Enamel steel cookware offers a lightweight and affordable option with excellent heat conduction, making it ideal for quick cooking tasks. Porcelain-enameled cast iron, on the other hand, provides superior heat retention and even cooking, perfect for slow simmering and roasting. Both types feature a durable, non-reactive enamel coating that resists rust and adds vibrant color options.
Table of Comparison
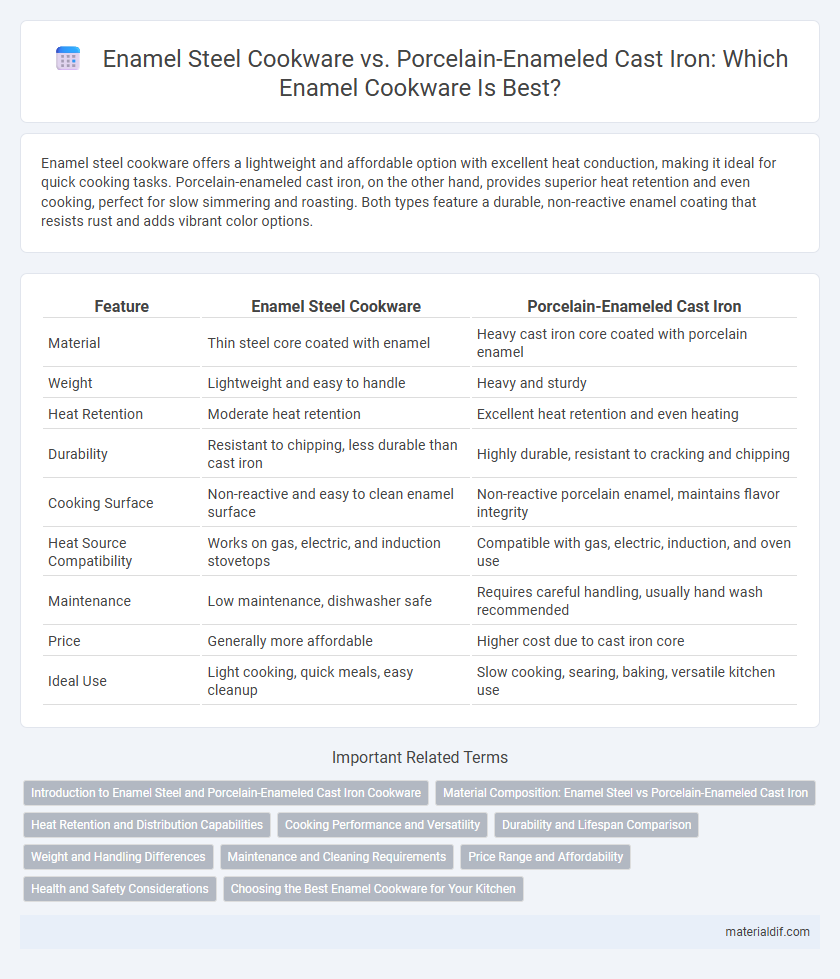
| Feature | Enamel Steel Cookware | Porcelain-Enameled Cast Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thin steel core coated with enamel | Heavy cast iron core coated with porcelain enamel |
| Weight | Lightweight and easy to handle | Heavy and sturdy |
| Heat Retention | Moderate heat retention | Excellent heat retention and even heating |
| Durability | Resistant to chipping, less durable than cast iron | Highly durable, resistant to cracking and chipping |
| Cooking Surface | Non-reactive and easy to clean enamel surface | Non-reactive porcelain enamel, maintains flavor integrity |
| Heat Source Compatibility | Works on gas, electric, and induction stovetops | Compatible with gas, electric, induction, and oven use |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, dishwasher safe | Requires careful handling, usually hand wash recommended |
| Price | Generally more affordable | Higher cost due to cast iron core |
| Ideal Use | Light cooking, quick meals, easy cleanup | Slow cooking, searing, baking, versatile kitchen use |
Introduction to Enamel Steel and Porcelain-Enameled Cast Iron Cookware
Enamel steel cookware features a smooth, durable coating of fused glass on steel, offering lightweight performance and resistance to rust and stains, ideal for everyday cooking. Porcelain-enameled cast iron cookware combines the heat retention and even heating properties of cast iron with a non-reactive, glossy enamel coating that prevents rust and eliminates the need for seasoning. Both types provide durability and easy maintenance, but enamel steel is lighter and more responsive to temperature changes, while porcelain-enameled cast iron excels in heat retention and is perfect for slow cooking and braising.
