EVA foam offers superior shock absorption and lightweight flexibility, making it ideal for footwear and sports equipment, while neoprene foam provides excellent thermal insulation and water resistance, often used in wetsuits and gloves. EVA foam is generally more cost-effective and resistant to UV damage, whereas neoprene foam offers enhanced durability in harsh chemical environments. Choosing between EVA and neoprene foam depends on the specific application requirements such as cushioning, insulation, and exposure conditions.
Table of Comparison
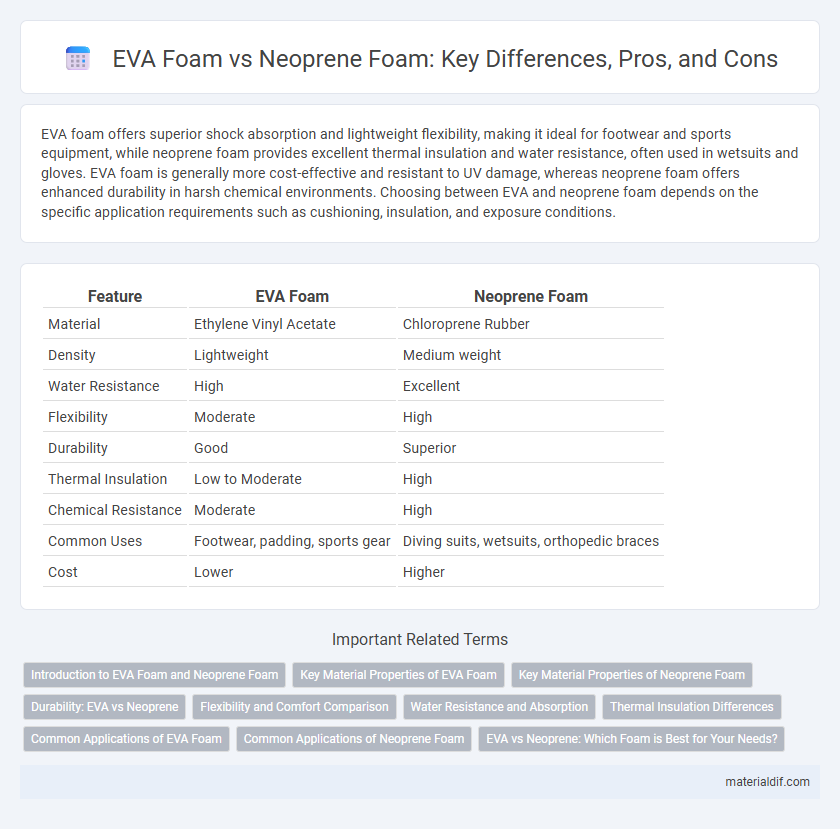
| Feature | EVA Foam | Neoprene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate | Chloroprene Rubber |
| Density | Lightweight | Medium weight |
| Water Resistance | High | Excellent |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Durability | Good | Superior |
| Thermal Insulation | Low to Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Common Uses | Footwear, padding, sports gear | Diving suits, wetsuits, orthopedic braces |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to EVA Foam and Neoprene Foam
EVA foam, or ethylene-vinyl acetate, is a lightweight, flexible material known for its shock absorption, making it ideal for footwear, sports equipment, and insulation. Neoprene foam, a synthetic rubber, excels in water resistance and thermal insulation, commonly used in wetsuits, laptop sleeves, and orthopedic braces. Both materials offer unique properties, with EVA prioritizing cushioning and comfort, while neoprene emphasizes durability and moisture protection.
Key Material Properties of EVA Foam
EVA foam exhibits exceptional flexibility, excellent cushioning, and high resistance to stress cracking, making it ideal for shock absorption and impact protection applications. Its lightweight nature combines with water resistance and chemical stability, ensuring durability in both wet and dry environments. Compared to neoprene foam, EVA offers superior tensile strength and UV resistance, enhancing its longevity in outdoor and sports equipment.
Key Material Properties of Neoprene Foam
Neoprene foam features superior chemical stability, excellent resistance to oil, heat, and weather conditions, and exceptional flexibility across a wide temperature range. Its closed-cell structure provides high water resistance and effective insulation against sound and vibration. These properties make Neoprene foam ideal for applications in wetsuits, sealing gaskets, and protective gear compared to EVA foam.
Durability: EVA vs Neoprene
EVA foam exhibits high durability due to its resistance to cracking, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for applications requiring prolonged wear. Neoprene foam offers exceptional durability in wet environments, maintaining flexibility and resistance to compression over time, especially in marine and sports gear. The choice between EVA and Neoprene foam depends on specific durability needs, with EVA excelling in dry or abrasive conditions and Neoprene outperforming in moisture-rich settings.
Flexibility and Comfort Comparison
EVA foam offers superior flexibility due to its closed-cell structure, making it lightweight and highly resilient for various applications. Neoprene foam provides enhanced comfort with its soft, cushioning texture and excellent thermal insulation properties, ideal for wetsuits and protective gear. When comparing both, EVA excels in flexibility and durability, while Neoprene stands out for softness and comfort in prolonged wear.
Water Resistance and Absorption
EVA foam offers superior water resistance due to its closed-cell structure, preventing water absorption and ensuring quick drying, making it ideal for marine and water sports applications. Neoprene foam, while also water-resistant, has a slightly higher water absorption rate because of its open-cell design, which can retain more moisture and affect buoyancy over time. Both materials provide effective water resistance, but EVA foam outperforms Neoprene in minimizing water retention and enhancing durability in wet environments.
Thermal Insulation Differences
EVA foam offers excellent thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, which effectively traps heat and resists water absorption. Neoprene foam provides superior thermal retention with its spongy texture and nitrogen gas-filled cells, making it ideal for maintaining warmth in wet conditions. Despite both foams insulating well, neoprene foam is preferred in extreme environments requiring enhanced thermal protection and flexibility.
Common Applications of EVA Foam
EVA foam is widely used in footwear, sports equipment, and packaging due to its lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbing properties. It is commonly found in insoles, yoga mats, and protective gear, providing comfort and durability in various active and everyday applications. EVA foam's resistance to cracking and UV damage makes it ideal for outdoor and recreational products.
Common Applications of Neoprene Foam
Neoprene foam is widely used in wetsuits, orthopedic braces, and industrial gaskets due to its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and thermal insulation properties. Unlike EVA foam, neoprene offers superior durability and water resistance, making it ideal for marine and medical applications. Its ability to maintain cushioning and support under varying temperatures enhances performance in sports and protective gear.
EVA vs Neoprene: Which Foam is Best for Your Needs?
EVA foam offers superior lightweight cushioning and excellent shock absorption, making it ideal for sports equipment and footwear, while neoprene foam provides better insulation, water resistance, and flexibility suited for wetsuits and protective gear. The choice between EVA and neoprene foam depends on the specific requirements for durability, thermal protection, and environmental exposure. Evaluating factors such as comfort, material resilience, and intended use ensures selecting the foam that best meets performance and longevity needs.
EVA foam vs Neoprene foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com