Manual enameling offers artisans precise control over design details, enabling unique, handcrafted finishes that highlight individual craftsmanship. Automated enameling increases production efficiency and consistency, ensuring uniform coatings across large batches with reduced labor costs. Balancing manual techniques with automation can optimize quality while scaling enamel production.
Table of Comparison
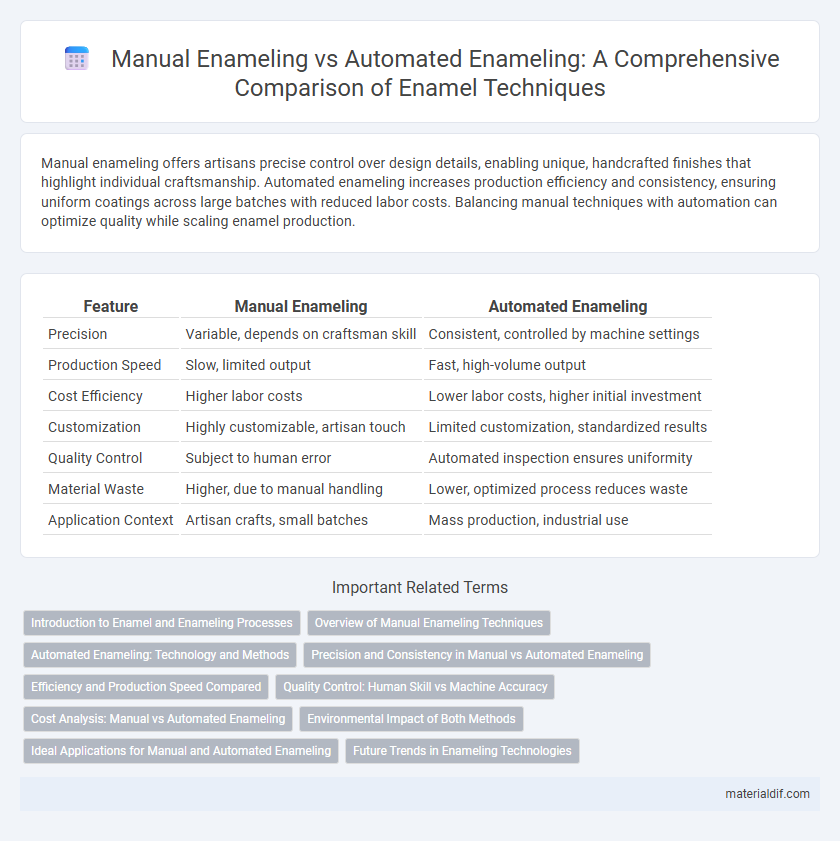
| Feature | Manual Enameling | Automated Enameling |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Variable, depends on craftsman skill | Consistent, controlled by machine settings |
| Production Speed | Slow, limited output | Fast, high-volume output |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher labor costs | Lower labor costs, higher initial investment |
| Customization | Highly customizable, artisan touch | Limited customization, standardized results |
| Quality Control | Subject to human error | Automated inspection ensures uniformity |
| Material Waste | Higher, due to manual handling | Lower, optimized process reduces waste |
| Application Context | Artisan crafts, small batches | Mass production, industrial use |
Introduction to Enamel and Enameling Processes
Manual enameling involves applying powdered glass onto metal surfaces by hand, allowing intricate designs and detailed craftsmanship essential for artisanal quality. Automated enameling uses advanced machinery to spray or dip metal parts, ensuring consistent coating thickness and higher production efficiency for industrial-scale applications. Both methods rely on controlled firing processes at temperatures between 750degC and 850degC to fuse enamel powders into a durable, glossy finish.
Overview of Manual Enameling Techniques
Manual enameling techniques involve hand application of enamel powders or liquids onto metal surfaces, allowing for intricate designs and detailed artistry in jewelry and decorative items. Common methods include cloisonne, champleve, and grisaille, each requiring skilled craftsmanship to control firing temperatures and layering for vibrant, durable finishes. This artisanal approach offers superior customization and artistic expression compared to automated enameling, which prioritizes speed and uniformity.
Automated Enameling: Technology and Methods
Automated enameling leverages advanced robotics and computer-controlled spray systems to ensure consistent coating thickness and uniform surface finish. Technologies like electrostatic deposition and robotic arms enable precise application on complex geometries, enhancing productivity and reducing material waste. Integration with real-time sensors and quality control software allows for immediate adjustments, optimizing process efficiency and product durability.
Precision and Consistency in Manual vs Automated Enameling
Manual enameling offers artisans the ability to adjust techniques in real-time, ensuring unique detailing and personalized finishes, but may result in slight variations between pieces due to human factors. Automated enameling employs precise machinery and computer-controlled processes, delivering consistent thickness, color uniformity, and repeated accuracy across large production runs. The choice between methods depends on balancing handcrafted individuality against the demand for high-volume, standardized quality in enamel work.
Efficiency and Production Speed Compared
Manual enameling offers artisans precise control and customization but is limited by slower production speed and lower efficiency, making it ideal for small batches or artistic work. Automated enameling significantly increases efficiency and production speed by using machines that apply consistent coatings quickly, suitable for large-scale manufacturing. The choice depends on balancing the detail and craftsmanship of manual methods against the volume and uniformity achievable through automation.
Quality Control: Human Skill vs Machine Accuracy
Manual enameling relies heavily on skilled artisans to apply precise layers of enamel, allowing for intricate detailing and real-time adjustments that enhance artistic quality. Automated enameling leverages machine accuracy and consistency to produce uniform coatings, reducing the risk of human error and increasing throughput while maintaining consistent quality standards. Quality control in manual processes is subjective and dependent on craftsmanship, whereas automated systems utilize precise calibration and sensors to ensure exact enamel thickness and curing conditions.
Cost Analysis: Manual vs Automated Enameling
Manual enameling involves higher labor costs due to skilled craftsmanship and longer production times, making it less cost-effective for large volume orders. Automated enameling significantly reduces labor expenses and increases throughput by utilizing machinery, leading to lower per-unit costs and faster production cycles. Initial investment in automated equipment can be high, but long-term savings and scalability make it ideal for industrial applications.
Environmental Impact of Both Methods
Manual enameling generates lower energy consumption and reduces emissions due to its small-scale processes, but it often involves higher waste of raw materials. Automated enameling optimizes resource use with precise material application and consistent kiln temperatures, significantly minimizing environmental pollution and energy waste. Both methods impact the environment differently, with automation trending toward sustainability through increased efficiency and controlled emissions.
Ideal Applications for Manual and Automated Enameling
Manual enameling is ideal for intricate, custom designs and small batch productions where precision and unique artistry are paramount. Automated enameling suits high-volume manufacturing environments, delivering consistent quality and efficiency for large-scale, repetitive enamel applications. Industries such as jewelry or specialized art pieces benefit from manual techniques, while appliance coatings and automotive parts favor automated processes for scalability and uniformity.
Future Trends in Enameling Technologies
Manual enameling offers artisanal precision and customization, while automated enameling delivers enhanced speed and consistency essential for high-volume production. Future trends emphasize integration of AI-driven robotics and laser technology to achieve superior surface uniformity and reduced material waste. Advances in nanocoatings and smart enamels promise increased durability and responsive color changes, redefining enamel applications in industrial and decorative sectors.
Manual enameling vs Automated enameling Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com