Material Composition: Enamel Steel vs Porcelain-Enameled Cast Iron
Enamel steel cookware features a carbon or stainless steel base coated with a layer of porcelain enamel, offering a lighter and more responsive heat conductor. Porcelain-enameled cast iron combines a heavy cast iron core with a durable porcelain enamel coating, enhancing heat retention and providing even cooking temperatures. The choice between enamel steel and porcelain-enameled cast iron largely depends on desired weight, heat distribution, and durability in cookware performance.
Heat Retention and Distribution Capabilities
Enamel steel cookware offers rapid heat responsiveness but generally has lower heat retention compared to porcelain-enameled cast iron, which excels at maintaining even temperatures for prolonged periods. Porcelain-enameled cast iron's thick core ensures superior heat distribution, reducing hot spots during cooking. This makes cast iron ideal for slow-cooking and simmering, while enamel steel suits quick temperature adjustments.
Cooking Performance and Versatility
Enamel steel cookware heats up quickly and offers excellent heat conductivity, making it ideal for fast, even cooking and high-temperature searing. Porcelain-enameled cast iron provides superior heat retention and distribution, which is perfect for slow-cooking, braising, and maintaining consistent simmering temperatures. Versatility in enamel steel is enhanced by its lightweight design, while porcelain-enameled cast iron excels in oven use and durability for a wide range of cooking techniques.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Enamel steel cookware features a thinner enamel coating over steel, which can chip or scratch more easily compared to porcelain-enameled cast iron known for its thicker, more resilient enamel layer. Porcelain-enameled cast iron provides superior durability, often lasting decades with proper care, while enamel steel cookware may show wear within a few years of regular use. The heavy-gauge cast iron core in porcelain-enameled cookware also contributes to its longevity by resisting warping and maintaining structural integrity over time.
Weight and Handling Differences
Enamel steel cookware is significantly lighter than porcelain-enameled cast iron, making it easier to handle and maneuver during cooking. Porcelain-enameled cast iron, known for its durability and heat retention, is much heavier and requires more strength to lift and move, especially when full. These weight differences impact the overall user experience, with enamel steel being more suitable for quick, everyday tasks and cast iron favored for slow-cooked meals requiring steady heat.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Enamel steel cookware offers a smooth, non-porous surface that resists staining and is generally dishwasher safe, simplifying routine cleaning. Porcelain-enameled cast iron requires gentle hand washing with non-abrasive sponges to preserve the enamel coating and prevent chipping, with occasional seasoning recommended to maintain performance. Both materials avoid rusting but porcelain-enameled cast iron demands more careful maintenance to ensure long-term durability.
Price Range and Affordability
Enamel steel cookware typically falls within a more affordable price range, making it accessible for everyday use while offering durability and ease of maintenance. Porcelain-enameled cast iron, although pricier due to its heavy-duty construction and superior heat retention, is considered a long-term investment for cooking enthusiasts. Budget-conscious buyers often choose enamel steel for cost efficiency, whereas porcelain-enameled cast iron appeals to those seeking performance and longevity despite the higher initial cost.
Health and Safety Considerations
Enamel steel cookware features a smooth, non-reactive surface that prevents the leaching of metals, ensuring food safety and reducing the risk of contamination. Porcelain-enameled cast iron offers excellent heat retention while its thick, durable coating resists chipping and cracking, minimizing exposure to iron and other metals. Both materials are non-toxic and easy to clean, but porcelain-enameled cast iron demands careful handling to avoid damaging its protective enamel layer, which could otherwise compromise its health benefits.
Choosing the Best Enamel Cookware for Your Kitchen
Enamel steel cookware offers lightweight durability and rapid heat responsiveness, making it ideal for everyday cooking and easy handling. Porcelain-enameled cast iron provides superior heat retention and even distribution, perfect for slow-cooking and braising dishes. Choosing the best enamel cookware depends on your cooking style: opt for enamel steel for versatility and portability, or porcelain-enameled cast iron for robust, long-lasting heat performance.
Enamel steel cookware vs Porcelain-enameled cast iron Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com