Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior cushioning and flexibility compared to polyolefin foam, making it ideal for pet beds and toys that require durability and comfort. Polyolefin foam, on the other hand, excels in moisture resistance and chemical stability, which benefits applications where hygiene and easy cleaning are essential. Choosing between these foams depends on prioritizing comfort and softness (EVA) or moisture barrier and resilience (polyolefin) for pet products.
Table of Comparison
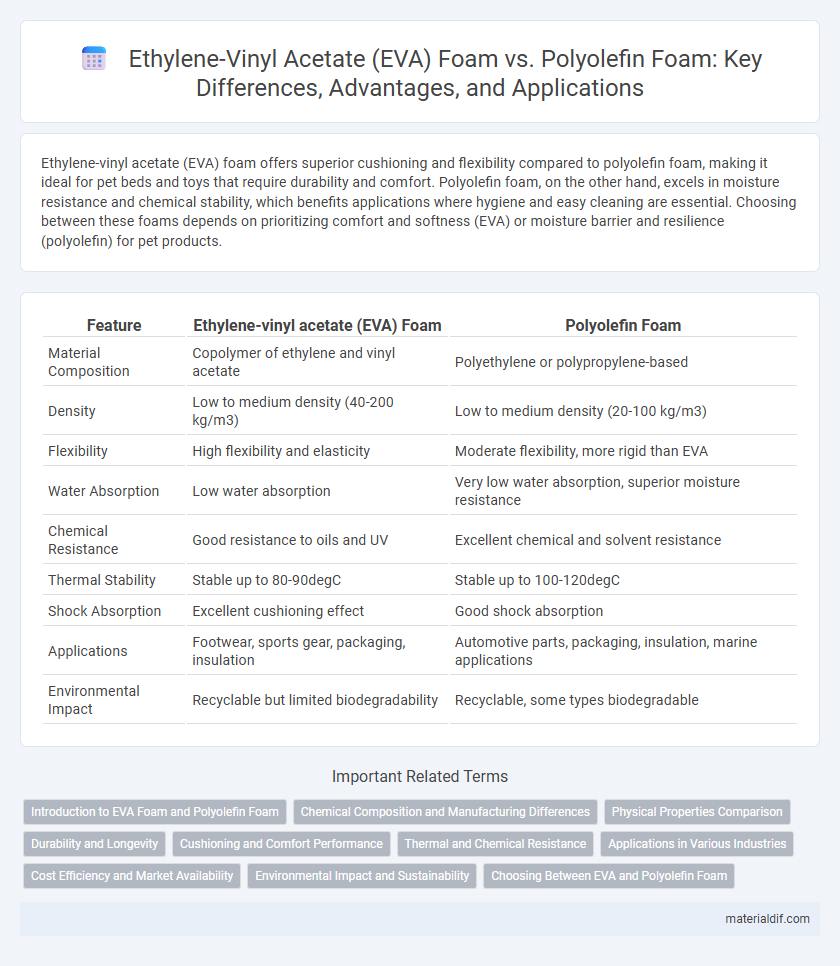
| Feature | Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) Foam | Polyolefin Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate | Polyethylene or polypropylene-based |
| Density | Low to medium density (40-200 kg/m3) | Low to medium density (20-100 kg/m3) |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Moderate flexibility, more rigid than EVA |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Very low water absorption, superior moisture resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and UV | Excellent chemical and solvent resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 80-90degC | Stable up to 100-120degC |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent cushioning effect | Good shock absorption |
| Applications | Footwear, sports gear, packaging, insulation | Automotive parts, packaging, insulation, marine applications |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable but limited biodegradability | Recyclable, some types biodegradable |
Introduction to EVA Foam and Polyolefin Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a soft, flexible material with excellent cushioning properties, commonly used in footwear, sports equipment, and packaging due to its shock absorption and water resistance. Polyolefin foam, made from polyethylene or polypropylene, offers higher chemical resistance, durability, and a closed-cell structure that provides superior thermal insulation and moisture barrier capabilities. Both foams are valued for lightweight, versatile applications, but EVA foam excels in elasticity and comfort while polyolefin foam is preferred for thermal insulation and resistance to environmental stress.
