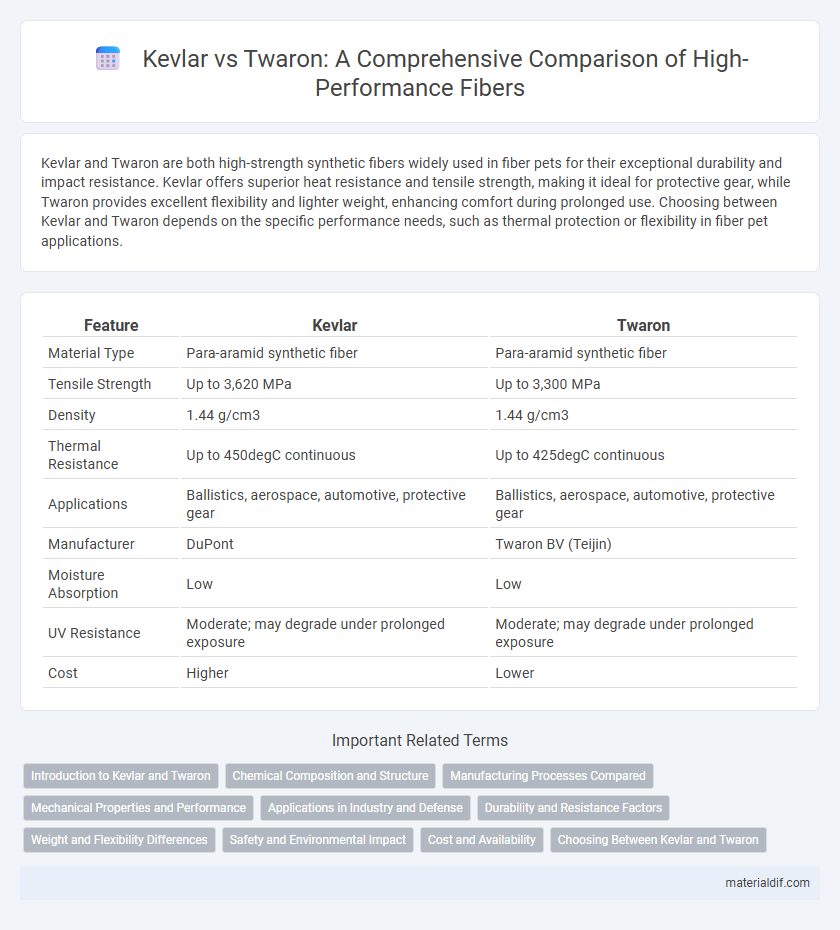
Kevlar and Twaron are both high-strength synthetic fibers widely used in fiber pets for their exceptional durability and impact resistance. Kevlar offers superior heat resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for protective gear, while Twaron provides excellent flexibility and lighter weight, enhancing comfort during prolonged use. Choosing between Kevlar and Twaron depends on the specific performance needs, such as thermal protection or flexibility in fiber pet applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Kevlar | Twaron |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Para-aramid synthetic fiber | Para-aramid synthetic fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3,620 MPa | Up to 3,300 MPa |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 450degC continuous | Up to 425degC continuous |
| Applications | Ballistics, aerospace, automotive, protective gear | Ballistics, aerospace, automotive, protective gear |
| Manufacturer | DuPont | Twaron BV (Teijin) |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Low |
| UV Resistance | Moderate; may degrade under prolonged exposure | Moderate; may degrade under prolonged exposure |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Kevlar and Twaron
Kevlar and Twaron are high-performance aramid fibers known for their exceptional strength and heat resistance, widely used in ballistic protection, aerospace, and industrial applications. Kevlar, developed by DuPont in the 1960s, features a para-aramid structure that provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance. Twaron, produced by Teijin Aramid, offers similar molecular composition and mechanical properties, with slight variations in fiber processing that influence durability and flexibility.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Kevlar is composed of poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide, featuring rigid rod-like polymer chains linked by hydrogen bonds, which contribute to its high tensile strength and thermal stability. Twaron, a para-aramid fiber similar to Kevlar, shares a comparable backbone of repeated aromatic amide units but distinguishes itself through variations in molecular weight and processing that enhance flexibility and impact resistance. Both fibers exhibit highly crystalline structures with aligned polymer chains, but subtle differences in chemical formulation affect their mechanical properties and suitability for applications like ballistic protection and composite reinforcement.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Kevlar is produced through a polycondensation process involving para-aramid fibers synthesized from the polymerization of para-phenylene diamine and terephthaloyl chloride, whereas Twaron is manufactured using a similar polycondensation method but with proprietary variations in polymerization and spinning techniques that influence fiber properties. Both fibers undergo spinning phases; Kevlar utilizes wet spinning to create water-soluble polymer solutions, while Twaron employs a more advanced dry-jet wet spinning process, enhancing fiber strength and uniformity. The differences in manufacturing processes result in distinct mechanical performances, with Twaron often exhibiting higher tensile strength and thermal stability due to optimized fiber orientation and molecular alignment.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Kevlar and Twaron, both aramid fibers, exhibit high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance crucial for protective applications; Kevlar typically offers superior tensile strength reaching around 3,620 MPa, while Twaron provides comparable performance with enhanced thermal stability and better resistance to UV degradation. Twaron's lower elongation at break, approximately 2.4%, contributes to its higher modulus of elasticity compared to Kevlar, making it preferred in applications requiring dimensional stability under stress. Both fibers demonstrate outstanding energy absorption capabilities, but Kevlar's slightly higher toughness gives it an edge in ballistic protection and high-impact environments.
