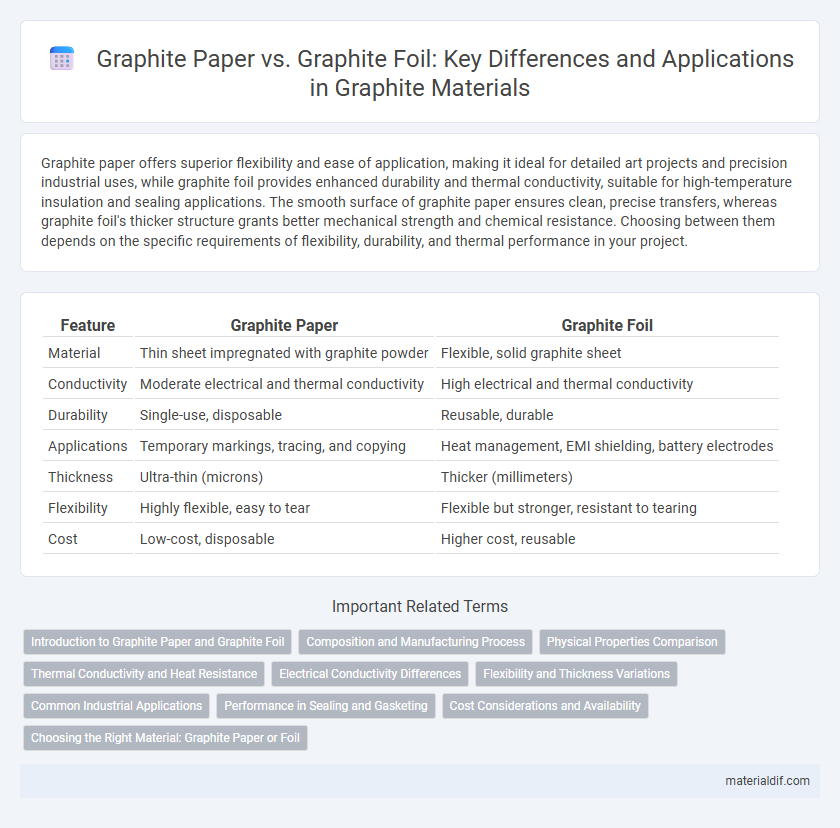
| Feature | Graphite Paper | Graphite Foil |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thin sheet impregnated with graphite powder | Flexible, solid graphite sheet |
| Conductivity | Moderate electrical and thermal conductivity | High electrical and thermal conductivity |
| Durability | Single-use, disposable | Reusable, durable |
| Applications | Temporary markings, tracing, and copying | Heat management, EMI shielding, battery electrodes |
| Thickness | Ultra-thin (microns) | Thicker (millimeters) |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, easy to tear | Flexible but stronger, resistant to tearing |
| Cost | Low-cost, disposable | Higher cost, reusable |
Introduction to Graphite Paper and Graphite Foil
Graphite paper is a thin, flexible sheet composed of compressed graphite particles, primarily used for carbon transfer and as a lubricant in various mechanical applications. Graphite foil consists of multiple layers of graphite material, offering enhanced thermal conductivity and durability compared to graphite paper, making it suitable for high-temperature sealing and electrical insulation. Both materials are essential in industries requiring efficient heat dissipation and chemical resistance, but graphite foil provides superior mechanical strength and longer service life.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Graphite paper consists of a thin layer of natural or synthetic graphite particles bonded onto a flexible paper substrate, produced through a coating process that ensures high conductivity and flexibility. Graphite foil, however, is composed entirely of compressed expanded graphite layers formed through heat and pressure without a binder, resulting in a more uniform and dense structure ideal for high-temperature and sealing applications. The manufacturing process differences lead to graphite paper being lighter and more adaptable for sketching or electrical applications, while graphite foil offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength for industrial uses.
Physical Properties Comparison
Graphite paper features a thin, flexible texture with moderate tensile strength and excellent electrical conductivity, making it suitable for surface protection and transfer applications. Graphite foil exhibits higher density, superior thermal resistance, and enhanced mechanical durability, ideal for high-temperature insulation and sealing tasks. Both materials share low thermal expansion and chemical inertness, but graphite foil outperforms graphite paper in mechanical robustness and thermal stability.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Resistance
Graphite foil offers higher thermal conductivity, typically reaching up to 1500 W/m*K, enabling efficient heat dissipation in applications requiring rapid thermal transfer. Graphite paper, with thermal conductivity generally around 300-700 W/m*K, provides moderate heat transfer but excels in conformability and flexibility for uneven surfaces. Heat resistance for both materials remains robust, with graphite foil often enduring temperatures above 3000degC in inert atmospheres, while graphite paper tolerates slightly lower ranges, making foil preferable for extreme thermal environments.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Graphite foil exhibits superior electrical conductivity compared to graphite paper due to its denser carbon layer alignment and fewer air gaps, enhancing electron flow. Graphite paper, composed of loosely bonded carbon fibers, shows relatively higher electrical resistance caused by increased scattering at fiber boundaries. These structural differences make graphite foil more suitable for applications requiring efficient current transfer and minimal energy loss.
Flexibility and Thickness Variations
Graphite paper offers superior flexibility compared to graphite foil, making it ideal for applications requiring intricate bending and shaping. Thickness variations in graphite foil tend to be more consistent, enabling uniform thermal conductivity and mechanical stability in high-precision uses. Choosing between graphite paper and foil depends on the specific flexibility needs and thickness tolerances of the intended application.
Common Industrial Applications
Graphite paper is commonly used in electronics manufacturing for shielding and thermal management due to its flexibility and ease of application, while graphite foil finds extensive use in high-temperature gasketing and sealing applications because of its superior heat resistance and compressibility. Industries such as aerospace and automotive rely on graphite foil for engine components and exhaust systems, benefiting from its durability under extreme conditions. Conversely, graphite paper often serves in battery manufacturing and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding to enhance performance and reliability.
Performance in Sealing and Gasketing
Graphite foil offers superior conformability and compressibility, enhancing its sealing performance by creating tighter, more reliable gaskets under varying pressures and temperatures. In contrast, graphite paper, being thinner and less dense, provides moderate sealing effectiveness but excels in applications requiring flexibility and ease of handling. The choice between graphite paper and foil depends on the specific sealing demands, with foil preferred for high-stress environments due to its durability and resistance to creep relaxation.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Graphite paper offers a cost-effective option for applications requiring thin, flexible graphite layers, generally available in standard sizes with widespread commercial distribution. In contrast, graphite foil tends to have higher production costs due to its denser and more uniform structure, limiting availability to specialized suppliers and often sold in custom dimensions. Budget-sensitive projects may favor graphite paper for its affordability and accessibility, whereas graphite foil suits demands for premium performance despite increased expense and procurement challenges.
Choosing the Right Material: Graphite Paper or Foil
Graphite paper offers superior flexibility and ease of application, making it ideal for detailed, intricate surfaces or temporary installations in electronics and automotive industries. In contrast, graphite foil provides enhanced thermal conductivity and durability, suitable for high-temperature insulation and sealing solutions in industrial setups. Selecting between graphite paper and foil depends on balancing flexibility needs versus thermal performance and mechanical strength requirements.
Graphite Paper vs Graphite Foil Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com