PVC foam offers superior chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for applications exposed to moisture and harsh environments. PU foam provides excellent cushioning and flexibility, preferred for insulation and comfort-focused uses. Selecting between PVC and PU foam depends on the specific performance requirements such as rigidity versus softness and exposure conditions.
Table of Comparison
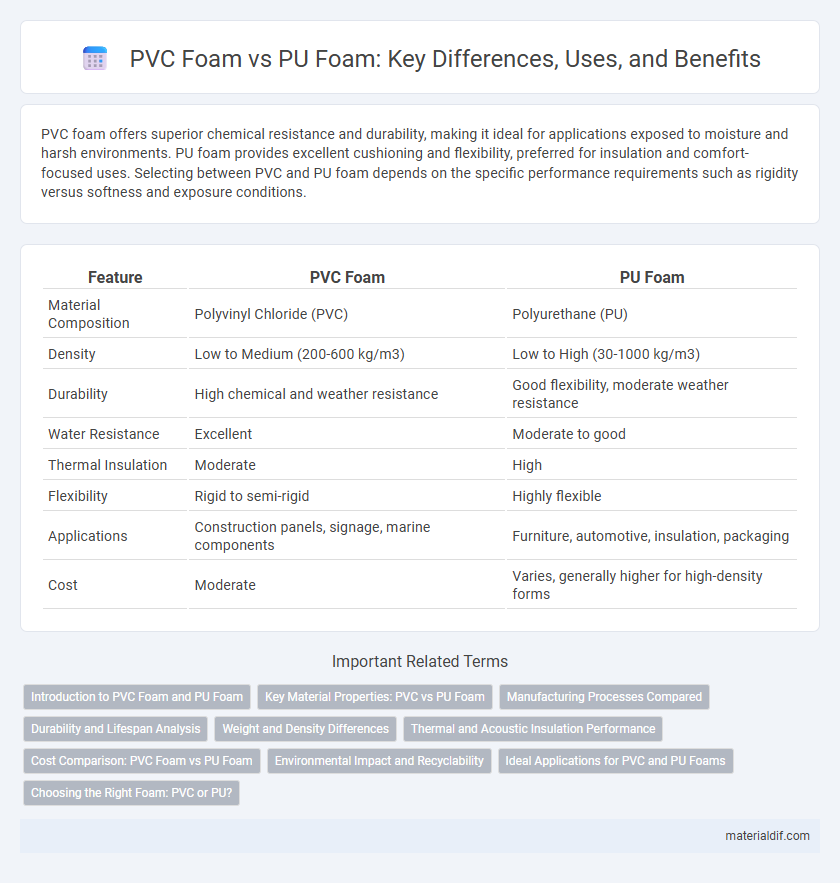
| Feature | PVC Foam | PU Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polyurethane (PU) |
| Density | Low to Medium (200-600 kg/m3) | Low to High (30-1000 kg/m3) |
| Durability | High chemical and weather resistance | Good flexibility, moderate weather resistance |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Moderate to good |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility | Rigid to semi-rigid | Highly flexible |
| Applications | Construction panels, signage, marine components | Furniture, automotive, insulation, packaging |
| Cost | Moderate | Varies, generally higher for high-density forms |
Introduction to PVC Foam and PU Foam
PVC foam, composed of polyvinyl chloride polymers, offers strong chemical resistance, excellent fire retardancy, and good mechanical durability, making it ideal for construction and automotive applications. PU foam, or polyurethane foam, provides superior cushioning, thermal insulation, and flexibility, commonly used in furniture, bedding, and packaging industries. Both materials vary significantly in density, compressive strength, and cost, influencing their specific usage based on performance requirements.
Key Material Properties: PVC vs PU Foam
PVC foam exhibits higher rigidity and better chemical resistance compared to PU foam, making it ideal for applications requiring structural durability and exposure to harsh environments. PU foam offers superior flexibility, excellent thermal insulation, and higher cushioning properties, which are advantageous in comfort and packaging industries. Density ranges typically vary, with PVC foam densities around 60-200 kg/m3 and PU foam from 30-100 kg/m3, influencing their respective mechanical performance and weight.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
PVC foam manufacturing involves polymerizing vinyl chloride monomers through suspension or emulsion polymerization, followed by expansion using chemical blowing agents, resulting in closed-cell structures with high rigidity and dimensional stability. PU foam is produced via a reaction between polyols and diisocyanates in a liquid state, where physical or chemical blowing agents create a cellular structure during curing, allowing adjustments for flexibility or firmness. PVC foam's manufacturing emphasizes thermal and chemical resistance through a rigid matrix, while PU foam's process enables diverse applications due to tunable density and mechanical properties.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
PVC foam offers superior durability compared to PU foam due to its high resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation, making it ideal for outdoor and marine applications. PU foam typically exhibits a shorter lifespan as it is more susceptible to degradation from prolonged exposure to sunlight and moisture. For long-term performance, PVC foam provides better structural integrity and maintains its properties over extended periods under harsh environmental conditions.
Weight and Density Differences
PVC foam typically exhibits higher density, ranging between 30 to 80 kg/m3, resulting in a heavier material compared to PU foam, which generally has a density around 20 to 60 kg/m3. The increased density of PVC foam contributes to greater weight per unit volume, making it more rigid and durable for structural applications. In contrast, PU foam's lower density offers lightweight properties ideal for cushioning and insulation where weight reduction is critical.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
PVC foam exhibits superior thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, which reduces heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency in construction applications. PU foam offers better acoustic insulation by absorbing sound waves effectively, making it ideal for noise reduction in residential and commercial buildings. Both foams serve distinct insulation needs, with PVC foam excelling in thermal resistance and PU foam providing advanced soundproofing capabilities.
Cost Comparison: PVC Foam vs PU Foam
PVC foam generally incurs lower production and raw material costs compared to PU foam, making it a more cost-effective option for large-scale manufacturing. PU foam offers superior insulation and flexibility but comes with higher expenses related to its chemical components and processing methods. Budget-sensitive projects often prioritize PVC foam for its affordability, while applications requiring enhanced performance may justify the additional investment in PU foam.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
PVC foam typically has a higher environmental impact due to the release of harmful dioxins during production and difficulties in recycling, often ending up in landfills. PU foam, while also challenging to recycle, is generally considered less toxic and offers more potential for chemical recycling methods that reduce waste. Both materials present challenges for end-of-life management, with PU foam showing better prospects for eco-friendly disposal and material recovery.
Ideal Applications for PVC and PU Foams
PVC foam excels in marine applications, signage, and construction due to its superior chemical resistance, durability, and lightweight properties. PU foam is ideal for insulation, cushioning, and packaging because of its excellent thermal insulation, flexibility, and impact absorption. Choosing between PVC and PU foam depends on specific requirements like environmental exposure, mechanical strength, and insulation needs.
Choosing the Right Foam: PVC or PU?
Choosing between PVC foam and PU foam depends on factors such as durability, flexibility, and application requirements. PVC foam offers higher resistance to moisture, UV exposure, and chemicals, making it ideal for outdoor and marine applications. PU foam excels in cushioning and insulation properties, suitable for automotive seating and furniture where comfort and lightweight material are priorities.
PVC foam vs PU foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com