Applications in Industry and Defense
Kevlar and Twaron are high-performance aramid fibers extensively used in industry and defense for ballistic protection and reinforcement applications. Kevlar's superior impact resistance and heat stability make it ideal for bulletproof vests, helmets, and composite materials in aerospace, while Twaron offers excellent tensile strength and chemical resistance, favored in ropes, cables, and automotive reinforcements. Both fibers contribute significantly to advanced protective gear, maintaining durability and lightweight characteristics critical to military and industrial safety equipment.
Durability and Resistance Factors
Kevlar and Twaron are both aramid fibers known for exceptional durability and resistance, with Kevlar offering higher tensile strength and superior abrasion resistance ideal for impact protection. Twaron provides excellent heat resistance and chemical stability, making it advantageous for environments with extreme temperatures and corrosive conditions. Both fibers exhibit outstanding cut resistance, but Kevlar generally surpasses Twaron in terms of durability under repeated stress and mechanical wear.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Kevlar and Twaron are both aramid fibers renowned for their high strength-to-weight ratio, but Kevlar typically offers a slightly lower weight, enhancing its use in lightweight applications. Twaron provides superior flexibility, making it ideal for products requiring greater bending and comfort without sacrificing durability. The choice between Kevlar and Twaron hinges on balancing weight sensitivity and flexibility needs in specialized fiber applications.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Kevlar and Twaron are both aramid fibers renowned for their high tensile strength and durability, making them essential in safety applications such as body armor and industrial protective gear. Kevlar, produced by DuPont, is widely recognized for its superior impact resistance, while Twaron, manufactured by Teijin, offers comparable strength with enhanced resistance to UV degradation and moisture. From an environmental perspective, Twaron benefits from a more eco-friendly production process with lower emissions and energy consumption, whereas Kevlar's manufacturing involves more intensive chemical treatments and higher environmental impact.
Cost and Availability
Kevlar generally offers broader availability and competitive pricing due to its longer market presence and established supply chains. Twaron, while similar in performance, tends to be priced slightly higher and may have more limited availability depending on regional suppliers. Cost efficiency and accessibility make Kevlar a preferred choice for large-scale manufacturing and budget-sensitive applications.
Choosing Between Kevlar and Twaron
Kevlar and Twaron are both aramid fibers renowned for their high tensile strength and heat resistance, commonly used in ballistic protection and composite materials. Kevlar offers superior impact resistance and is widely recognized for its extensive use in body armor, while Twaron provides better tensile strength and flexibility, making it ideal for industrial applications like ropes and cables. Selecting between Kevlar and Twaron depends on the specific performance requirements, such as flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance, with Kevlar favored in personal protection and Twaron preferred in heavy-duty industrial uses.
Kevlar vs Twaron Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com