Direct-on enamel is applied directly onto the metal surface, providing a smooth, durable finish with strong adhesion, ideal for decorative and protective purposes. Ground coat enamel serves as an intermediary layer, enhancing the bond between the metal substrate and the subsequent enamel layers, ensuring better durability and resistance to thermal stress. Choosing between direct-on enamel and ground coat enamel depends on the desired finish quality, durability requirements, and the type of metal being coated.
Table of Comparison
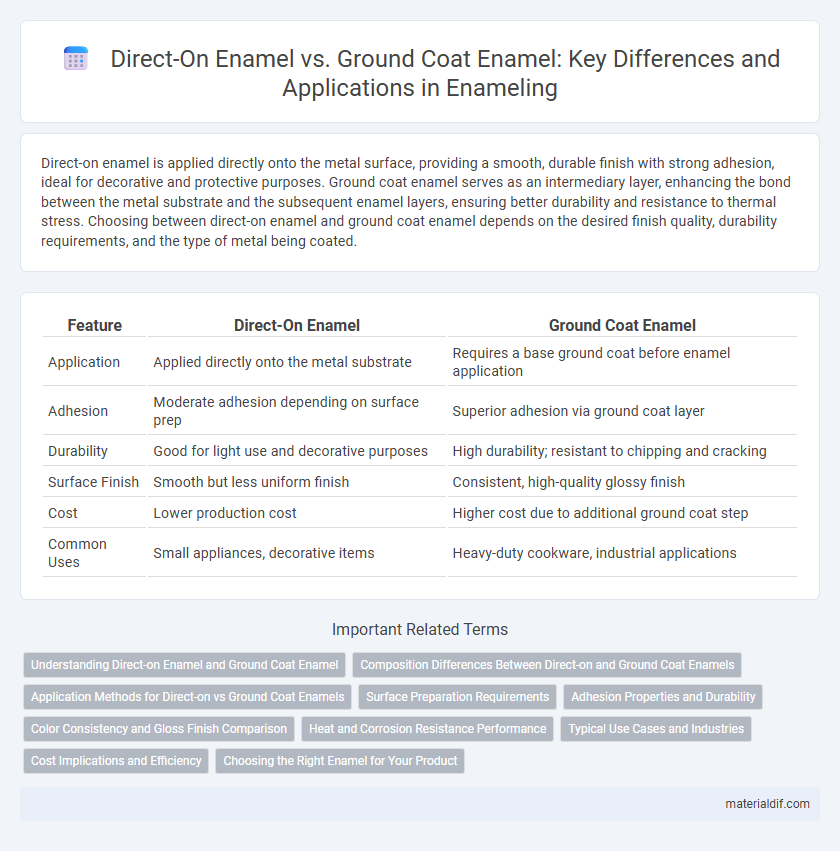
| Feature | Direct-On Enamel | Ground Coat Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Applied directly onto the metal substrate | Requires a base ground coat before enamel application |
| Adhesion | Moderate adhesion depending on surface prep | Superior adhesion via ground coat layer |
| Durability | Good for light use and decorative purposes | High durability; resistant to chipping and cracking |
| Surface Finish | Smooth but less uniform finish | Consistent, high-quality glossy finish |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher cost due to additional ground coat step |
| Common Uses | Small appliances, decorative items | Heavy-duty cookware, industrial applications |
Understanding Direct-on Enamel and Ground Coat Enamel
Direct-on enamel is applied directly onto metal surfaces, providing a durable and glossy finish while enhancing corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Ground coat enamel acts as an intermediate layer between the metal substrate and the decorative enamel, improving adhesion, thermal compatibility, and overall durability of the final coating. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the appropriate enamel type based on the specific requirements of durability, appearance, and substrate compatibility in industrial applications.
