Polyester foam offers excellent thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for automotive and insulation applications, whereas polyether foam provides superior flexibility, resilience, and water resistance, commonly used in bedding and upholstery. The chemical structure of polyester foam gives it higher tensile strength but lower hydrolytic stability compared to the more hydrolysis-resistant polyether foam. Selecting between polyester and polyether foam depends on the specific requirements for mechanical strength, moisture exposure, and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
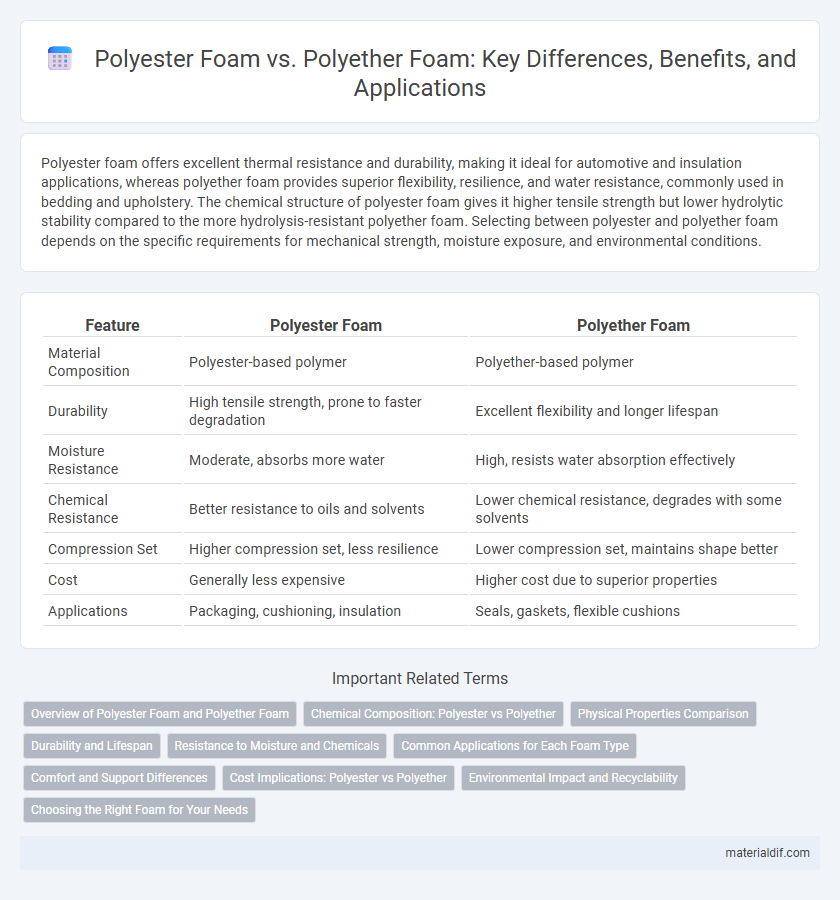
| Feature | Polyester Foam | Polyether Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyester-based polymer | Polyether-based polymer |
| Durability | High tensile strength, prone to faster degradation | Excellent flexibility and longer lifespan |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, absorbs more water | High, resists water absorption effectively |
| Chemical Resistance | Better resistance to oils and solvents | Lower chemical resistance, degrades with some solvents |
| Compression Set | Higher compression set, less resilience | Lower compression set, maintains shape better |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Higher cost due to superior properties |
| Applications | Packaging, cushioning, insulation | Seals, gaskets, flexible cushions |
Overview of Polyester Foam and Polyether Foam
Polyester foam is a durable polyurethane-based material known for its high resilience, chemical resistance, and moisture stability, making it ideal for automotive seating and industrial applications. Polyether foam, also a type of polyurethane foam, offers superior elasticity, excellent tear strength, and better resistance to hydrolysis, commonly used in mattresses, furniture, and medical cushioning. Both foams differ in their polymer chain structure, with polyester foam featuring ester groups that enhance durability, while polyether foam contains ether groups that improve flexibility and hydrolytic stability.
Chemical Composition: Polyester vs Polyether
Polyester foam is derived from polyester polyols, characterized by ester linkages that provide higher resistance to oils, solvents, and bacteria, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Polyether foam is synthesized from polyether polyols, featuring ether linkages that offer superior hydrolytic stability and greater elasticity, commonly used in cushioning and bedding products. The chemical composition difference primarily influences foam durability, moisture resistance, and flexibility in varied environments.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyester foam exhibits higher tensile strength and greater resistance to heat and chemicals compared to polyether foam, making it suitable for more demanding industrial applications. Polyether foam offers superior resilience, flexibility, and hydrolytic stability, which enhances comfort and durability in furniture and bedding products. The density of polyester foam typically ranges from 27 to 32 kg/m3, whereas polyether foam tends to have a lower density around 18 to 25 kg/m3, affecting their respective cushioning and load-bearing capabilities.
Durability and Lifespan
Polyester foam exhibits superior durability due to its resistance to solvents, oils, and moisture, resulting in a longer lifespan compared to polyether foam, which tends to degrade faster under similar conditions. The structural integrity of polyester foam remains stable in high-temperature environments, making it ideal for applications requiring extended use and exposure to harsh elements. Polyether foam, while softer and more elastic, generally has a shorter lifespan due to its lower resistance to physical wear and chemical exposure.
Resistance to Moisture and Chemicals
Polyester foam exhibits superior resistance to moisture and chemicals compared to polyether foam, making it ideal for applications in humid or chemically aggressive environments. Its dense, hydrophobic structure limits water absorption and resists alkalis, acids, and solvents more effectively. In contrast, polyether foam tends to absorb more moisture and degrade faster when exposed to harsh chemicals, reducing its durability in such conditions.
Common Applications for Each Foam Type
Polyester foam is frequently used in automotive seating, filtration, and packaging due to its durability and resistance to oils and solvents. Polyether foam is commonly found in furniture cushions, mattresses, and medical applications because of its excellent flexibility and hydrolytic stability. Both foams serve distinct purposes based on performance requirements in industries such as automotive, furniture manufacturing, and healthcare.
Comfort and Support Differences
Polyester foam offers firmer support and greater durability, making it ideal for applications requiring resilient cushioning and long-lasting comfort. Polyether foam provides softer comfort with excellent elasticity, which enhances pressure relief but may compress faster under heavy use. Choosing between polyester and polyether foam depends on the desired balance between support longevity and initial softness in seating or bedding products.
Cost Implications: Polyester vs Polyether
Polyester foam generally incurs higher production costs due to its chemical composition and durability, making it more expensive than polyether foam. Polyether foam offers a cost-effective alternative with lower raw material prices and simpler manufacturing processes. Budget considerations often favor polyether foam for applications where cost efficiency is critical without compromising basic elasticity and cushioning.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyester foam is generally more biodegradable and breaks down faster in landfill conditions compared to polyether foam, making it a more environmentally friendly option. Polyether foam, known for its higher durability and resistance to moisture, poses challenges in recycling due to its chemical structure and slower degradation rate. Efficient recycling programs for polyester foam can reduce landfill waste, whereas polyether foam often requires specialized processing to reclaim materials, impacting overall environmental sustainability.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Needs
Polyester foam offers higher resistance to heat and chemicals, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and long-lasting performance. Polyether foam provides superior elasticity and excellent resistance to water absorption, suitable for cushioning and insulation purposes where moisture exposure is common. Selecting the right foam depends on factors such as environmental conditions, mechanical stress, and specific use cases to ensure optimal functionality and longevity.
Polyester Foam vs Polyether Foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com