Ground coat enamel serves as the initial layer that provides adhesion and corrosion resistance on metal surfaces, ensuring a strong foundation for subsequent coatings. Cover coat enamel is applied over the ground coat to deliver the final color, gloss, and protective finish, enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal. The combination of both types ensures optimal performance, with the ground coat promoting bonding and the cover coat offering visual and protective qualities.
Table of Comparison
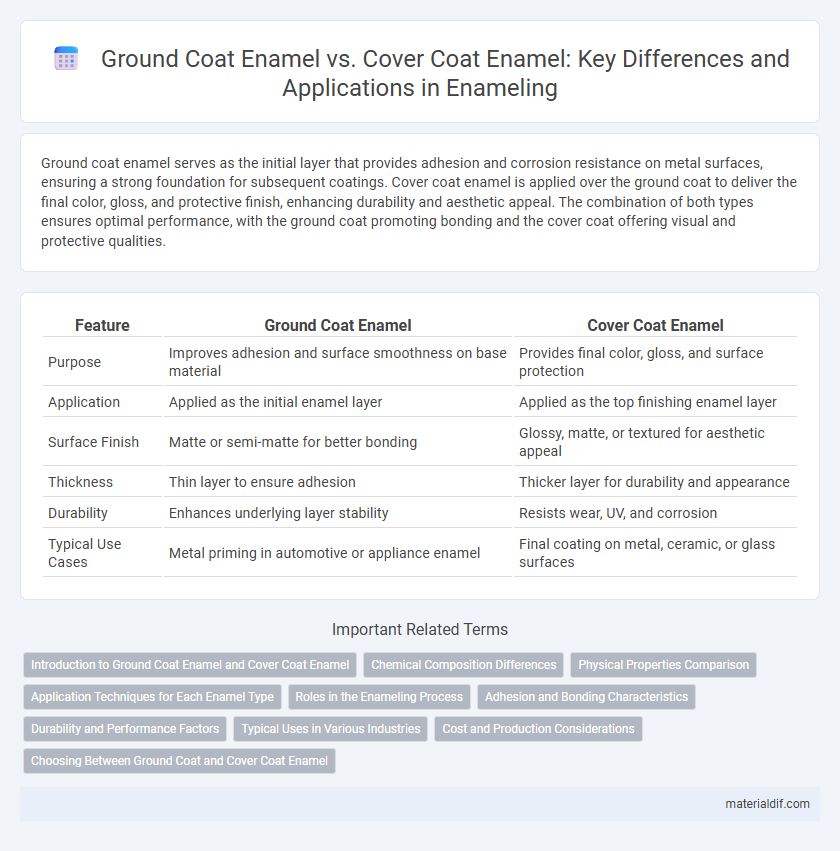
| Feature | Ground Coat Enamel | Cover Coat Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Improves adhesion and surface smoothness on base material | Provides final color, gloss, and surface protection |
| Application | Applied as the initial enamel layer | Applied as the top finishing enamel layer |
| Surface Finish | Matte or semi-matte for better bonding | Glossy, matte, or textured for aesthetic appeal |
| Thickness | Thin layer to ensure adhesion | Thicker layer for durability and appearance |
| Durability | Enhances underlying layer stability | Resists wear, UV, and corrosion |
| Typical Use Cases | Metal priming in automotive or appliance enamel | Final coating on metal, ceramic, or glass surfaces |
Introduction to Ground Coat Enamel and Cover Coat Enamel
Ground coat enamel serves as the foundational layer, designed to improve adhesion and provide a smooth surface for subsequent enamel layers. Cover coat enamel acts as the final decorative and protective layer, offering enhanced color, gloss, and resistance to wear and environmental factors. Both layers work synergistically to ensure durability and aesthetic appeal in coated surfaces.
Chemical Composition Differences
Ground coat enamel typically contains higher concentrations of alumina and silica components, providing strong adhesion and thermal stability. Cover coat enamel has a richer content of fluxing agents like lead or boron oxides, which enhance surface gloss and color uniformity. The chemical composition differences result in distinct functional roles: ground coats ensure bonding and durability, while cover coats optimize aesthetics and smoothness.
Physical Properties Comparison
Ground coat enamel exhibits higher adhesion and better corrosion resistance due to its fine particle size and optimized chemical composition, making it ideal for the initial layering on metal substrates. Cover coat enamel demonstrates superior gloss, color retention, and weather resistance, attributed to its smooth texture and enhanced pigment dispersion. Physical properties such as hardness and impact resistance vary, with cover coat enamel typically offering improved surface durability while ground coat enamel ensures robust foundational protection.
Application Techniques for Each Enamel Type
Ground coat enamel is applied as a base layer using spray or dip methods to ensure strong adhesion and surface smoothness, essential for preventing metal oxidation. Cover coat enamel is typically applied by spraying or brushing over the ground coat to provide a durable, glossy finish with enhanced color and resistance to wear. Precise temperature control during firing is critical for both coats to optimize enamel fusion and durability.
Roles in the Enameling Process
Ground coat enamel serves as the foundational layer in the enameling process, providing a smooth, adhesive surface that enhances the bond between the metal substrate and subsequent enamel layers. Cover coat enamel functions as the final, protective, and decorative layer, offering color, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Both coatings play critical roles in ensuring the enamel's overall performance, longevity, and aesthetic appeal.
Adhesion and Bonding Characteristics
Ground coat enamel provides superior adhesion by creating a strong bond with the metal substrate, enhancing durability and preventing delamination. Cover coat enamel, while offering excellent aesthetic properties and corrosion resistance, primarily bonds to the ground coat layer rather than directly to the base material. The combination of ground coat enamel's robust bonding characteristics and cover coat enamel's protective surface ensures a long-lasting and resilient enamel finish.
Durability and Performance Factors
Ground coat enamel provides superior adhesion and corrosion resistance, forming a durable base layer that enhances the longevity of the final coating system. Cover coat enamel offers enhanced aesthetic appeal and weather resistance, protecting against UV degradation and chemical exposure for sustained performance. The combined use of ground coat and cover coat enamels ensures optimal durability by balancing structural integrity with surface protection in demanding environments.
Typical Uses in Various Industries
Ground coat enamel is primarily used as a base layer to enhance adhesion and corrosion resistance in industries like automotive manufacturing and appliance production, providing a durable foundation. Cover coat enamel serves as the final decorative and protective finish in sectors such as architectural metalwork and consumer electronics, offering UV resistance and aesthetic appeal. Both types are essential in industrial painting processes to ensure long-lasting performance and surface quality.
Cost and Production Considerations
Ground coat enamel typically costs less than cover coat enamel due to simpler formulations and lower pigment density, making it more economical for base layer applications. Production considerations highlight that ground coat enamel requires shorter curing times and less precise application, which streamlines manufacturing and reduces labor expenses. Cover coat enamel demands higher-quality pigments and more controlled application processes, increasing both material and production costs for enhanced finish durability and aesthetics.
Choosing Between Ground Coat and Cover Coat Enamel
Ground coat enamel provides a smooth, adherent base layer that enhances the durability and corrosion resistance of metal surfaces, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring strong bonding. Cover coat enamel offers superior color vibrancy and surface finish, improving aesthetic appeal and providing additional protection against environmental factors. Selecting between ground coat and cover coat enamel depends on whether the priority is foundational adhesion and protection or enhanced appearance and final surface quality.
Ground coat enamel vs Cover coat enamel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com