Epoxy enamel offers excellent adhesion and chemical resistance, making it ideal for protective coatings on metals exposed to moisture and harsh environments. Ceramic enamel provides superior heat resistance and durability, commonly used in high-temperature applications such as cookware and industrial equipment. Choosing between epoxy and ceramic enamel depends on the required thermal stability and exposure conditions of the coated surface.
Table of Comparison
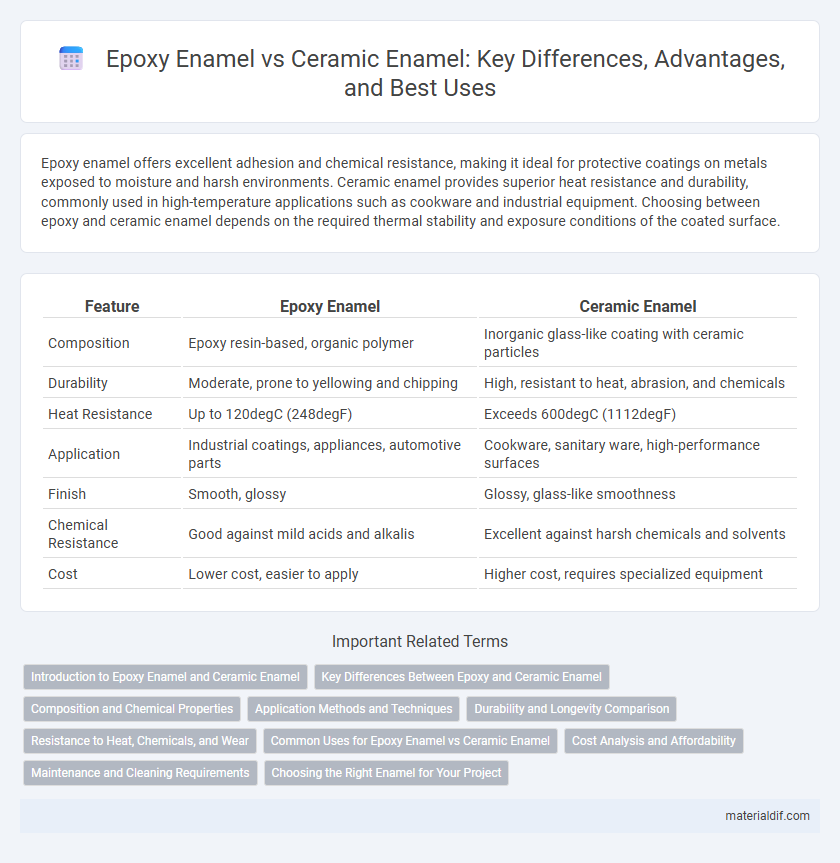
| Feature | Epoxy Enamel | Ceramic Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Epoxy resin-based, organic polymer | Inorganic glass-like coating with ceramic particles |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to yellowing and chipping | High, resistant to heat, abrasion, and chemicals |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 120degC (248degF) | Exceeds 600degC (1112degF) |
| Application | Industrial coatings, appliances, automotive parts | Cookware, sanitary ware, high-performance surfaces |
| Finish | Smooth, glossy | Glossy, glass-like smoothness |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against mild acids and alkalis | Excellent against harsh chemicals and solvents |
| Cost | Lower cost, easier to apply | Higher cost, requires specialized equipment |
Introduction to Epoxy Enamel and Ceramic Enamel
Epoxy enamel is a durable coating composed of epoxy resins known for excellent adhesion and chemical resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications and metal protection. Ceramic enamel, derived from inorganic glassy materials fused at high temperatures, offers superior heat resistance and durability, commonly used for cookware and decorative finishes. Both types of enamel provide protective and aesthetic benefits but differ significantly in composition, thermal properties, and typical use cases.
