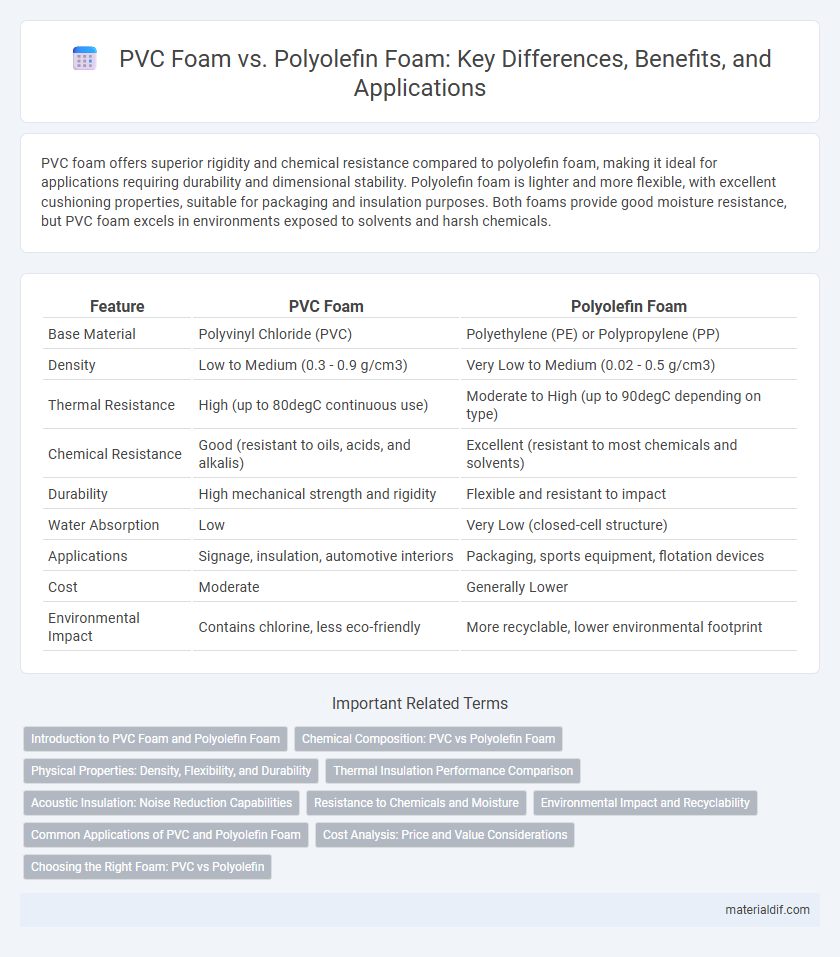
PVC foam offers superior rigidity and chemical resistance compared to polyolefin foam, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and dimensional stability. Polyolefin foam is lighter and more flexible, with excellent cushioning properties, suitable for packaging and insulation purposes. Both foams provide good moisture resistance, but PVC foam excels in environments exposed to solvents and harsh chemicals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | PVC Foam | Polyolefin Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polyethylene (PE) or Polypropylene (PP) |
| Density | Low to Medium (0.3 - 0.9 g/cm3) | Very Low to Medium (0.02 - 0.5 g/cm3) |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 80degC continuous use) | Moderate to High (up to 90degC depending on type) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (resistant to oils, acids, and alkalis) | Excellent (resistant to most chemicals and solvents) |
| Durability | High mechanical strength and rigidity | Flexible and resistant to impact |
| Water Absorption | Low | Very Low (closed-cell structure) |
| Applications | Signage, insulation, automotive interiors | Packaging, sports equipment, flotation devices |
| Cost | Moderate | Generally Lower |
| Environmental Impact | Contains chlorine, less eco-friendly | More recyclable, lower environmental footprint |
Introduction to PVC Foam and Polyolefin Foam
PVC foam, or polyvinyl chloride foam, is a rigid, closed-cell material known for its durability, chemical resistance, and lightweight structure, making it ideal for construction, signage, and marine applications. Polyolefin foam, derived from polyethylene or polypropylene, is a flexible, closed-cell foam valued for its excellent cushioning, thermal insulation, and moisture resistance, commonly used in packaging, automotive, and sports equipment. Both foams offer unique mechanical properties and environmental benefits tailored to specific industrial needs.
