Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility, resilience, and higher load-bearing capacity compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for cushioning and insulation. Polyethylene foam is more resistant to moisture, chemicals, and abrasion, providing excellent durability and impact absorption for packaging and protective applications. Choosing between polyurethane and polyethylene foam depends on the specific requirements of comfort, durability, and environmental exposure in the intended use.
Table of Comparison
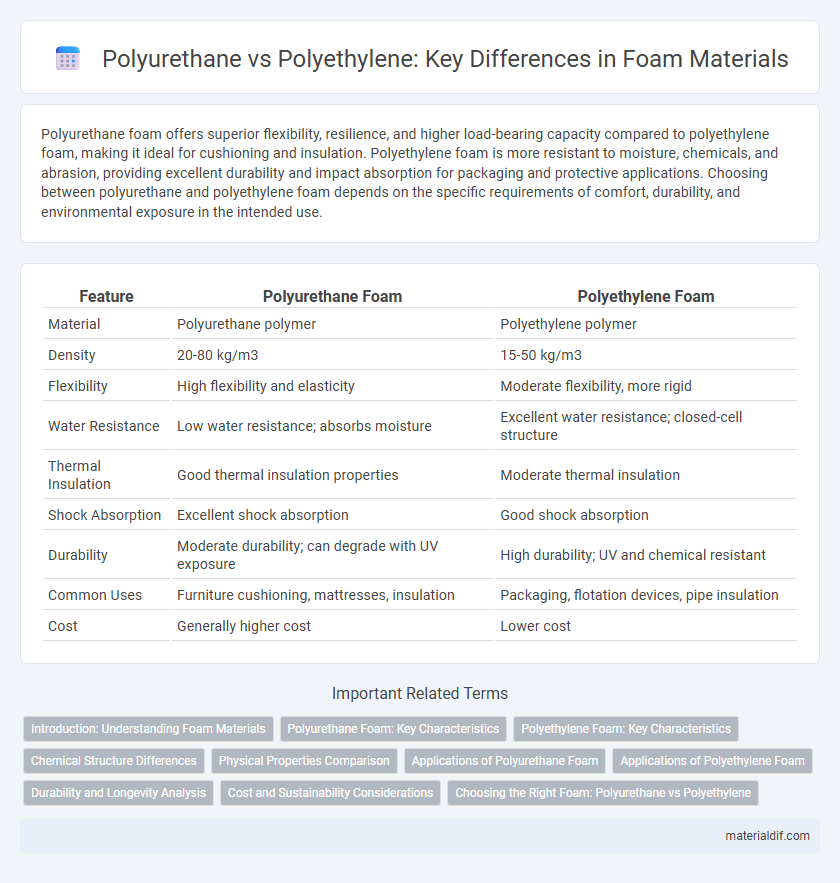
| Feature | Polyurethane Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyurethane polymer | Polyethylene polymer |
| Density | 20-80 kg/m3 | 15-50 kg/m3 |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Moderate flexibility, more rigid |
| Water Resistance | Low water resistance; absorbs moisture | Excellent water resistance; closed-cell structure |
| Thermal Insulation | Good thermal insulation properties | Moderate thermal insulation |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent shock absorption | Good shock absorption |
| Durability | Moderate durability; can degrade with UV exposure | High durability; UV and chemical resistant |
| Common Uses | Furniture cushioning, mattresses, insulation | Packaging, flotation devices, pipe insulation |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Lower cost |
Introduction: Understanding Foam Materials
Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and resilience compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for cushioning and insulation applications. Polyethylene foam provides excellent moisture resistance and impact absorption, commonly used in packaging and protective padding. Understanding the distinct properties of polyurethane and polyethylene foams helps optimize material selection based on durability, cost, and environmental factors.
Polyurethane Foam: Key Characteristics
Polyurethane foam exhibits exceptional flexibility, high resilience, and superior insulation properties compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for cushioning, thermal insulation, and soundproofing applications. Its open-cell structure allows for breathability and moisture resistance, enhancing comfort in furniture and mattress products. The material also demonstrates strong chemical resistance and long-term durability under varied temperature conditions, distinguishing it from polyethylene's denser, more rigid characteristics.
Polyethylene Foam: Key Characteristics
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight material known for its exceptional durability, water resistance, and excellent cushioning properties. Its high impact absorption and chemical resistance make it ideal for packaging, insulation, and protective applications. Compared to polyurethane foam, polyethylene foam offers superior moisture resistance and dimensional stability, ensuring long-lasting performance in harsh environments.
Chemical Structure Differences
Polyurethane foam is formed through a reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, creating urethane linkages characterized by carbamate (-NHCOO-) groups in its polymer chain. Polyethylene foam is composed of long hydrocarbon chains with repeating ethylene (-CH2CH2-) units, featuring a simple, non-polar structure without functional groups. These chemical structure differences result in polyurethane's flexibility and resilience compared to polyethylene's chemical inertness and density.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyurethane foam exhibits higher density and superior tensile strength compared to polyethylene foam, making it more durable under mechanical stress. Polyethylene foam offers better resistance to water absorption and has a lower thermal conductivity, ideal for insulation purposes. Both materials differ significantly in compression resistance, with polyurethane providing enhanced cushioning and support.
Applications of Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam is widely used in furniture cushioning, automotive seating, and insulation due to its excellent flexibility, durability, and thermal resistance. Its ability to absorb impact and provide comfort makes it ideal for bedding and packaging applications. Unlike polyethylene foam, polyurethane foam offers superior support and resilience in applications requiring prolonged use and high-performance cushioning.
Applications of Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam is widely used in packaging due to its excellent cushioning properties and resistance to moisture, chemicals, and impact, making it ideal for protecting delicate electronics, glassware, and medical equipment during transport. Its lightweight and closed-cell structure also enable effective thermal insulation in construction and automotive industries, where durability and moisture resistance are critical. Unlike polyurethane foam, polyethylene foam offers superior water resistance and chemical stability, enhancing its performance in outdoor and marine applications.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Polyurethane foam exhibits superior durability compared to polyethylene foam due to its higher resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and temperature variations, making it ideal for long-term applications. Polyethylene foam, while more resistant to water and UV exposure, tends to degrade faster under mechanical stress, reducing its overall longevity. Analyzing lifespan data, polyurethane foams generally maintain structural integrity for 10-15 years, whereas polyethylene foams last around 5-8 years under similar environmental conditions.
Cost and Sustainability Considerations
Polyurethane foam generally has a higher production cost compared to polyethylene foam due to more complex chemical processes and raw material expenses. From a sustainability perspective, polyethylene foam is often favored for its recyclability and lower environmental impact during manufacturing, whereas polyurethane foam poses challenges in biodegradability and recycling due to its chemical composition. Choosing between these materials requires balancing budget constraints with environmental goals, considering factors like lifecycle emissions and end-of-life disposal options.
Choosing the Right Foam: Polyurethane vs Polyethylene
Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility, durability, and cushioning, making it ideal for furniture, mattresses, and automotive seating applications. Polyethylene foam provides excellent water resistance, impact absorption, and lightweight properties, often used in packaging, flotation devices, and protective equipment. Selecting the right foam depends on specific requirements like comfort, moisture resistance, and durability for the intended use.
Polyurethane vs polyethylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com