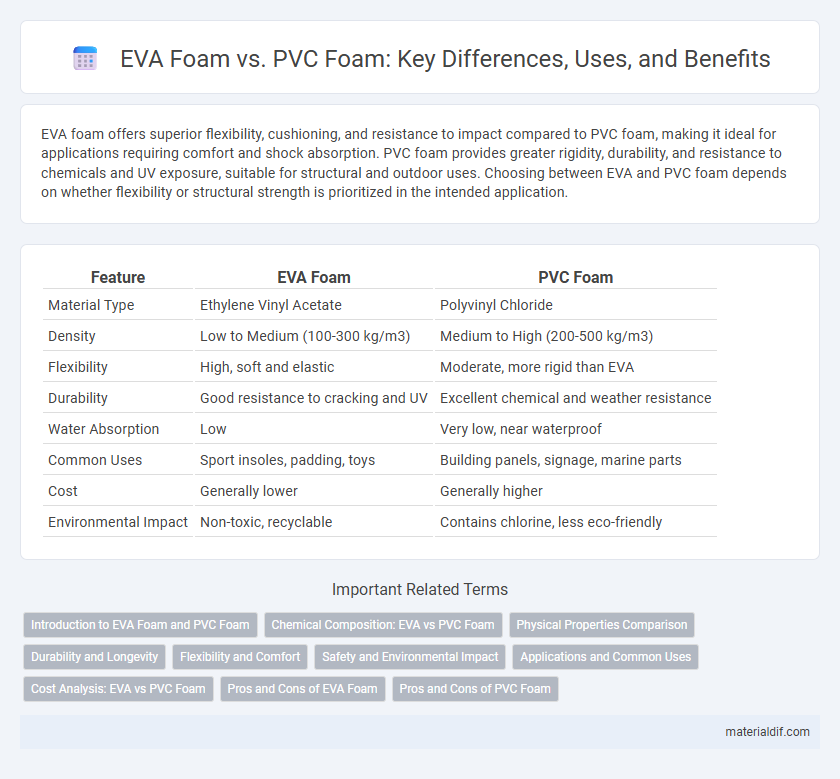
EVA foam offers superior flexibility, cushioning, and resistance to impact compared to PVC foam, making it ideal for applications requiring comfort and shock absorption. PVC foam provides greater rigidity, durability, and resistance to chemicals and UV exposure, suitable for structural and outdoor uses. Choosing between EVA and PVC foam depends on whether flexibility or structural strength is prioritized in the intended application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | EVA Foam | PVC Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate | Polyvinyl Chloride |
| Density | Low to Medium (100-300 kg/m3) | Medium to High (200-500 kg/m3) |
| Flexibility | High, soft and elastic | Moderate, more rigid than EVA |
| Durability | Good resistance to cracking and UV | Excellent chemical and weather resistance |
| Water Absorption | Low | Very low, near waterproof |
| Common Uses | Sport insoles, padding, toys | Building panels, signage, marine parts |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Environmental Impact | Non-toxic, recyclable | Contains chlorine, less eco-friendly |
Introduction to EVA Foam and PVC Foam
EVA foam is a lightweight, flexible material known for its excellent shock absorption and cushioning properties, making it ideal for footwear, sports equipment, and packaging. PVC foam features a rigid, durable structure with strong resistance to chemicals and weathering, commonly used in construction, signage, and marine applications. Both materials offer distinct advantages in terms of density, flexibility, and environmental resistance, tailored to specific industrial needs.
Chemical Composition: EVA vs PVC Foam
EVA foam is composed of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers, providing flexibility, elasticity, and resistance to UV radiation, whereas PVC foam consists of polyvinyl chloride polymers, offering rigidity, chemical resistance, and durability. EVA foam's chemical structure includes vinyl acetate units that enhance softness and cushioning, while PVC foam's chlorinated polymer matrix results in a denser, more robust material ideal for structural applications. The inherent chemical differences influence EVA foam's lightweight, shock-absorbing properties compared to PVC foam's higher tensile strength and resistance to solvents and weathering.
Physical Properties Comparison
EVA foam offers superior flexibility and resilience with a lower density of approximately 70-150 kg/m3, making it ideal for cushioning applications, whereas PVC foam typically has a higher density ranging from 200-400 kg/m3, resulting in increased rigidity and durability suited for structural uses. EVA foam exhibits excellent impact absorption and compressibility, while PVC foam provides better chemical resistance and dimensional stability under varying temperatures. Both materials have distinct tensile strengths, with EVA foam generally ranging from 1.0 to 3.0 MPa and PVC foam around 5.0 to 10.0 MPa, influencing their selection based on specific mechanical performance requirements.
Durability and Longevity
EVA foam offers superior durability due to its excellent resistance to abrasion, UV exposure, and chemical degradation, making it ideal for outdoor and high-wear applications. PVC foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and chemical contact, limiting its longevity. The inherent resilience of EVA foam ensures longer service life and sustained performance compared to PVC foam in demanding environments.
Flexibility and Comfort
EVA foam offers superior flexibility compared to PVC foam, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent bending and movement. Its lightweight and soft texture enhances comfort, providing better cushioning underfoot or during prolonged use. PVC foam is stiffer and less flexible, often leading to reduced comfort in products where pliability is essential.
Safety and Environmental Impact
EVA foam offers superior safety benefits due to its non-toxic, hypoallergenic properties and absence of harmful chemicals like phthalates found in some PVC foams. EVA foam is more environmentally friendly as it is biodegradable and recyclable, contrasting with PVC foam's production process that releases hazardous dioxins and its limited recyclability. Choosing EVA foam reduces both health risks and environmental pollution compared to PVC foam.
Applications and Common Uses
EVA foam is commonly used in footwear insoles, sports equipment, and packaging due to its flexibility, shock absorption, and non-toxicity, making it ideal for products requiring comfort and durability. PVC foam excels in construction, signage, and automotive components because of its rigid structure, chemical resistance, and weather durability. Both materials serve diverse industries, with EVA foam favored for cushioning and impact resistance, while PVC foam is preferred for structural support and outdoor applications.
Cost Analysis: EVA vs PVC Foam
EVA foam generally offers a higher upfront cost compared to PVC foam due to its enhanced flexibility and durability features, making it suitable for more specialized applications. PVC foam, being more economical and lightweight, is widely used in cost-sensitive projects without compromising on basic performance. In long-term cost analysis, EVA foam's resilience may reduce replacement frequency, potentially offsetting the initial expense over time.
Pros and Cons of EVA Foam
EVA foam offers excellent flexibility, shock absorption, and water resistance, making it ideal for footwear insoles, sports equipment, and packaging. Its non-toxic and lightweight properties enhance comfort and reduce fatigue, but EVA foam tends to have lower structural strength and durability compared to PVC foam. While PVC foam provides superior rigidity and chemical resistance, EVA foam excels in cushioning and environmental friendliness, though it may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure.
Pros and Cons of PVC Foam
PVC foam offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for applications exposed to moisture and harsh environments. However, it tends to be heavier and less flexible compared to EVA foam, which can limit its use in projects requiring cushioning or shock absorption. Cost-wise, PVC foam is generally more affordable, but its lower elasticity may reduce comfort in certain uses like sports equipment or footwear.
EVA foam vs PVC foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com