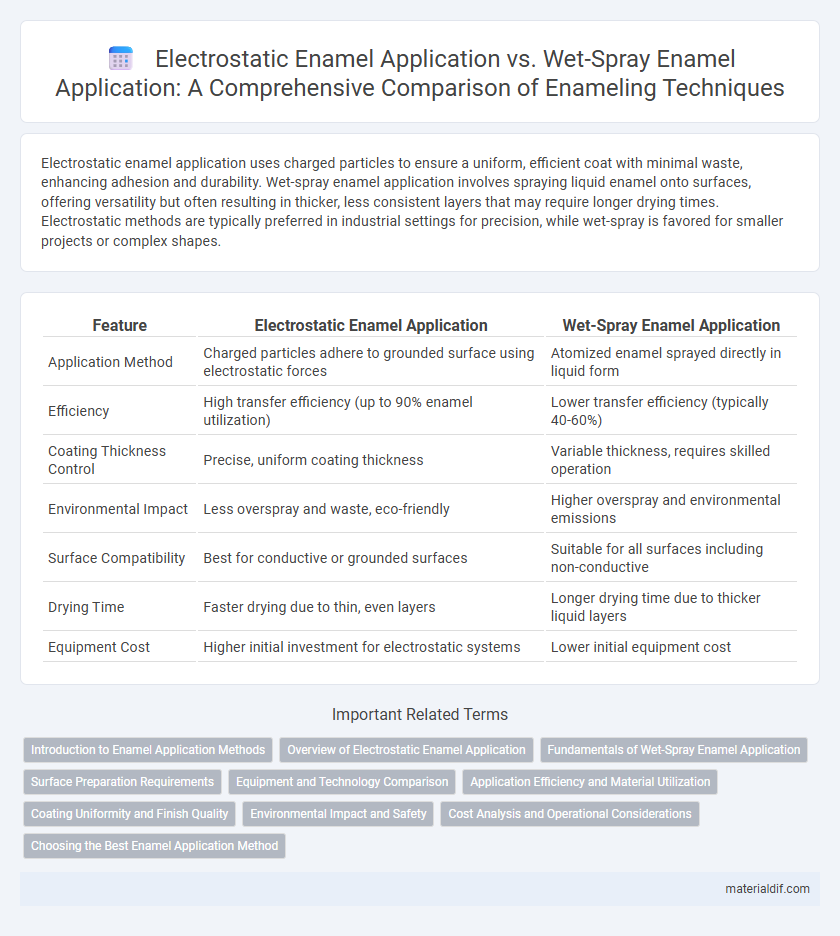
Electrostatic enamel application uses charged particles to ensure a uniform, efficient coat with minimal waste, enhancing adhesion and durability. Wet-spray enamel application involves spraying liquid enamel onto surfaces, offering versatility but often resulting in thicker, less consistent layers that may require longer drying times. Electrostatic methods are typically preferred in industrial settings for precision, while wet-spray is favored for smaller projects or complex shapes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrostatic Enamel Application | Wet-Spray Enamel Application |
|---|---|---|
| Application Method | Charged particles adhere to grounded surface using electrostatic forces | Atomized enamel sprayed directly in liquid form |
| Efficiency | High transfer efficiency (up to 90% enamel utilization) | Lower transfer efficiency (typically 40-60%) |
| Coating Thickness Control | Precise, uniform coating thickness | Variable thickness, requires skilled operation |
| Environmental Impact | Less overspray and waste, eco-friendly | Higher overspray and environmental emissions |
| Surface Compatibility | Best for conductive or grounded surfaces | Suitable for all surfaces including non-conductive |
| Drying Time | Faster drying due to thin, even layers | Longer drying time due to thicker liquid layers |
| Equipment Cost | Higher initial investment for electrostatic systems | Lower initial equipment cost |
Introduction to Enamel Application Methods
Electrostatic enamel application uses charged particles to attract enamel powder onto surfaces, ensuring uniform coverage and minimal waste, ideal for metal substrates requiring corrosion resistance. Wet-spray enamel application involves spraying liquid enamel onto surfaces, allowing intricate detailing and thicker coatings suitable for diverse industrial uses. Both methods optimize enamel adhesion and durability but differ in process efficiency and coating characteristics.
