High-resilience foam offers superior durability and support compared to conventional foam, maintaining its shape and comfort over extended use. Its open-cell structure allows better air circulation, enhancing breathability and reducing heat retention. Conventional foam, while cost-effective, tends to compress more quickly and may lead to uneven wear and reduced comfort over time.
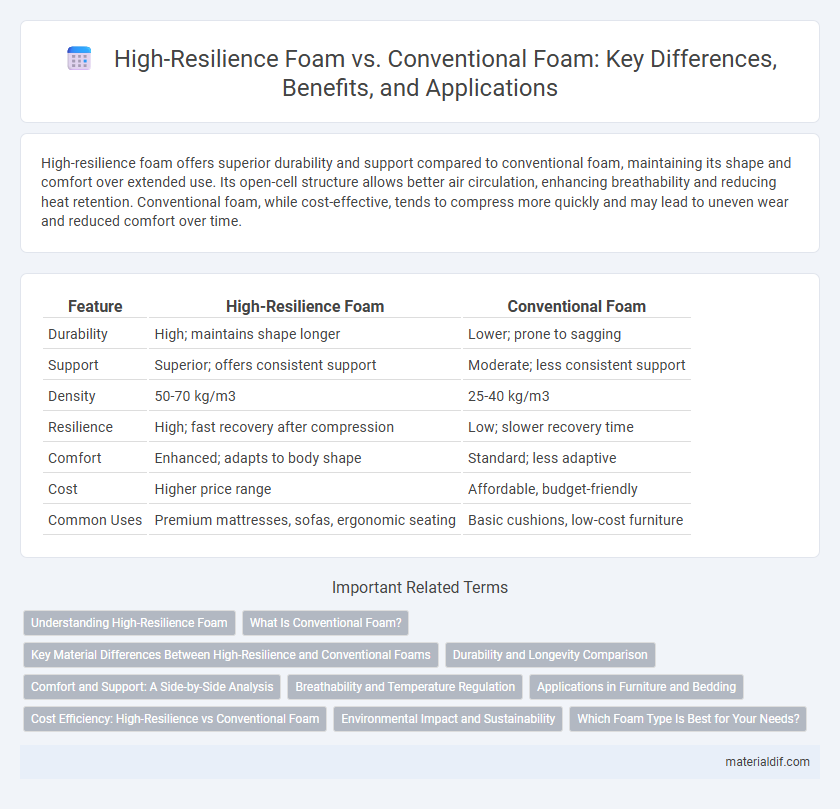
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High-Resilience Foam | Conventional Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High; maintains shape longer | Lower; prone to sagging |
| Support | Superior; offers consistent support | Moderate; less consistent support |
| Density | 50-70 kg/m3 | 25-40 kg/m3 |
| Resilience | High; fast recovery after compression | Low; slower recovery time |
| Comfort | Enhanced; adapts to body shape | Standard; less adaptive |
| Cost | Higher price range | Affordable, budget-friendly |
| Common Uses | Premium mattresses, sofas, ergonomic seating | Basic cushions, low-cost furniture |
Understanding High-Resilience Foam
High-resilience foam features an open-cell structure that offers superior durability, breathability, and support compared to conventional foam, making it ideal for furniture and bedding applications. Its higher density and enhanced elasticity enable better weight distribution and pressure relief, which improves comfort and longevity. Understanding the material properties of high-resilience foam highlights its advantages in resilience and performance over traditional polyurethane foam.
What Is Conventional Foam?
Conventional foam, typically composed of polyurethane, is widely used in furniture and mattresses for its affordability and basic cushioning properties. It offers moderate durability and comfort but tends to break down faster under frequent use compared to high-resilience foam. Conventional foam has a lower density and slower recovery time, resulting in less support and quicker formation of body impressions.
Key Material Differences Between High-Resilience and Conventional Foams
High-resilience foam features a more open cell structure and higher density, typically ranging from 1.8 to 2.8 pounds per cubic foot, compared to conventional foam's denser but less elastic makeup around 1.2 to 1.6 pounds per cubic foot. The polyurethane base in high-resilience foam is engineered with a unique catalyst blend, increasing its ability to recover quickly after compression, while conventional foam exhibits slower response and reduced durability. These material differences contribute to high-resilience foam's superior breathability, elasticity, and long-term support in applications like mattresses and upholstery.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
High-resilience foam offers superior durability compared to conventional foam due to its higher density and improved cell structure, enabling it to maintain shape and support longer under repeated use. Conventional foam tends to compress and degrade faster, resulting in sagging and reduced comfort over time. Studies indicate that high-resilience foam can last up to twice as long, making it a preferred option for long-term applications in furniture and bedding.
Comfort and Support: A Side-by-Side Analysis
High-resilience foam offers superior comfort and support by providing enhanced elasticity and faster recovery compared to conventional foam, resulting in better pressure distribution and durability. Conventional foam tends to compress more quickly, causing reduced support and less consistent comfort over time. The advanced cell structure in high-resilience foam promotes increased airflow and resilience, making it ideal for prolonged use and improved ergonomic benefits.
Breathability and Temperature Regulation
High-resilience foam offers superior breathability compared to conventional foam due to its open-cell structure, which facilitates better airflow and moisture dissipation. This enhanced ventilation helps maintain a cooler sleeping surface by preventing heat buildup and promoting temperature regulation throughout the night. Conventional foam tends to trap heat and moisture, leading to discomfort and reduced sleep quality.
Applications in Furniture and Bedding
High-resilience foam offers superior support and durability compared to conventional foam, making it ideal for high-traffic furniture and bedding applications. Its open-cell structure enhances airflow, providing better temperature regulation and increased comfort for mattresses and upholstered furniture. Conventional foam, while cost-effective, tends to compress faster and offers less resilience, limiting its long-term performance in cushions and mattress cores.
Cost Efficiency: High-Resilience vs Conventional Foam
High-resilience foam offers superior durability and support compared to conventional foam, leading to longer product lifespan and reduced replacement frequency. While initial costs are higher for high-resilience foam, its ability to maintain shape and comfort over time results in better cost efficiency. Conventional foam may have lower upfront expenses but tends to degrade faster, increasing long-term maintenance and replacement costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
High-resilience foam typically offers greater durability and longer lifespan compared to conventional foam, reducing the frequency of replacement and minimizing waste. It is often made using more eco-friendly manufacturing processes, with lower emissions and less use of harmful chemicals, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. Conventional foam, while cheaper, tends to degrade faster and is less recyclable, leading to higher environmental impact and sustainability concerns.
Which Foam Type Is Best for Your Needs?
High-resilience foam offers superior durability, enhanced support, and better pressure distribution compared to conventional foam, making it ideal for those seeking long-lasting comfort. Conventional foam, typically cheaper and softer, suits users preferring a plush feel for short-term use or lower impact cushioning. Assessing factors like budget, weight support requirements, and intended use helps determine whether high-resilience or conventional foam best meets your specific comfort and durability needs.
High-resilience Foam vs Conventional Foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com