Neoprene foam offers superior resistance to water, oils, and temperature variations, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Polyurethane foam provides excellent cushioning and flexibility, commonly used in upholstery, mattresses, and packaging. Choosing between neoprene and polyurethane foam depends on specific requirements for durability, comfort, and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
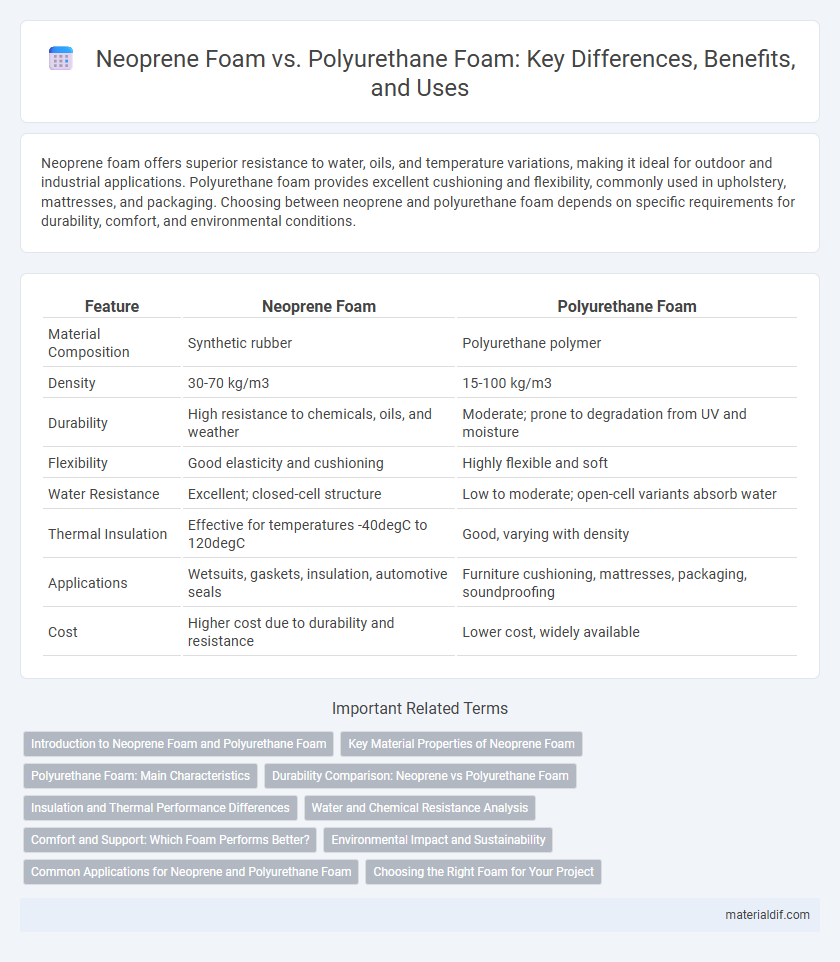
| Feature | Neoprene Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Synthetic rubber | Polyurethane polymer |
| Density | 30-70 kg/m3 | 15-100 kg/m3 |
| Durability | High resistance to chemicals, oils, and weather | Moderate; prone to degradation from UV and moisture |
| Flexibility | Good elasticity and cushioning | Highly flexible and soft |
| Water Resistance | Excellent; closed-cell structure | Low to moderate; open-cell variants absorb water |
| Thermal Insulation | Effective for temperatures -40degC to 120degC | Good, varying with density |
| Applications | Wetsuits, gaskets, insulation, automotive seals | Furniture cushioning, mattresses, packaging, soundproofing |
| Cost | Higher cost due to durability and resistance | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Neoprene Foam and Polyurethane Foam
Neoprene foam, a synthetic rubber material known for its excellent weather, chemical, and temperature resistance, is widely used in wetsuits, gaskets, and insulation. Polyurethane foam, characterized by its versatile density and cushioning properties, finds extensive application in furniture, automotive seating, and thermal insulation. Both foams offer unique benefits tailored to specific industrial and consumer needs, making them essential materials across various sectors.
