Melamine foam offers superior sound absorption and fire resistance compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for acoustic insulation and safety applications. Polystyrene foam is lightweight and provides excellent thermal insulation but lacks the durability and flame-retardant properties of melamine foam. Choosing between these foams depends on the specific requirements for insulation, fire safety, and acoustic performance.
Table of Comparison
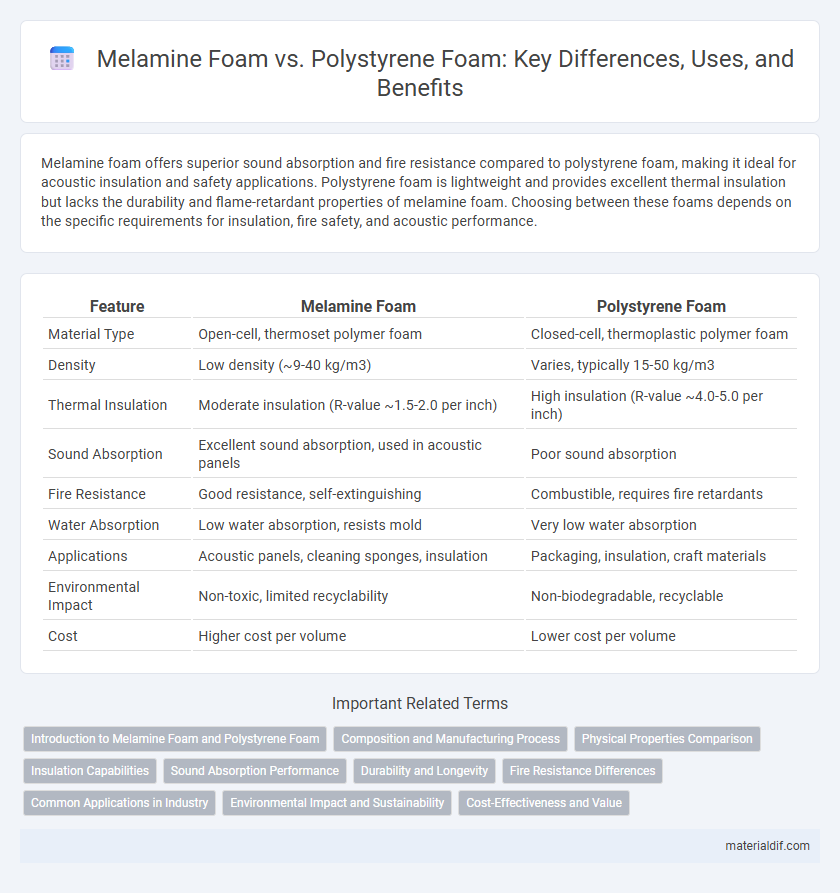
| Feature | Melamine Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Open-cell, thermoset polymer foam | Closed-cell, thermoplastic polymer foam |
| Density | Low density (~9-40 kg/m3) | Varies, typically 15-50 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation (R-value ~1.5-2.0 per inch) | High insulation (R-value ~4.0-5.0 per inch) |
| Sound Absorption | Excellent sound absorption, used in acoustic panels | Poor sound absorption |
| Fire Resistance | Good resistance, self-extinguishing | Combustible, requires fire retardants |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption, resists mold | Very low water absorption |
| Applications | Acoustic panels, cleaning sponges, insulation | Packaging, insulation, craft materials |
| Environmental Impact | Non-toxic, limited recyclability | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Cost | Higher cost per volume | Lower cost per volume |
Introduction to Melamine Foam and Polystyrene Foam
Melamine foam is a lightweight, open-cell material known for its excellent sound absorption and thermal insulation properties, widely used in construction and automotive industries. Polystyrene foam, available in expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) forms, is characterized by its rigid structure and high compressive strength, commonly utilized in packaging, insulation, and cushioning applications. Both foams offer distinct advantages, with melamine foam excelling in fire resistance and noise reduction, while polystyrene foam provides superior moisture resistance and structural support.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Melamine foam is composed of a thermosetting polymer derived from melamine and formaldehyde, created through a unique polymerization and foaming process that results in a rigid, open-celled structure. Polystyrene foam consists of expanded polystyrene beads, produced by polymerizing styrene monomers and then expanding the beads using steam in a mold or extruder to form a closed-cell foam with excellent insulating properties. The difference in composition and manufacturing processes affects the density, thermal insulation, and mechanical properties, making melamine foam lightweight and fire-resistant, while polystyrene foam is known for its rigidity and moisture resistance.