Key Differences Between Epoxy and Ceramic Enamel
Epoxy enamel offers excellent adhesion and chemical resistance, making it ideal for protective coatings on metal surfaces, while ceramic enamel provides superior heat resistance and durability, suitable for high-temperature applications like cookware and industrial equipment. Epoxy enamel typically cures at lower temperatures and forms a flexible, glossy finish, whereas ceramic enamel requires higher firing temperatures and results in a hard, glass-like surface. The main differences lie in their chemical composition, temperature tolerance, and typical use cases, with epoxy favoring corrosion resistance and ceramic emphasizing thermal stability.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Epoxy enamel consists of a polymer matrix formed from epoxy resins, offering strong adhesion and chemical resistance, particularly against moisture and alkalis. Ceramic enamel is composed of powdered glass fused to the metal substrate at high temperatures, resulting in a hard, glossy surface highly resistant to heat, corrosion, and chemical attack. The chemical stability of ceramic enamel surpasses epoxy enamel, which may degrade under prolonged UV exposure and high temperatures.
Application Methods and Techniques
Epoxy enamel coatings are typically applied through spray or brush methods, providing excellent adhesion and chemical resistance ideal for industrial equipment and machinery surfaces. Ceramic enamel requires kiln firing techniques, where glassy coatings are fused onto metal substrates, offering superior heat resistance and durability for cookware and decorative items. Understanding these application differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate enamel type based on performance requirements and substrate compatibility.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Epoxy enamel features a strong chemical resistance and excellent adhesion, making it highly durable for industrial applications but susceptible to UV damage over time. Ceramic enamel offers superior hardness and exceptional resistance to heat and abrasion, resulting in significantly longer longevity, especially in harsh environmental conditions. Comparing the two, ceramic enamel outperforms epoxy enamel in maintaining aesthetic quality and structural integrity after prolonged exposure to extreme wear.
Resistance to Heat, Chemicals, and Wear
Epoxy enamel offers excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for environments exposed to solvents and corrosive substances, though its heat resistance typically maxes out around 150degC. Ceramic enamel outperforms epoxy in heat resistance, withstanding temperatures exceeding 800degC while maintaining structural integrity and resistance to thermal shock. Both coatings provide strong wear resistance, but ceramic enamel's hardness and durability excel in high-friction or abrasive applications.
Common Uses for Epoxy Enamel vs Ceramic Enamel
Epoxy enamel is commonly used for industrial coatings, metal surfaces, and protective finishes due to its strong adhesion, chemical resistance, and durability. Ceramic enamel is typically applied to cookware, decorative objects, and architectural elements for its high heat resistance, glass-like finish, and corrosion protection. Both enamels provide robust surface protection but cater to distinct functional demands in manufacturing and design.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Epoxy enamel offers a cost-effective solution with lower initial expenses and faster application, making it ideal for budget-conscious projects and indoor use where chemical resistance is moderate. Ceramic enamel, while more expensive due to its superior durability, high-temperature resistance, and long lifespan, provides greater value for industrial applications requiring extreme wear and heat protection. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and longevity, reveals epoxy enamel as affordable short-term, while ceramic enamel often delivers cost savings in demanding environments over time.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Epoxy enamel requires frequent maintenance to prevent chipping and discoloration, and cleaning should be done with mild detergents to avoid surface damage. Ceramic enamel offers superior resistance to scratches, stains, and chemicals, making it easier to clean and maintain with minimal effort over time. Both coatings benefit from regular wiping, but ceramic enamel's durability reduces the need for intensive upkeep compared to epoxy enamel.
Choosing the Right Enamel for Your Project
Epoxy enamel offers superior chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring strong protective coatings. Ceramic enamel provides excellent heat resistance and a smooth, glossy finish, perfect for cookware and decorative surfaces exposed to high temperatures. Choosing the right enamel depends on the project's environment, desired finish, and performance requirements, with epoxy enamel suited for harsh conditions and ceramic enamel optimal for thermal and aesthetic needs.
Epoxy Enamel vs Ceramic Enamel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com