Key Material Properties of Neoprene Foam
Neoprene foam exhibits superior chemical resistance, excellent weatherability, and high elasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and flexibility. It resists oils, solvents, and UV radiation better than polyurethane foam, which often lacks long-term exposure resilience. Neoprene's closed-cell structure provides enhanced insulation and water resistance compared to the open-cell nature of many polyurethane foams.
Polyurethane Foam: Main Characteristics
Polyurethane foam is a versatile material known for its excellent cushioning, lightweight structure, and high durability across various applications. It offers superior insulation properties, resistance to abrasion, and can be manufactured in flexible or rigid forms to suit different needs. Unlike neoprene foam, polyurethane foam provides enhanced breathability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for furniture, automotive seating, and thermal insulation.
Durability Comparison: Neoprene vs Polyurethane Foam
Neoprene foam exhibits superior durability compared to polyurethane foam due to its enhanced resistance to oil, ozone, and weathering, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Polyurethane foam tends to degrade faster under exposure to UV light and moisture, limiting its lifespan in harsh environments. Choosing neoprene foam ensures longer-lasting performance where toughness and environmental resistance are critical.
Insulation and Thermal Performance Differences
Neoprene foam offers superior insulation due to its closed-cell structure, providing excellent thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties compared to polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam, while flexible and cost-effective, typically has a lower R-value, resulting in less effective thermal insulation performance. For applications demanding high thermal efficiency and durability, neoprene foam is the preferred choice over polyurethane foam.
Water and Chemical Resistance Analysis
Neoprene foam exhibits superior water resistance and chemical stability compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications exposed to harsh environments. Its closed-cell structure effectively prevents water absorption and resists oils, solvents, and acids, whereas polyurethane foam's open-cell configuration allows for higher water retention and susceptibility to chemical degradation. Performance tests indicate neoprene foam maintains structural integrity and functionality after prolonged exposure to water and aggressive chemicals, unlike polyurethane foam which tends to swell and lose resilience.
Comfort and Support: Which Foam Performs Better?
Neoprene foam offers superior support due to its dense, closed-cell structure that maintains shape under pressure, making it ideal for applications requiring firm comfort and durability. Polyurethane foam provides enhanced cushioning and softer comfort with an open-cell design that allows better airflow but may compress more quickly over time. For long-lasting support and resilience, neoprene foam outperforms polyurethane foam, while polyurethane excels in softer, breathable comfort.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Neoprene foam, derived from synthetic rubber, poses environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and energy-intensive production process, contributing to significant carbon emissions. Polyurethane foam, while also synthetic, often allows for more sustainable formulations using bio-based polyols, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and improving recyclability. Both foams require careful waste management, but advances in polyurethane recycling and bio-based alternatives position it as a more eco-friendly choice compared to traditional neoprene foam.
Common Applications for Neoprene and Polyurethane Foam
Neoprene foam is commonly used in wetsuits, laptop sleeves, orthopedic braces, and automotive gaskets due to its excellent water resistance, flexibility, and chemical stability. Polyurethane foam finds widespread application in furniture cushioning, mattresses, insulation panels, and packaging because of its superior comfort, cushioning properties, and thermal insulation capabilities. Both foams serve crucial roles in sports equipment, soundproofing, and sealing materials, tailored to their distinct physical characteristics.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Project
Neoprene foam offers superior resistance to water, chemicals, and temperature extremes, making it ideal for outdoor and marine applications, while polyurethane foam excels in cushioning, insulation, and flexibility for indoor furniture and packaging. When choosing the right foam for your project, consider environmental exposure, required durability, and specific performance needs such as compression and resilience. Cost differences and ease of fabrication also influence the selection between neoprene foam's dense, closed-cell structure and the more lightweight, open-cell polyurethane foam.
Neoprene foam vs Polyurethane foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com