Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and cushioning, making it ideal for upholstery and bedding applications, whereas polyethylene foam excels in durability and impact resistance, commonly used for packaging and protective gear. Polyurethane foam can absorb more energy and is more breathable, while polyethylene foam has a closed-cell structure that provides excellent moisture resistance and chemical stability. Choosing between them depends on the need for softness versus structural integrity and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
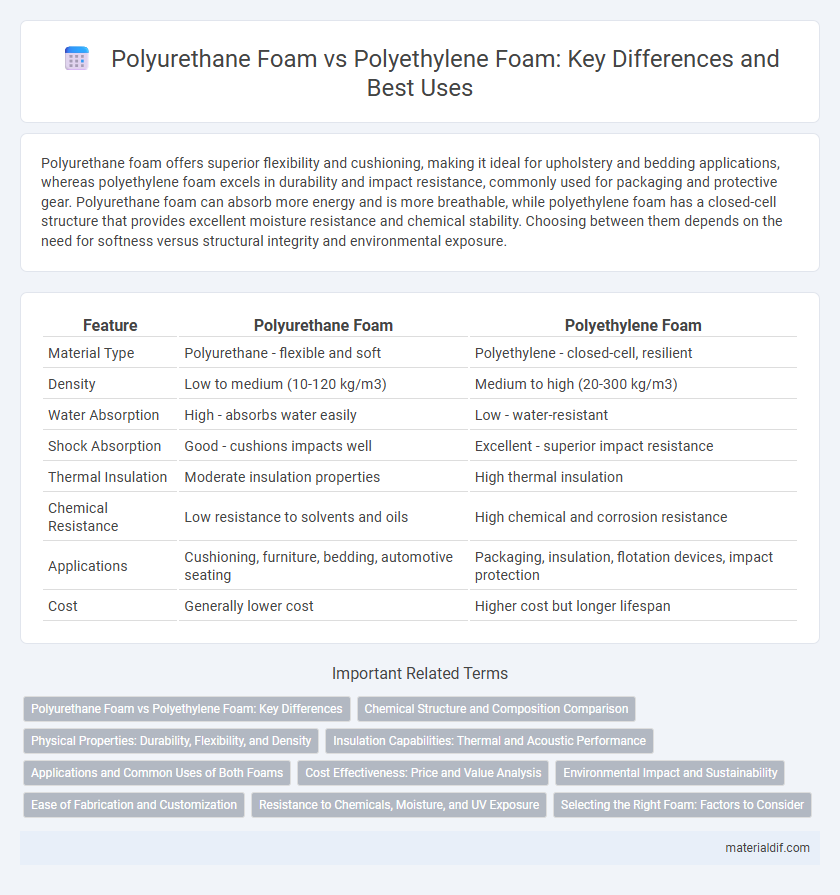
| Feature | Polyurethane Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyurethane - flexible and soft | Polyethylene - closed-cell, resilient |
| Density | Low to medium (10-120 kg/m3) | Medium to high (20-300 kg/m3) |
| Water Absorption | High - absorbs water easily | Low - water-resistant |
| Shock Absorption | Good - cushions impacts well | Excellent - superior impact resistance |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation properties | High thermal insulation |
| Chemical Resistance | Low resistance to solvents and oils | High chemical and corrosion resistance |
| Applications | Cushioning, furniture, bedding, automotive seating | Packaging, insulation, flotation devices, impact protection |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost but longer lifespan |
Polyurethane Foam vs Polyethylene Foam: Key Differences
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and flexibility compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for furniture and automotive applications. Polyethylene foam is denser and more resistant to moisture, chemicals, and impact, often used in packaging and insulation. The key differences lie in their cellular structure, durability, and specific use cases within industry sectors.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polyurethane foam consists of polymer chains formed by reacting diisocyanates with polyols, creating a versatile structure with urethane linkages that provide excellent flexibility and cushioning. Polyethylene foam is made from polymerizing ethylene monomers into a thermoplastic with a simple, saturated hydrocarbon chain, resulting in a chemically inert, closed-cell structure offering durability and water resistance. The chemical differences between polyurethane's segmented urethane blocks and polyethylene's linear hydrocarbon chains directly influence their mechanical properties and typical applications.
Physical Properties: Durability, Flexibility, and Density
Polyurethane foam exhibits superior flexibility and higher durability due to its open-cell structure, making it ideal for cushioning and insulation applications where resilience is critical. Polyethylene foam, characterized by a closed-cell structure, offers greater density and excellent moisture resistance, enhancing its performance in packaging and flotation devices. The choice between polyurethane and polyethylene foam depends on the specific balance required between flexibility, durability, and density in the intended use.
Insulation Capabilities: Thermal and Acoustic Performance
Polyurethane foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for energy-efficient building applications. Polyethylene foam provides enhanced acoustic insulation with excellent sound-dampening properties, suitable for noise reduction in industrial and commercial environments. Both foams exhibit distinct advantages, with polyurethane excelling in thermal performance and polyethylene providing better acoustic absorption.
Applications and Common Uses of Both Foams
Polyurethane foam is widely used in furniture cushioning, bedding, automotive seating, and insulation due to its excellent flexibility, cushioning properties, and thermal resistance. Polyethylene foam finds common applications in packaging, shock absorption, flotation devices, and pipe insulation because of its closed-cell structure, lightweight nature, and water resistance. Both foams serve distinct purposes: polyurethane foam excels in comfort and thermal insulation, while polyethylene foam is preferred for protective packaging and impact resistance.
Cost Effectiveness: Price and Value Analysis
Polyurethane foam generally offers a higher initial cost compared to polyethylene foam but provides superior cushioning and durability, making it more cost-effective for long-term use in applications like furniture and automotive seating. Polyethylene foam, being more affordable and lightweight, excels in packaging and insulation where budget constraints and moisture resistance are critical considerations. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including lifespan and functional performance, helps determine the best value between polyurethane and polyethylene foams based on specific application needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane foam typically has a higher environmental impact due to its reliance on petrochemical-based raw materials and challenges in recycling, leading to increased landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions. Polyethylene foam offers better sustainability prospects as it is more readily recyclable and often produced with lower carbon footprints, contributing to reduced environmental harm. Choosing polyethylene foam aligns more closely with sustainable practices, minimizing ecological footprints and promoting circular economy principles.
Ease of Fabrication and Customization
Polyurethane foam offers superior ease of fabrication compared to polyethylene foam due to its open-cell structure, allowing for precise cutting, shaping, and gluing. Customization of polyurethane foam is highly versatile, including density variations and chemical formulations tailored for specific applications such as insulation, cushioning, or acoustic treatment. Polyethylene foam, while durable and resilient, presents more challenges in customization and fabrication because of its closed-cell, denser structure that limits complex modifications.
Resistance to Chemicals, Moisture, and UV Exposure
Polyurethane foam exhibits moderate resistance to chemicals and moisture but tends to degrade under prolonged UV exposure, making it less suitable for outdoor applications without protective coatings. Polyethylene foam offers superior chemical resistance and excellent moisture repellency, maintaining structural integrity even with continuous exposure to water and various solvents. Its high UV resistance enables polyethylene foam to withstand harsh sunlight, rendering it ideal for extended outdoor use where durability is critical.
Selecting the Right Foam: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right foam involves evaluating factors such as density, cushioning properties, and durability, where polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and resilience, making it ideal for furniture and bedding applications. Polyethylene foam provides excellent water resistance, chemical stability, and shock absorption, which suits packaging and insulation needs. Understanding the specific demands of your project ensures optimal performance by matching foam characteristics to the environment and load requirements.
Polyurethane foam vs Polyethylene foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com