Enamel coating provides a hard, glossy finish that enhances durability and resistance to scratches and corrosion, making it ideal for household appliances and metal surfaces. Ceramic coating offers superior protection with its advanced nanotechnology, creating a hydrophobic layer that repels water, dirt, and chemicals while maintaining a high level of heat resistance. Choosing between enamel and ceramic coatings depends on the desired toughness, longevity, and specific application needs.
Table of Comparison
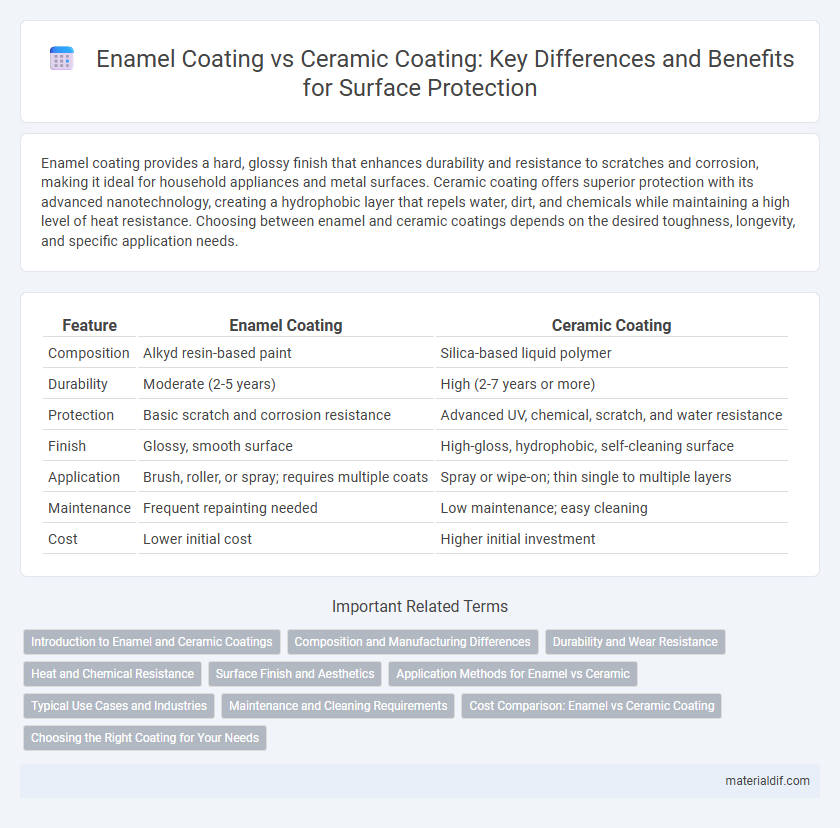
| Feature | Enamel Coating | Ceramic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alkyd resin-based paint | Silica-based liquid polymer |
| Durability | Moderate (2-5 years) | High (2-7 years or more) |
| Protection | Basic scratch and corrosion resistance | Advanced UV, chemical, scratch, and water resistance |
| Finish | Glossy, smooth surface | High-gloss, hydrophobic, self-cleaning surface |
| Application | Brush, roller, or spray; requires multiple coats | Spray or wipe-on; thin single to multiple layers |
| Maintenance | Frequent repainting needed | Low maintenance; easy cleaning |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial investment |
Introduction to Enamel and Ceramic Coatings
Enamel coating consists of a hard, glossy finish primarily made from powdered glass fused onto metal, providing durable protection and aesthetic appeal. Ceramic coating uses silica-based polymers to create a thin, transparent layer that offers superior scratch resistance and hydrophobic properties. Both coatings enhance surface durability, but ceramic coatings excel in long-term protection and resistance to environmental damage.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Enamel coatings consist of a glass-like substance formed by fusing powdered glass to a substrate through high-temperature firing, creating a hard, durable surface with excellent resistance to corrosion and chemicals. Ceramic coatings are composed mainly of silicon dioxide (SiO2) and other inorganic materials, applied as a liquid and cured into a thin, protective layer with heat or UV light, offering superior hardness and hydrophobic properties. The manufacturing of enamel involves melting and bonding glass particles, whereas ceramic coatings rely on advanced chemical formulations and curing processes for enhanced surface protection.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Enamel coating offers excellent durability with a hard, glossy finish resistant to scratches and heat, making it ideal for long-term protection on metal surfaces. Ceramic coating provides superior wear resistance due to its nano-ceramic particles, delivering enhanced hardness and chemical stability that effectively guards against abrasion and corrosion. Both coatings extend the lifespan of surfaces, but ceramic coatings generally outperform enamel in resisting wear under high-stress or harsh environmental conditions.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
Enamel coating offers excellent heat resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 1,200degF, making it ideal for cookware and industrial applications exposed to high heat. Ceramic coating provides superior chemical resistance against acidic and alkaline substances, ensuring durability in harsh chemical environments. Both coatings enhance surface protection, but enamel excels in high-heat scenarios while ceramic outperforms in chemical resistance.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
