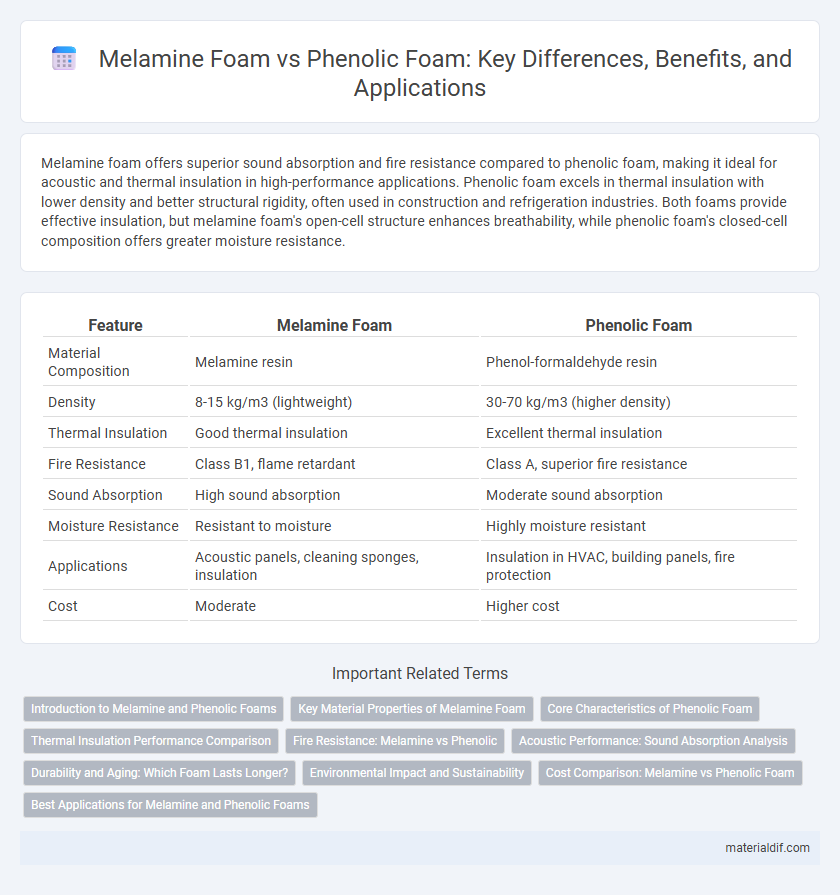
Melamine foam offers superior sound absorption and fire resistance compared to phenolic foam, making it ideal for acoustic and thermal insulation in high-performance applications. Phenolic foam excels in thermal insulation with lower density and better structural rigidity, often used in construction and refrigeration industries. Both foams provide effective insulation, but melamine foam's open-cell structure enhances breathability, while phenolic foam's closed-cell composition offers greater moisture resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Melamine Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Melamine resin | Phenol-formaldehyde resin |
| Density | 8-15 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 30-70 kg/m3 (higher density) |
| Thermal Insulation | Good thermal insulation | Excellent thermal insulation |
| Fire Resistance | Class B1, flame retardant | Class A, superior fire resistance |
| Sound Absorption | High sound absorption | Moderate sound absorption |
| Moisture Resistance | Resistant to moisture | Highly moisture resistant |
| Applications | Acoustic panels, cleaning sponges, insulation | Insulation in HVAC, building panels, fire protection |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher cost |
Introduction to Melamine and Phenolic Foams
Melamine foam is a lightweight, open-cell material known for its excellent sound absorption and thermal insulation properties, commonly used in acoustic panels and cleaning products. Phenolic foam is a rigid, closed-cell foam characterized by high flame resistance and structural strength, often utilized in fireproofing and thermal insulation applications. Both foams serve distinct roles in insulation and safety, with melamine foam excelling in sound control and phenolic foam providing superior fire performance.