Chemical Composition: PVC vs Polyolefin Foam
PVC foam consists of polyvinyl chloride polymers characterized by chloride atoms in its chemical structure, offering excellent rigidity, flame resistance, and chemical stability. Polyolefin foam, composed primarily of polyethylene or polypropylene chains without chlorine atoms, provides superior flexibility, chemical inertness, and resistance to moisture and solvents. The presence of chlorine in PVC foam imparts higher density and durability, whereas polyolefin foam's hydrocarbon-based composition results in lighter weight and enhanced thermal insulation properties.
Physical Properties: Density, Flexibility, and Durability
PVC foam offers higher density ranging from 30 to 200 kg/m3, providing enhanced rigidity and durability compared to polyolefin foam, which typically has a lower density between 20 and 100 kg/m3. Polyolefin foam exhibits superior flexibility and impact absorption due to its cellular structure, making it ideal for cushioning applications, while PVC foam is more resistant to chemicals and UV exposure, ensuring longer lifespan in harsh environments. The durability of PVC foam outperforms polyolefin in terms of compressive strength and resistance to deformation under load.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
PVC foam exhibits superior thermal insulation properties due to its closed-cell structure, which effectively reduces heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency. Polyolefin foam, while offering good thermal insulation, typically has a more open-cell structure, resulting in slightly higher thermal conductivity values. The lower thermal conductivity of PVC foam makes it more suitable for applications requiring stringent temperature control and energy savings.
Acoustic Insulation: Noise Reduction Capabilities
PVC foam exhibits superior noise reduction capabilities compared to polyolefin foam due to its higher density and closed-cell structure, effectively dampening sound waves. Polyolefin foam offers moderate acoustic insulation but tends to transmit higher frequencies more readily because of its open-cell nature. Optimizing acoustic performance in construction or automotive applications often favors PVC foam for its enhanced sound absorption and durability.
Resistance to Chemicals and Moisture
PVC foam exhibits superior resistance to chemicals and moisture compared to polyolefin foam, making it ideal for applications exposed to harsh environments. Its closed-cell structure prevents water absorption and resists solvents, acids, and alkalis effectively. Polyolefin foam, while lightweight and flexible, offers lower chemical resistance and may degrade faster when exposed to aggressive substances or prolonged moisture exposure.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
PVC foam contains chlorine, which poses environmental challenges during production and disposal due to the release of toxic dioxins, making it less eco-friendly compared to polyolefin foam. Polyolefin foam, derived from polyethylene or polypropylene, offers superior recyclability and lower environmental impact as it is free of halogens and more readily accepted by recycling facilities. The biodegradability of neither foam is significant, but polyolefin's compatibility with mechanical recycling systems makes it a preferred choice for sustainable applications.
Common Applications of PVC and Polyolefin Foam
PVC foam is frequently used in construction, signage, and automotive industries due to its durability, chemical resistance, and excellent insulation properties. Polyolefin foam is preferred in packaging, sports equipment, and medical devices for its lightweight nature, impact absorption, and chemical inertness. Both foams serve essential roles in cushioning, insulation, and structural support across diverse industrial applications.
Cost Analysis: Price and Value Considerations
PVC foam typically costs more than polyolefin foam due to its higher density and durability, making it suitable for applications requiring greater strength and chemical resistance. Polyolefin foam offers a more economical option with lower material and production costs, ideal for lightweight and cushioning uses. Evaluating the total value involves balancing initial price against performance characteristics such as resilience, flexibility, and lifespan.
Choosing the Right Foam: PVC vs Polyolefin
PVC foam offers excellent rigidity, chemical resistance, and fire retardancy, making it ideal for construction and industrial applications requiring durability. Polyolefin foam provides superior flexibility, impact absorption, and moisture resistance, suited for packaging, automotive, and sports equipment cushioning. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing mechanical properties, environmental exposure, and application-specific performance requirements.
PVC foam vs polyolefin foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com