Physical Properties Comparison
Melamine foam exhibits a highly open-cell structure, resulting in superior sound absorption and excellent thermal insulation properties compared to polystyrene foam, which has a closed-cell structure enhancing its rigidity and moisture resistance. The density of melamine foam typically ranges from 9 to 18 kg/m3, providing lightweight and flexible characteristics, whereas polystyrene foam's density varies between 15 and 50 kg/m3, offering higher compressive strength and impact resistance. Melamine foam's fire retardant nature contrasts with polystyrene foam's higher flammability, making melamine foam safer for applications requiring fire performance.
Insulation Capabilities
Melamine foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its open-cell structure, providing effective sound absorption and fire resistance, making it ideal for building acoustics and HVAC systems. Polystyrene foam, available in expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) forms, delivers high compressive strength and moisture resistance, widely used in wall insulation and roofing applications for energy efficiency. Melamine foam excels in flame retardancy and breathability, whereas polystyrene foam provides better vapor barrier properties and structural support in insulation.
Sound Absorption Performance
Melamine foam exhibits superior sound absorption performance due to its open-cell structure, which effectively traps and dissipates acoustic energy across a broad frequency range. Polystyrene foam, with its closed-cell composition, offers limited sound absorption, primarily reflecting sound waves rather than absorbing them. Acoustic applications prioritize melamine foam for its enhanced noise reduction capabilities in environments such as recording studios and industrial settings.
Durability and Longevity
Melamine foam exhibits superior durability compared to polystyrene foam due to its robust open-cell structure that resists compression and wear over time. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, is more prone to cracking, crumbling, and degradation under prolonged exposure to stress and environmental factors. This enhanced longevity makes melamine foam a preferred choice for applications demanding sustained performance in insulation, soundproofing, and cleaning.
Fire Resistance Differences
Melamine foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to polystyrene foam due to its inherent flame-retardant properties and ability to self-extinguish when exposed to flames. Polystyrene foam is highly flammable, melting and releasing toxic fumes rapidly during combustion, which poses significant fire hazards. These characteristics make melamine foam a preferred choice for applications requiring enhanced fire safety standards, such as insulation and acoustic panels.
Common Applications in Industry
Melamine foam is widely used in soundproofing, thermal insulation, and cleaning products due to its excellent fire resistance and open-cell structure, making it ideal for automotive, construction, and aerospace industries. Polystyrene foam, known for its high rigidity and moisture resistance, is commonly employed in packaging, insulation panels, and disposable food containers, serving the electronics, building, and food service sectors. Each foam type is selected based on specific application requirements such as flame retardancy, durability, and cushioning properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Melamine foam exhibits superior environmental sustainability compared to polystyrene foam due to its biodegradable composition and lower carbon footprint during production. Polystyrene foam, primarily derived from petroleum, poses significant pollution risks as it decomposes very slowly and contributes heavily to plastic waste accumulation in landfills and oceans. Choosing melamine foam reduces long-term environmental damage by minimizing non-biodegradable waste and supporting lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Cost-Effectiveness and Value
Melamine foam offers superior sound and thermal insulation properties at a moderate price, making it a cost-efficient choice for acoustic treatments and insulation applications. Polystyrene foam is generally less expensive upfront and widely used for packaging and insulation, but it provides lower performance in sound absorption and durability. When evaluating cost-effectiveness and value, melamine foam delivers better long-term benefits through enhanced energy savings and noise reduction despite its higher initial cost.
Melamine foam vs Polystyrene foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com