Key Material Properties of Melamine Foam
Melamine foam features remarkable thermal insulation and sound absorption capabilities due to its open-cell structure and low density, making it highly effective in noise reduction applications. Its excellent fire resistance, with a self-extinguishing property and low smoke emission, ensures enhanced safety compared to phenolic foam. The material's superior chemical stability and lightweight nature contribute to its widespread use in construction, automotive, and acoustic treatments where durability and performance are critical.
Core Characteristics of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is distinguished by its superior fire resistance and low smoke emission, making it ideal for building insulation where safety is paramount. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent thermal insulation and moisture resistance, enhancing durability in various environments. The foam's inherent rigidity and dimensional stability contribute to its effectiveness in structural applications compared to melamine foam.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Melamine foam exhibits superior thermal insulation properties with a low thermal conductivity typically around 0.032 W/m*K, making it highly effective for sound absorption and temperature regulation. Phenolic foam offers excellent fire resistance and slightly higher thermal insulation efficiency, with thermal conductivity values ranging from 0.020 to 0.025 W/m*K, ideal for high-temperature applications. The choice between melamine and phenolic foam depends on specific thermal insulation requirements, balancing fire safety and insulation performance.
Fire Resistance: Melamine vs Phenolic
Melamine foam exhibits superior fire resistance by self-extinguishing and producing minimal smoke compared to phenolic foam, which is inherently fire retardant but can emit more smoke and toxic gases when burned. Melamine foam's open-cell structure and nitrogen-rich composition contribute to its enhanced flame retardancy, making it ideal for fire-sensitive applications. Phenolic foam offers good thermal stability but tends to char rather than melt, influencing its performance under prolonged high temperatures.
Acoustic Performance: Sound Absorption Analysis
Melamine foam exhibits superior sound absorption properties due to its open-cell structure, effectively reducing noise across a broad frequency range from 100 Hz to 10 kHz. Phenolic foam, while offering better thermal insulation, has a denser, closed-cell composition that limits its acoustic absorption capabilities, particularly at lower frequencies. Acoustic performance tests reveal melamine foam achieves NRC (Noise Reduction Coefficient) values typically between 0.75 and 0.95, outperforming phenolic foam which ranges around 0.4 to 0.6.
Durability and Aging: Which Foam Lasts Longer?
Melamine foam demonstrates superior durability and resistance to aging compared to phenolic foam, maintaining its structural integrity and performance over extended periods in harsh environments. Phenolic foam, while effective for insulation, tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to moisture and UV radiation, leading to reduced lifespan. Industry tests confirm melamine foam's enhanced longevity, making it the preferred choice for applications requiring sustained durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Melamine foam offers superior biodegradability and lower toxicity, making it a more environmentally friendly option compared to phenolic foam, which relies on formaldehyde-based resins linked to higher emissions and less recyclability. The production of phenolic foam generates significant greenhouse gas emissions, whereas melamine foam manufacturing typically involves less energy-intensive processes, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. Sustainable disposal practices favor melamine foam due to its enhanced degradation capabilities and reduced environmental persistence compared to phenolic counterparts.
Cost Comparison: Melamine vs Phenolic Foam
Melamine foam generally incurs higher manufacturing costs due to its complex production process, resulting in a pricier material compared to phenolic foam. Phenolic foam offers a cost-effective alternative with lower raw material expenses and simpler fabrication, making it more economical for large-scale applications. Despite the higher initial price, melamine foam's superior thermal and acoustic properties can justify its cost in specialized uses.
Best Applications for Melamine and Phenolic Foams
Melamine foam excels in soundproofing and thermal insulation for architectural and automotive applications due to its open-cell structure and lightweight properties. Phenolic foam is ideal for high-temperature environments and fire-resistant insulation in industrial settings, owing to its closed-cell composition and excellent flame retardancy. Both foams offer unique advantages, with melamine foam preferred for acoustic treatments and phenolic foam favored for robust thermal protection and fire safety.
Melamine foam vs Phenolic foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com