Chemical Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam features a copolymer structure combining ethylene and vinyl acetate units, resulting in flexible, soft foam with excellent stress-crack resistance, produced through a chemical expansion process involving azodicarbonamide as a foaming agent. Polyolefin foam, composed primarily of polyethylene or polypropylene, is created via physical or chemical foaming techniques that involve blowing agents such as hydrocarbons or CO2, yielding a closed-cell, durable, and highly resilient foam. The distinct polymer matrices and foaming mechanisms directly influence the mechanical properties, thermal stability, and environmental resistance of EVA and polyolefin foams, making them suitable for diverse industrial applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior elasticity, resilience, and softness compared to polyolefin foam, making it ideal for applications requiring cushioning and impact absorption. Polyolefin foam offers higher chemical resistance, thermal stability, and durability under harsh conditions, suitable for industrial and insulation uses. Both foams demonstrate low water absorption, but EVA foam typically provides better compression set recovery and flexibility across a wider temperature range.
Durability and Longevity
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers excellent durability due to its resistance to stress cracking and UV radiation, contributing to a longer lifespan in outdoor applications. Polyolefin foam demonstrates superior chemical and moisture resistance, enhancing its longevity in harsh environments and industrial settings. Both foams maintain structural integrity over time, but EVA's elasticity and cushioning properties provide added durability in dynamic conditions.
Cushioning and Comfort Performance
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior cushioning with excellent shock absorption and high resilience, making it ideal for footwear midsoles and sports equipment. Polyolefin foam provides good comfort due to its lightweight structure and flexibility but generally exhibits lower impact resistance compared to EVA. EVA's enhanced elasticity supports prolonged comfort and durability, whereas polyolefin foam prioritizes softness and breathability in applications requiring moderate cushioning.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior flexibility and excellent resilience at low temperatures, but its thermal resistance is limited to around 85degC, making it less suitable for high-heat applications. Polyolefin foam offers enhanced thermal stability withstanding temperatures up to approximately 120degC, along with greater chemical resistance to oils, solvents, and acids, which makes it ideal for industrial environments. The choice between EVA and polyolefin foams largely depends on the specific thermal and chemical exposure conditions of the application.
Applications in Various Industries
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is widely used in the footwear industry for its lightweight, cushioning properties and shock absorption, making it ideal for midsoles and insoles. Polyolefin foam finds extensive application in packaging and automotive sectors due to its excellent chemical resistance, thermal insulation, and impact protection. Both foams serve crucial roles in sports equipment, construction, and medical devices, with EVA favored for flexibility and comfort, while polyolefin provides durability and moisture resistance.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers higher cost efficiency due to its lower production expenses and enhanced durability, making it favorable for budget-sensitive applications. Polyolefin foam, while typically more expensive, boasts wider market availability and superior environmental resistance, which supports diverse industrial uses. The trade-off between EVA's affordability and polyolefin's accessibility influences purchasing decisions across packaging, automotive, and sports sectors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam typically exhibits lower recyclability compared to polyolefin foam, which is often more easily recycled and biodegradable, contributing to reduced environmental impact. Polyolefin foam, derived from polyethylene or polypropylene, has a smaller carbon footprint and generates fewer hazardous byproducts during production and disposal. The sustainability of EVA foam is limited by its reliance on petroleum-based vinyl acetate, whereas polyolefin foam benefits from advances in bio-based polyolefin alternatives and improved end-of-life recycling technologies.
Choosing Between EVA and Polyolefin Foam
Choosing between Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam and Polyolefin foam depends largely on the specific application requirements; EVA foam offers superior softness, flexibility, and stress-crack resistance, making it ideal for footwear and sports equipment. Polyolefin foam excels in chemical resistance, closed-cell structure, and durability, which suits packaging, insulation, and automotive uses. Evaluating factors like water absorption, cushioning, and environmental exposure ensures optimal material selection for performance and longevity.
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam vs Polyolefin foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com