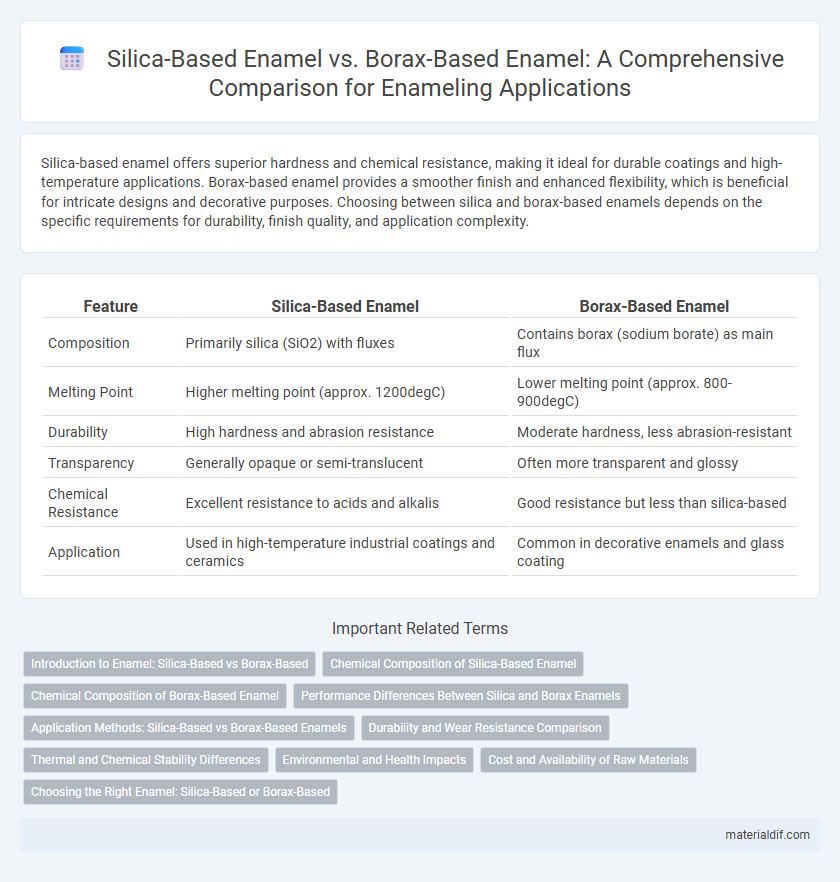
Silica-based enamel offers superior hardness and chemical resistance, making it ideal for durable coatings and high-temperature applications. Borax-based enamel provides a smoother finish and enhanced flexibility, which is beneficial for intricate designs and decorative purposes. Choosing between silica and borax-based enamels depends on the specific requirements for durability, finish quality, and application complexity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Silica-Based Enamel | Borax-Based Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Primarily silica (SiO2) with fluxes | Contains borax (sodium borate) as main flux |
| Melting Point | Higher melting point (approx. 1200degC) | Lower melting point (approx. 800-900degC) |
| Durability | High hardness and abrasion resistance | Moderate hardness, less abrasion-resistant |
| Transparency | Generally opaque or semi-translucent | Often more transparent and glossy |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids and alkalis | Good resistance but less than silica-based |
| Application | Used in high-temperature industrial coatings and ceramics | Common in decorative enamels and glass coating |
Introduction to Enamel: Silica-Based vs Borax-Based
Silica-based enamels feature a high silica content that enhances thermal resistance and durability, making them ideal for applications requiring strong protective coatings. Borax-based enamels incorporate borax as a flux, which lowers the melting point and improves the enamel's adhesion to metal substrates. The choice between silica-based and borax-based enamels depends on specific performance requirements such as temperature tolerance, finish quality, and substrate compatibility.
Chemical Composition of Silica-Based Enamel
Silica-based enamel primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2), which forms a glassy matrix that provides high hardness and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal shock. The chemical composition typically includes fluxes such as sodium oxide (Na2O) or potassium oxide (K2O) to lower the melting point and facilitate fusion with the substrate. Compared to borax-based enamel, the silica content enhances durability and adhesion on metal surfaces, making it ideal for industrial and decorative coatings.
Chemical Composition of Borax-Based Enamel
Borax-based enamel primarily contains sodium borate compounds that act as fluxes, lowering the melting temperature and enhancing the glassy matrix formation. Its chemical composition typically includes boron oxide (B2O3), which improves enamel durability and resistance to thermal shock compared to silica-based enamel. The borax flux facilitates better adherence to metal surfaces and creates a smoother, more translucent finish.
Performance Differences Between Silica and Borax Enamels
Silica-based enamels offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to borax-based enamels, making them ideal for high-temperature applications and exposure to harsh environments. Borax-based enamels typically provide better adhesion and smoother finishes but may degrade faster under cyclic thermal stress. The choice between silica and borax enamels depends on balancing durability requirements with aesthetic considerations for optimal performance.
Application Methods: Silica-Based vs Borax-Based Enamels
Silica-based enamels require firing at higher temperatures, typically between 1400degC and 1600degC, making them ideal for applications on ceramics and high-temperature metals. Borax-based enamels, melting at lower temperatures around 900degC to 1100degC, are commonly used for coating low-temperature metals, such as steel and iron, with techniques including wet spraying or dipping. Choosing between silica-based and borax-based enamels depends on substrate material and desired firing temperature, influencing application methods and final enamel durability.
Durability and Wear Resistance Comparison
Silica-based enamel exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to borax-based enamel due to its higher hardness and better thermal stability. Its refined microstructure allows for enhanced resistance to abrasion and long-term mechanical stress. Borax-based enamel tends to be less resilient under heavy wear conditions, making silica-based formulations preferable for applications requiring robust surface protection.
Thermal and Chemical Stability Differences
Silica-based enamel exhibits superior thermal stability with higher melting points, making it more resistant to high-temperature environments compared to borax-based enamel. Chemically, silica-based enamel demonstrates enhanced resistance to acids and alkalis, reducing corrosion and wear over time. Borax-based enamel tends to be more prone to thermal cracking and chemical degradation due to its lower thermal resistance and solubility in various chemicals.
Environmental and Health Impacts
Silica-based enamel formulations typically exhibit lower toxicity and reduced environmental impact compared to borax-based enamels, as silica is a naturally abundant and inert material. Borax, while effective as a flux, can release boron compounds that pose potential health risks such as respiratory irritation and have been linked to reproductive toxicity. Choosing silica-based enamels minimizes hazardous emissions and aligns better with sustainable manufacturing practices in the ceramics and glass industries.
Cost and Availability of Raw Materials
Silica-based enamel generally offers lower raw material costs due to the widespread availability of silica sand, a common and abundant mineral. Borax-based enamel relies on borax, which tends to be less abundant and more expensive, impacting overall production expenses. The choice between these enamels often depends on budget constraints and the regional accessibility of raw materials.
Choosing the Right Enamel: Silica-Based or Borax-Based
Silica-based enamel offers superior hardness and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring strong abrasion resistance and thermal stability. Borax-based enamel provides better flow and melt characteristics, resulting in smoother finishes and enhanced adhesion on metals with complex shapes. Selecting the right enamel depends on the specific requirements of the project, such as desired surface hardness, thermal properties, and application technique.
Silica-based enamel vs borax-based enamel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com