Enamel coating offers a glossy and smooth surface finish that enhances color vibrancy and provides a classic, polished look, making it ideal for decorative applications. Ceramic coating provides a highly durable and scratch-resistant surface with a sleek, often matte or semi-gloss appearance, which maintains aesthetic appeal over time. The choice between enamel and ceramic coating depends on desired surface texture and long-term finish preservation.
Application Methods for Enamel vs Ceramic
Enamel coating is typically applied through dipping, spraying, or brushing, offering a thick, durable layer that bonds well to metal surfaces after proper surface preparation. Ceramic coating usually involves spray or wipe-on application methods that create a thin, highly resistant layer through chemical bonding at a molecular level, providing superior heat and scratch resistance. The application of enamel requires curing at high temperatures, while ceramic coatings often cure at lower temperatures or air-dry, influencing the overall durability and finish characteristics.
Typical Use Cases and Industries
Enamel coating is widely used in industrial applications requiring strong chemical and heat resistance, such as cookware, automotive parts, and electrical appliances, providing durable protection and an attractive finish. Ceramic coating excels in automotive and aerospace industries where high-temperature tolerance, corrosion resistance, and enhanced surface hardness are critical, often applied on engine components and high-performance vehicles. Enamel coatings are preferred for indoor equipment and household items, while ceramic coatings dominate in demanding environments requiring advanced wear resistance and thermal insulation.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Enamel coating requires regular cleaning with gentle detergents and periodic polishing to maintain its glossy finish and prevent chipping, while ceramic coating offers a more durable, hydrophobic surface that resists dirt, stains, and minor scratches with minimal maintenance. Enamel surfaces may deteriorate faster under harsh cleaning agents, whereas ceramic coatings provide long-lasting protection and easier cleaning through their self-cleaning properties. Choosing ceramic coating reduces the frequency and effort of cleaning, making it ideal for maintaining a pristine appearance with less intensive upkeep.
Cost Comparison: Enamel vs Ceramic Coating
Enamel coating generally costs less upfront, averaging between $20 to $50 per square foot, while ceramic coating prices range from $100 to $150 per square foot due to advanced chemical composition and durability. Enamel coating requires more frequent reapplication, increasing long-term maintenance expenses compared to the highly durable and scratch-resistant ceramic coatings that can last up to 5 years or more. Choosing between enamel and ceramic coatings depends on budget constraints and desired longevity, with ceramic coating offering higher initial investment but superior performance.
Choosing the Right Coating for Your Needs
Enamel coating offers a durable, glossy finish ideal for metal surfaces exposed to high heat and frequent wear, while ceramic coating provides superior scratch resistance and hydrophobic properties, making it perfect for automotive and outdoor equipment. Choosing the right coating depends on factors like the surface material, exposure conditions, and desired longevity; enamel suits household appliances and cookware, whereas ceramic excels in protecting vehicle exteriors and machinery. Understanding these differences ensures optimal performance and durability tailored to specific needs.
Enamel Coating vs Ceramic Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com