Memory foam offers superior comfort and pressure relief by contouring to the body's shape, whereas polyurethane foam is more affordable and provides firmer support with quicker responsiveness. Memory foam typically has higher density, enhancing durability and motion isolation, while polyurethane foam tends to be lighter and less dense, making it more breathable but less resilient over time. Choosing between the two depends on preferences for softness, longevity, and budget considerations.
Table of Comparison
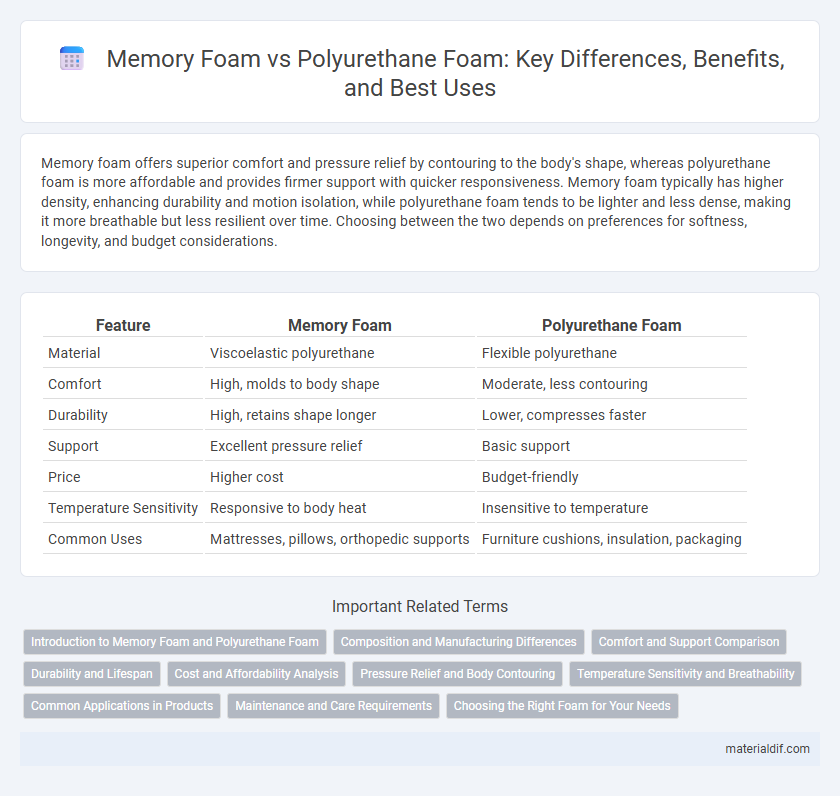
| Feature | Memory Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Viscoelastic polyurethane | Flexible polyurethane |
| Comfort | High, molds to body shape | Moderate, less contouring |
| Durability | High, retains shape longer | Lower, compresses faster |
| Support | Excellent pressure relief | Basic support |
| Price | Higher cost | Budget-friendly |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Responsive to body heat | Insensitive to temperature |
| Common Uses | Mattresses, pillows, orthopedic supports | Furniture cushions, insulation, packaging |
Introduction to Memory Foam and Polyurethane Foam
Memory foam, a viscoelastic polyurethane foam, is engineered to respond to temperature and pressure, providing superior body contouring and pressure relief compared to traditional polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam, a versatile polymer, varies in density and firmness and is widely used for cushioning, insulation, and packaging due to its lightweight and flexible properties. Understanding the structural and functional differences between memory foam and polyurethane foam is essential for selecting the right material in applications like mattresses, furniture, and medical support products.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Memory foam is primarily composed of viscoelastic polyurethane with additional chemicals to enhance its density and viscosity, providing slow response to pressure and superior contouring properties. Polyurethane foam consists mainly of polyether or polyester polyols reacted with diisocyanates, resulting in a lightweight and flexible material with faster recovery times and varied firmness. Manufacturing memory foam involves a curing process that controls the foam's open-cell structure for breathability and pressure absorption, whereas polyurethane foam production focuses on creating a closed-cell or open-cell matrix, tailoring the foam's durability and resilience.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Memory foam contours closely to the body, providing superior pressure relief and personalized comfort by evenly distributing weight. Polyurethane foam offers firmer support with quicker response times but lacks the same level of adaptive cushioning, making it less effective for pressure point reduction. The choice between memory foam and polyurethane foam ultimately depends on preference for contouring comfort versus resilient support.
Durability and Lifespan
Memory foam typically offers superior durability compared to polyurethane foam, as it maintains its shape and resilience over time without significant sagging. The lifespan of memory foam ranges from 7 to 10 years, whereas polyurethane foam generally lasts between 3 to 5 years before noticeable degradation occurs. High-density polyurethane foam can improve longevity, but it still usually falls short of the extended durability provided by quality memory foam.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Memory foam typically costs between $25 and $85 per cubic foot, making it more expensive than polyurethane foam, which ranges from $10 to $30 per cubic foot. Despite its higher price, memory foam provides superior comfort, pressure relief, and durability, often justifying the increased investment for consumers seeking long-term value. Budget-conscious buyers often prefer polyurethane foam due to its affordability and decent performance for short-term applications or lighter use.
Pressure Relief and Body Contouring
Memory foam offers superior pressure relief by evenly distributing body weight and reducing stress on pressure points, making it ideal for alleviating joint and back pain. Its viscoelastic properties allow it to contour closely to the body's shape, providing customized support and enhancing comfort during sleep. In contrast, polyurethane foam typically lacks the same level of conforming ability and pressure redistribution, often resulting in less effective body contouring and support.
Temperature Sensitivity and Breathability
Memory foam exhibits high temperature sensitivity, softening in response to body heat which allows it to contour closely for personalized comfort, whereas polyurethane foam maintains a more consistent firmness regardless of temperature changes. Breathability in memory foam is generally lower due to its dense structure, which can trap heat and limit airflow, while polyurethane foam offers improved ventilation and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing overall cooling and comfort. Selecting between these foams depends on prioritizing temperature-adaptive cushioning versus enhanced airflow and breathability in applications like mattresses and seating.
Common Applications in Products
Memory foam is widely used in mattresses, pillows, and cushioning for its superior pressure relief and contouring properties, making it ideal for sleep and comfort products. Polyurethane foam is commonly found in furniture upholstery, automotive seating, and packaging due to its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Both foams serve distinct roles in product design, with memory foam prioritizing comfort and polyurethane foam balancing support and resilience.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Memory foam requires gentle cleaning with mild soap and water, avoiding excessive moisture to prevent breakdown of viscoelastic properties. Polyurethane foam is more durable with a higher resistance to stains and can handle occasional deeper cleaning but may degrade faster under frequent exposure to harsh chemicals or heat. Regular vacuuming and using protective covers extend the lifespan of both foam types, ensuring optimal support and hygiene.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Needs
Memory foam, known for its high density and viscoelastic properties, provides superior contouring and pressure relief, making it ideal for mattresses and cushioning applications where comfort and support are priorities. Polyurethane foam, characterized by its lightweight and versatile nature, offers a more affordable solution with varying firmness levels suited for insulation, packaging, and furniture padding. Selecting the right foam depends on factors such as desired durability, budget constraints, and specific use cases, with memory foam excelling in comfort-focused scenarios and polyurethane foam serving broader industrial needs.
Memory foam vs Polyurethane foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com