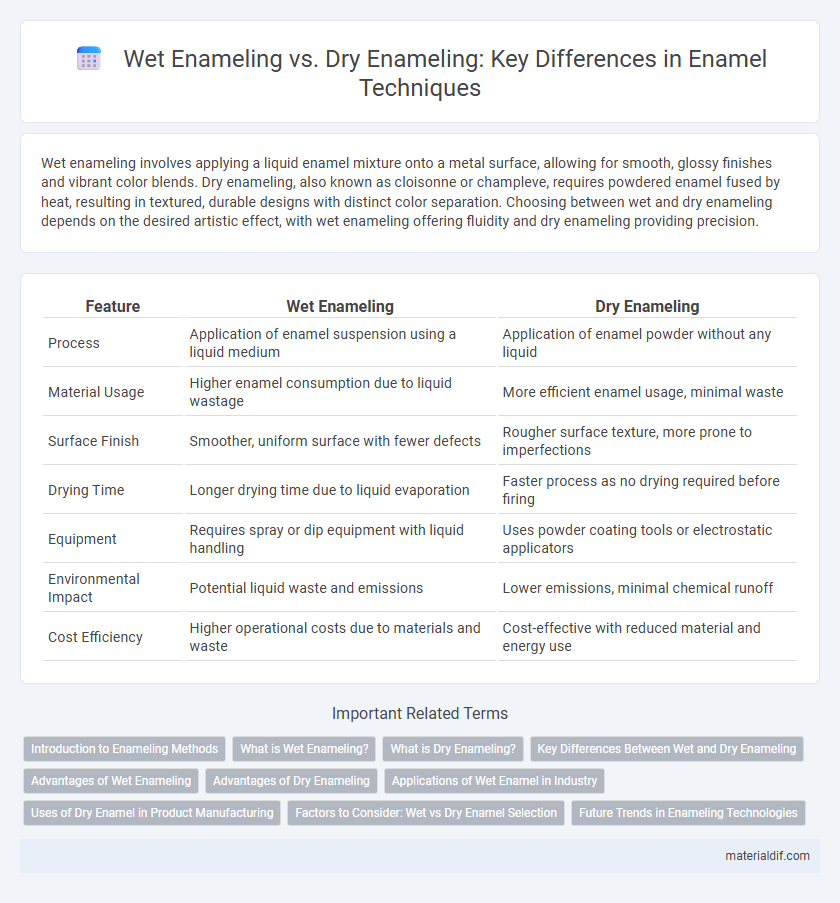
Wet enameling involves applying a liquid enamel mixture onto a metal surface, allowing for smooth, glossy finishes and vibrant color blends. Dry enameling, also known as cloisonne or champleve, requires powdered enamel fused by heat, resulting in textured, durable designs with distinct color separation. Choosing between wet and dry enameling depends on the desired artistic effect, with wet enameling offering fluidity and dry enameling providing precision.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wet Enameling | Dry Enameling |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Application of enamel suspension using a liquid medium | Application of enamel powder without any liquid |
| Material Usage | Higher enamel consumption due to liquid wastage | More efficient enamel usage, minimal waste |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, uniform surface with fewer defects | Rougher surface texture, more prone to imperfections |
| Drying Time | Longer drying time due to liquid evaporation | Faster process as no drying required before firing |
| Equipment | Requires spray or dip equipment with liquid handling | Uses powder coating tools or electrostatic applicators |
| Environmental Impact | Potential liquid waste and emissions | Lower emissions, minimal chemical runoff |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs due to materials and waste | Cost-effective with reduced material and energy use |
Introduction to Enameling Methods
Wet enameling involves applying powdered glass mixed with a liquid binder onto a metal surface, resulting in a smooth and glossy finish after firing. Dry enameling, also known as cloisonne or champleve, uses powdered glass without added liquid, applied directly to recessed areas or enclosed compartments on the metal, creating detailed and textured designs. Both methods require high-temperature kiln firing to fuse the glass particles, ensuring durability and vibrant color retention on jewelry and decorative art pieces.
What is Wet Enameling?
Wet enameling involves applying powdered glass suspended in a liquid binder onto a metal surface, which is then fired at high temperatures to create a smooth, glossy coating. This technique allows for vivid color blending and detailed designs by manipulating the liquid medium before firing. Wet enameling is favored for its ability to produce vibrant, durable finishes commonly used in jewelry and decorative art.
What is Dry Enameling?
Dry enameling, also known as powder coating, involves applying fine powdered glass particles onto a metal surface before heating it to fuse the glass into a smooth, durable coating. This technique creates a hard, glossy finish that is resistant to scratches, corrosion, and chemicals, making it ideal for industrial applications. Unlike wet enameling, dry enameling does not use liquid suspensions, resulting in less mess and faster curing times.
Key Differences Between Wet and Dry Enameling
Wet enameling involves applying powdered glass mixed with water onto a metal surface, providing smoother finishes and greater color blending flexibility. Dry enameling, also known as cloisonne, uses powdered glass without liquid, resulting in more precise, texture-rich designs ideal for detailed artwork. The primary differences lie in application methods, drying times, and the resulting surface texture and color vibrancy.
Advantages of Wet Enameling
Wet enameling offers superior color vibrancy and a smoother finish compared to dry enameling due to its liquid glass-based composition. This technique enhances adhesion on metal surfaces, reducing the risk of cracking or chipping during firing and handling. Wet enameling also allows for greater blending and layering possibilities, making it ideal for intricate designs and artistic applications.
Advantages of Dry Enameling
Dry enameling offers enhanced precision and control in the application process, resulting in smoother, more consistent coatings that resist chipping and cracking. This technique eliminates the use of liquids, reducing the risk of contamination and enabling faster curing times compared to wet enameling. Dry enameling is ideal for intricate designs and small-scale projects where detail and durability are paramount.
Applications of Wet Enamel in Industry
Wet enameling is extensively used in the automotive and cookware industries due to its ability to create smooth, durable, and chemically resistant coatings. This technique allows for precise color control and adhesion on intricate surfaces, making it ideal for decorative and protective finishes on steel and cast iron products. Its applications include appliance panels, kitchenware, and exterior automotive parts where glossy, corrosion-resistant finishes are critical.
Uses of Dry Enamel in Product Manufacturing
Dry enameling is commonly used in product manufacturing for its precise application and durability, particularly in automotive parts, household appliances, and electronic devices. This technique allows for thin, uniform coatings that resist corrosion and wear, enhancing product longevity. Its compatibility with heat-sensitive materials makes dry enamel ideal for intricate designs and functional surfaces.
Factors to Consider: Wet vs Dry Enamel Selection
When selecting between wet and dry enameling, consider the artwork's durability requirements and precision details. Wet enameling offers smoother, more vibrant colors ideal for intricate designs but requires longer drying times and careful handling to avoid imperfections. Dry enameling provides faster application with better control over texture, making it suitable for bold patterns and surfaces needing quick finishing.
Future Trends in Enameling Technologies
Future trends in enameling technologies emphasize sustainable wet enameling processes that reduce water usage and chemical waste, enhancing environmental compliance. Advancements in dry enameling focus on energy-efficient powder coatings with improved adhesion and durability for industrial applications. Integration of AI-driven precision controls is set to revolutionize quality consistency and customization in both wet and dry enameling methods.
Wet Enameling vs Dry Enameling Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com