Overview of Electrostatic Enamel Application
Electrostatic enamel application utilizes electrically charged particles to achieve a uniform and efficient coating on metal surfaces, enhancing adhesion and reducing overspray compared to wet-spray methods. This technique improves enamel coverage, resulting in a consistent finish with minimal waste and environmental impact. Industries favor electrostatic application for its precision and cost-effectiveness in enamel coating processes.
Fundamentals of Wet-Spray Enamel Application
Wet-spray enamel application involves atomizing liquid enamel into fine droplets using a spray gun, allowing for uniform coating on complex surfaces and rapid drying times. This method enables precise control over film thickness and reduces material waste compared to traditional brushing techniques. Wet-spray application is ideal for achieving smooth, consistent finishes on metal substrates with enhanced adhesion and corrosion resistance.
Surface Preparation Requirements
Electrostatic enamel application requires a meticulously clean and dry surface to ensure optimal adhesion and uniform coating, often involving thorough degreasing and abrasive blasting. Wet-spray enamel application tolerates slightly less stringent surface conditions but still demands removal of rust, oils, and contaminants to prevent defects like peeling or poor coverage. Proper surface preparation directly impacts the durability and finish quality of both electrostatic and wet-spray enamel coatings.
Equipment and Technology Comparison
Electrostatic enamel application utilizes charged particles to attract enamel powder onto metal surfaces, resulting in efficient transfer and minimal waste, whereas wet-spray enamel application employs liquid enamel sprayed under pressure, requiring advanced spray guns and extensive ventilation systems. Electrostatic technology demands specialized high-voltage equipment and grounded workpieces to ensure uniform coating thickness, while wet-spray systems rely on precise pump controls and atomization technology for consistent film formation. Maintenance complexity and operational costs tend to be lower for electrostatic setups due to reduced material usage and simplified equipment compared to the solvent handling and drying infrastructure essential in wet-spray enamel processes.
Application Efficiency and Material Utilization
Electrostatic enamel application maximizes application efficiency by using electrically charged particles that adhere uniformly to substrates, reducing overspray and minimizing material waste. Wet-spray enamel application typically involves higher material loss due to gravity and air currents, leading to lower transfer efficiency. Consequently, electrostatic methods optimize material utilization, decreasing consumption and operational costs compared to traditional wet-spray techniques.
Coating Uniformity and Finish Quality
Electrostatic enamel application achieves superior coating uniformity by using charged particles that evenly adhere to metal surfaces, minimizing overspray and reducing material waste. Wet-spray enamel application often results in variable thickness and potential runs or drips, affecting finish consistency and requiring more extensive drying times. The precision of electrostatic methods ensures a smoother, more durable finish with enhanced resistance to chipping and corrosion compared to traditional wet-spray techniques.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Electrostatic enamel application reduces environmental impact by minimizing overspray and waste through charged particle attraction, leading to higher transfer efficiency and less solvent emission compared to wet-spray enamel application. Wet-spray methods tend to release more volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to air pollution and requiring extensive ventilation and protective equipment for worker safety. Electrostatic techniques enhance operator safety by reducing airborne particles and chemical exposure, promoting a healthier work environment.
Cost Analysis and Operational Considerations
Electrostatic enamel application reduces paint waste by up to 30% due to improved transfer efficiency, leading to lower material costs compared to wet-spray enamel. Operationally, electrostatic systems require higher initial investment for equipment and maintenance but offer faster curing times and less overspray cleanup. Wet-spray enamel application incurs lower upfront costs but demands increased labor for masking, cleanup, and longer drying periods, impacting overall production efficiency.
Choosing the Best Enamel Application Method
Electrostatic enamel application offers superior coating efficiency and uniformity by using charged particles to adhere enamel more precisely, reducing overspray and material waste compared to wet-spray enamel application. Wet-spray enamel provides versatility for complex shapes and thicker layers but often results in uneven coverage and longer drying times. Choosing the best enamel application method depends on factors such as production speed, part complexity, and desired finish quality, with electrostatic application preferred for high-volume, consistent results.
Electrostatic enamel application vs Wet-spray enamel application Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com