Structural foam provides rigidity and support, making it ideal for maintaining the shape and durability of pet products like beds and carriers. Cushioning foam, on the other hand, offers softness and comfort, ensuring pets have a plush and cozy resting surface. Selecting the right foam type balances firmness and comfort tailored to your pet's needs.
Table of Comparison
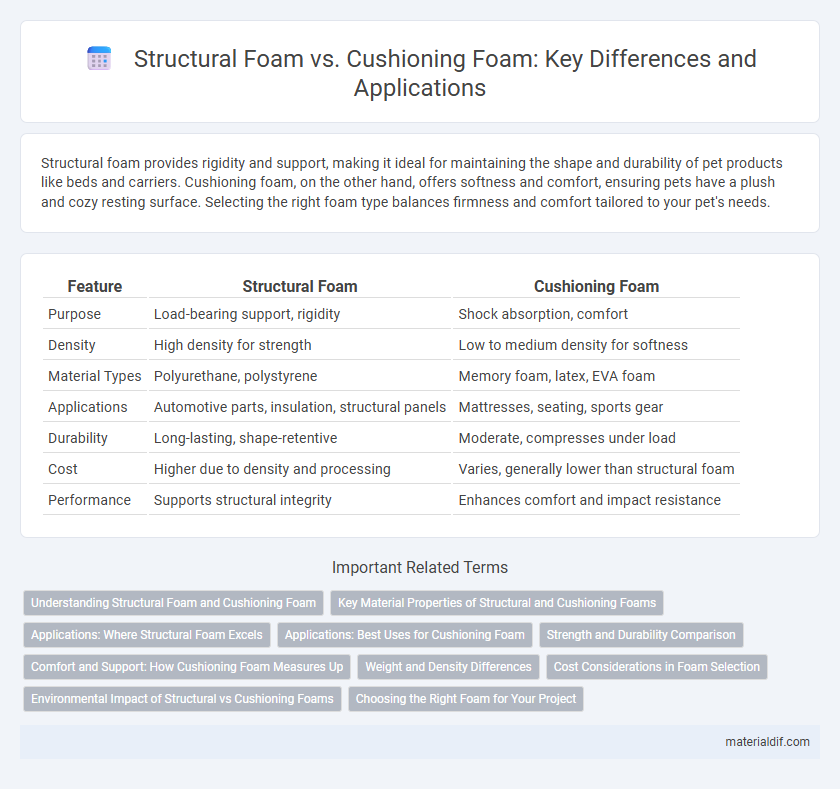
| Feature | Structural Foam | Cushioning Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Load-bearing support, rigidity | Shock absorption, comfort |
| Density | High density for strength | Low to medium density for softness |
| Material Types | Polyurethane, polystyrene | Memory foam, latex, EVA foam |
| Applications | Automotive parts, insulation, structural panels | Mattresses, seating, sports gear |
| Durability | Long-lasting, shape-retentive | Moderate, compresses under load |
| Cost | Higher due to density and processing | Varies, generally lower than structural foam |
| Performance | Supports structural integrity | Enhances comfort and impact resistance |
Understanding Structural Foam and Cushioning Foam
Structural foam is a rigid, high-density material designed to provide strength and support in applications such as automotive parts, packaging, and construction components. Cushioning foam, on the other hand, offers softness and flexibility, absorbing impact and providing comfort in products like mattresses, upholstery, and protective gear. Understanding the distinct properties of structural foam and cushioning foam helps in selecting the appropriate type for durability, shock absorption, and comfort requirements.
Key Material Properties of Structural and Cushioning Foams
Structural foam exhibits high compressive strength, rigidity, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for load-bearing and impact-resistant applications. Cushioning foam prioritizes flexibility, resilience, and energy absorption, providing superior shock absorption and comfort. Key material properties of structural foam include elevated density and stiffness, whereas cushioning foam features lower density and enhanced elasticity.
Applications: Where Structural Foam Excels
Structural foam excels in automotive and aerospace industries due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity, making it ideal for load-bearing components and structural parts. Its resistance to impact and ability to maintain form under stress suits applications such as instrument panels, door panels, and protective casings. Unlike cushioning foam, structural foam is preferred for parts requiring durability and dimensional stability rather than shock absorption or comfort.
Applications: Best Uses for Cushioning Foam
Cushioning foam is primarily used in packaging, automotive seating, and furniture to absorb impact and provide comfort, making it ideal for protecting delicate electronics, fragile goods, and enhancing ergonomics. Its open-cell structure allows for superior shock absorption and breathability compared to structural foam, which is denser and designed for load-bearing applications. Industries such as medical, sports equipment, and consumer electronics rely heavily on cushioning foam to reduce vibration and prevent damage during transportation and everyday use.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Structural foam offers superior strength and durability due to its dense, closed-cell composition, making it ideal for load-bearing applications and long-term structural support. Cushioning foam prioritizes flexibility and shock absorption, but typically lacks the resilience needed for heavy stress or prolonged wear. Understanding the distinct mechanical properties helps in choosing the right foam type for either structural integrity or comfort-focused use.
Comfort and Support: How Cushioning Foam Measures Up
Cushioning foam excels in providing superior comfort by contouring to the body's shape, distributing pressure evenly to reduce fatigue and discomfort. Structural foam offers robust support with a firmer density, maintaining shape under weight but often sacrificing softness. When comparing comfort and support, cushioning foam delivers a balanced experience ideal for seating and bedding applications, whereas structural foam prioritizes durability and load-bearing capacity.
Weight and Density Differences
Structural foam typically exhibits higher density ranging from 30 to 60 lb/ft3, providing greater rigidity and load-bearing capacity ideal for demanding industrial applications. Cushioning foam generally presents lower density between 1 to 10 lb/ft3, emphasizing lightweight properties and superior shock absorption for comfort and protection. Weight differences result from this density variance, with structural foam being significantly heavier and more durable compared to the lighter, softer cushioning foam.
Cost Considerations in Foam Selection
Structural foam typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to its complex production process and material density, making it ideal for load-bearing applications. Cushioning foam is generally more cost-effective, as it uses less dense materials primarily aimed at comfort and impact absorption. Selecting between the two hinges on balancing budget constraints with the required mechanical properties and durability for the intended application.
Environmental Impact of Structural vs Cushioning Foams
Structural foam typically uses denser, rigid polymers that involve higher energy consumption and generate more waste during production, contributing to a larger carbon footprint compared to cushioning foam. Cushioning foam often incorporates more biodegradable or recycled materials, resulting in lower environmental impact through reduced emissions and improved end-of-life recyclability. Manufacturers increasingly prioritize sustainable sourcing and eco-friendly formulations to minimize environmental harm across both foam types.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Project
Structural foam offers high rigidity and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for applications requiring dimensional stability and strength, such as automotive parts and construction panels. Cushioning foam prioritizes comfort and shock absorption, perfect for furniture, packaging, and sports equipment where impact resistance and softness are essential. Selecting the right foam depends on whether your project demands durability and support or flexibility and comfort.
Structural foam vs Cushioning foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com