High-density foam offers superior durability, support, and longevity, making it ideal for furniture, mattresses, and insulation where resilience is crucial. Low-density foam provides greater softness and flexibility, often used in cushions and packaging to absorb shock and enhance comfort. Choosing between high-density and low-density foam depends on the required balance of firmness, durability, and comfort for specific applications.
Table of Comparison
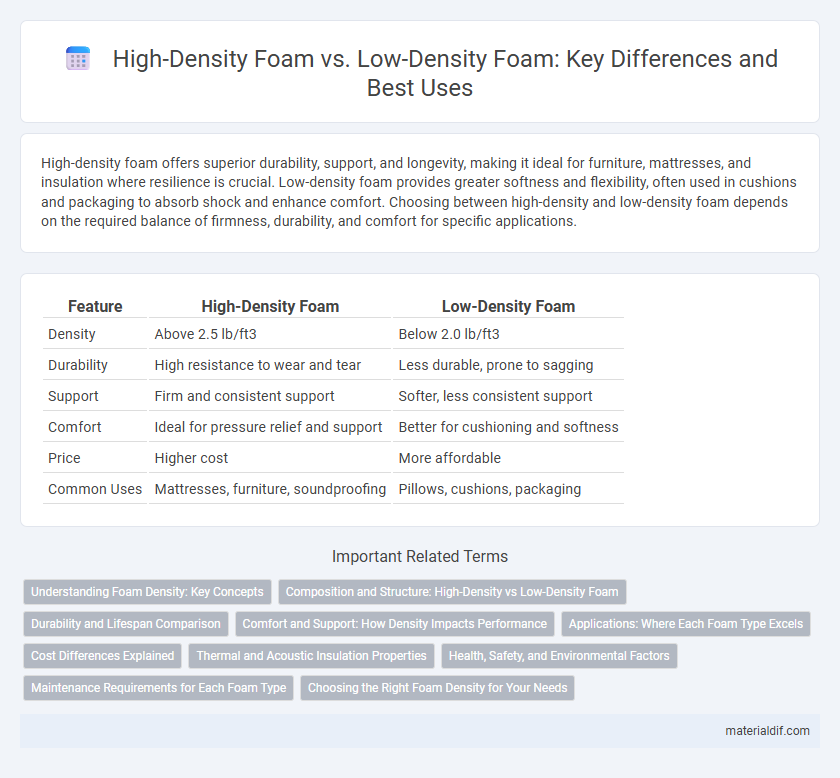
| Feature | High-Density Foam | Low-Density Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Above 2.5 lb/ft3 | Below 2.0 lb/ft3 |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear | Less durable, prone to sagging |
| Support | Firm and consistent support | Softer, less consistent support |
| Comfort | Ideal for pressure relief and support | Better for cushioning and softness |
| Price | Higher cost | More affordable |
| Common Uses | Mattresses, furniture, soundproofing | Pillows, cushions, packaging |
Understanding Foam Density: Key Concepts
High-density foam contains a greater mass of polyurethane per cubic foot, resulting in enhanced durability, support, and longevity compared to low-density foam, which is lighter and less resilient. Foam density, measured in pounds per cubic foot (PCF), directly influences factors such as firmness, compression resistance, and overall comfort. Understanding foam density is crucial for applications in mattresses, cushions, and insulation where performance and lifespan vary significantly between high-density and low-density foams.
Composition and Structure: High-Density vs Low-Density Foam
High-density foam features a tighter cell structure composed of smaller, more compact cells, resulting in greater durability and support compared to low-density foam, which has larger, more open cells that offer increased softness and flexibility. The chemical composition of high-density foam typically includes higher concentrations of polymer chains, enhancing its firmness and resistance to compression. Low-density foam, with fewer polymer chains and a more porous composition, provides enhanced breathability and cushioning but tends to break down faster under prolonged use.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
High-density foam offers superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to low-density foam, making it ideal for heavy-use applications such as upholstery and mattresses. Its tightly packed cells provide better resistance to wear, deformation, and sagging over time. Low-density foam, while more affordable and softer, tends to break down faster and lose resilience, resulting in a shorter functional lifespan.
Comfort and Support: How Density Impacts Performance
High-density foam offers superior support and durability, making it ideal for applications needing prolonged cushioning and structural integrity, such as mattresses and upholstery. In contrast, low-density foam provides softer comfort and better cushioning for short-term use but tends to compress quickly, reducing its supportive capabilities over time. The density of foam directly impacts its ability to distribute weight evenly and maintain shape, with higher densities enhancing comfort and long-term performance.
Applications: Where Each Foam Type Excels
High-density foam excels in applications requiring superior durability and support, such as high-traffic furniture cushions, orthopedic mattresses, and soundproofing panels. Low-density foam is ideal for lightweight packaging, disposable cushions, and insulation in temperature-sensitive environments due to its flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Understanding these application-specific strengths ensures selecting the appropriate foam type for optimal performance and longevity.
Cost Differences Explained
High-density foam typically costs more due to its increased material usage and superior durability, making it ideal for long-term applications like mattresses and upholstery. Low-density foam is less expensive but offers reduced support and longevity, often used in temporary or budget-conscious products. Price differences reflect the balance between upfront investment and the foam's performance over time.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
High-density foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its compact cell structure, reducing heat transfer more effectively than low-density foam. It also provides enhanced acoustic insulation by absorbing sound waves and minimizing noise transmission, making it ideal for soundproofing applications. Low-density foam, while lighter and more flexible, typically exhibits lower insulation performance in both thermal and acoustic contexts.
Health, Safety, and Environmental Factors
High-density foam offers superior durability and support but may release higher levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing, impacting indoor air quality and health. Low-density foam typically contains fewer chemicals and is more biodegradable, reducing environmental footprint and exposure to harmful substances. Both types require proper ventilation during use and disposal to minimize respiratory risks and ecological damage.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Foam Type
High-density foam requires less frequent replacement due to its durability and resistance to sagging, making it ideal for high-traffic areas where longevity is essential. Low-density foam, while initially softer and more comfortable, demands more regular maintenance and quicker replacement because it compresses faster and loses support over time. Proper cleaning and careful use can extend the lifespan of both foam types, but high-density foam generally offers superior performance with lower upkeep costs.
Choosing the Right Foam Density for Your Needs
High-density foam offers superior durability and support, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting cushioning and firm support, such as mattress cores or heavy-use furniture. Low-density foam provides greater softness and flexibility, suitable for comfort layers, seating cushions, or lightweight packaging where plushness and ease of compression are essential. Selecting the right foam density depends on balancing factors like required support, durability, and comfort tailored to specific use cases.
High-density foam vs Low-density foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com