Composition Differences Between Direct-on and Ground Coat Enamels
Direct-on enamels typically contain higher concentrations of fluxes such as borax and soda to promote fusion directly onto metal substrates without an intermediary layer. Ground coat enamels incorporate a base layer rich in silica and alumina to enhance adhesion and thermal compatibility between the metal and the overlying enamel layer. The compositional variance primarily revolves around the balance of fluxes and refractory oxides designed to optimize bonding strength and thermal expansion properties.
Application Methods for Direct-on vs Ground Coat Enamels
Direct-on enamels are applied directly onto metal surfaces, providing a uniform, durable finish ideal for intricate designs or thin coatings. Ground coat enamels require a preliminary base layer to improve adhesion and surface smoothness, enhancing the enamel's durability and gloss. Application methods for direct-on enamels often involve spraying or dipping, while ground coat enamels typically involve brushing or baking after base layer preparation.
Surface Preparation Requirements
Direct-on enamel requires a meticulously cleaned and smooth substrate to ensure optimal adhesion and durability, often involving degreasing and light abrasion. Ground coat enamel necessitates applying a specialized base layer that acts as a bonding intermediary, improving enamel adherence on less ideal surfaces. Proper surface preparation for direct-on enamel minimizes defects, whereas ground coat enamel allows for enhanced compatibility with varied materials.
Adhesion Properties and Durability
Direct-on enamel provides strong adhesion through a chemical bond formed directly with the metal substrate, enhancing durability by resisting chipping and cracking under mechanical stress. Ground coat enamel involves an intermediate layer that improves surface uniformity, promoting better adhesion and reducing thermal mismatch, which results in superior long-term durability in harsh environments. Both enamel types exhibit distinct advantages in adhesion properties, with ground coat enamel offering enhanced protection against thermal and mechanical fatigue.
Color Consistency and Gloss Finish Comparison
Direct-on enamel offers superior color consistency by applying pigment directly to the substrate, ensuring vibrant and uniform hues without the risk of the underlying material altering the shade. Ground coat enamel provides a smoother gloss finish due to its intermediary layer, which enhances surface evenness and reflects light more evenly than direct application. Comparing both, direct-on enamel excels in maintaining precise color fidelity while ground coat enamel achieves a higher, more durable gloss finish.
Heat and Corrosion Resistance Performance
Direct-on enamel provides superior heat resistance due to its strong adhesion and uniform layer applied directly on metal substrates, effectively withstanding temperatures up to 900degC. Ground coat enamel, typically used as an intermediate layer beneath decorative enamels, offers enhanced corrosion resistance by forming a robust barrier that prevents metal oxidation and chemical degradation. Both coatings improve metal durability, but direct-on enamel excels in high-temperature environments, while ground coat enamel is optimized for anti-corrosive protection.
Typical Use Cases and Industries
Direct-on enamel is commonly used in cookware and sanitaryware industries due to its excellent adhesion and durability on metal substrates without the need for a base layer. Ground coat enamel is preferred in appliance manufacturing and automotive parts where a smooth, protective base layer enhances corrosion resistance and facilitates the application of decorative topcoats. Both types are integral in producing long-lasting, aesthetic finishes tailored to specific functional and environmental demands.
Cost Implications and Efficiency
Direct-on enamel offers lower upfront material costs due to its simplified application process, reducing labor and time expenses. Ground coat enamel requires an additional preparatory layer, increasing production complexity and overall costs but often enhancing durability and finish quality. Efficiency gains with direct-on enamel manifest in faster turnaround times, while ground coat enamel investments may lead to longer product lifespan, balancing initial cost differences.
Choosing the Right Enamel for Your Product
Direct-on enamel offers superior adhesion and vibrant color retention by applying enamel directly onto metal surfaces, making it ideal for products requiring durable finishes and detailed designs. Ground coat enamel provides a smooth, consistent base layer that enhances corrosion resistance and ensures the top enamel layer adheres uniformly, benefiting items exposed to harsh environments. Selecting the right enamel depends on the product's intended use, required durability, and exposure conditions to optimize both aesthetics and longevity.
Direct-on enamel vs Ground coat enamel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com